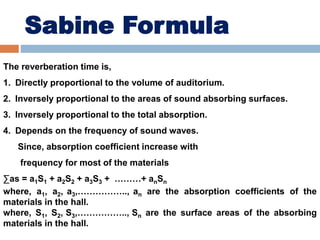
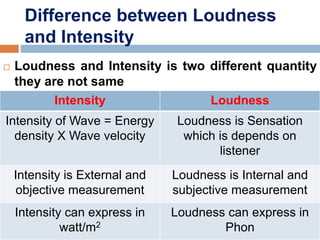
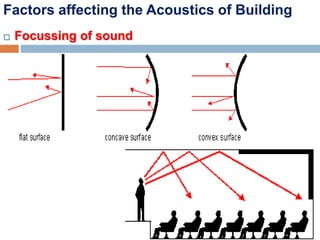
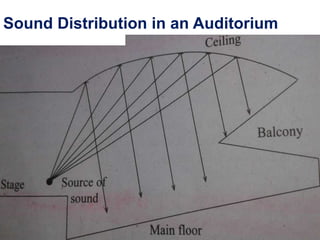
Acoustics is the study of sound waves and how they are generated, propagated, and received. When designing buildings, several acoustical factors must be considered, including reverberation, focusing of sound, echoes, unwanted resonance, interference, and extraneous noise. Reverberation is the persistence of sound after the sound source stops emitting sound, and the reverberation time depends on the size, surface materials, and absorption coefficients of the space. The Sabine formula relates reverberation time to the volume and absorption of a space. Proper acoustics in buildings ensures sound is uniformly distributed and factors like echoes, resonance, and interference are minimized.