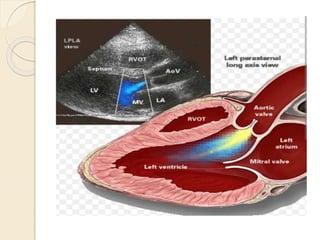
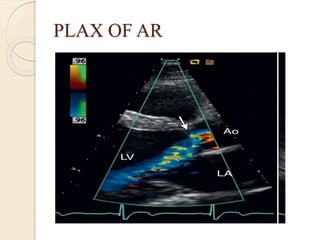
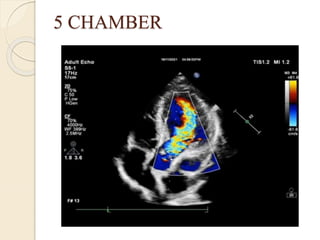
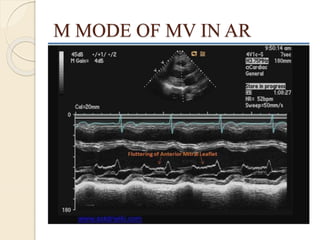
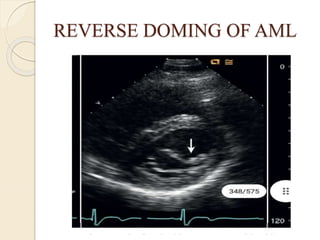
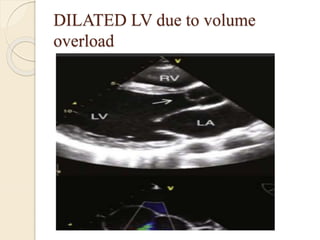
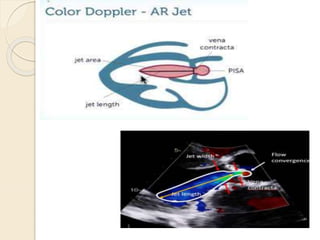
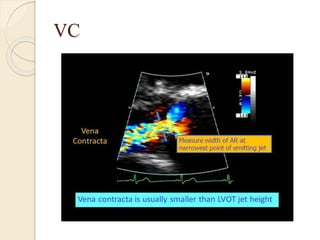
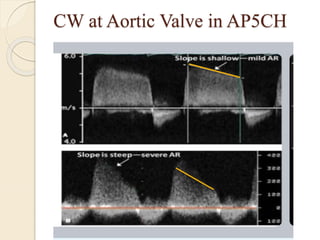
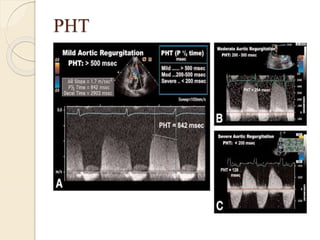
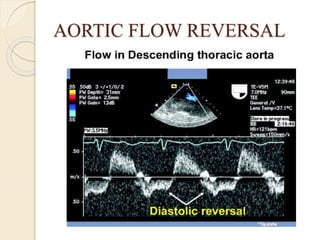
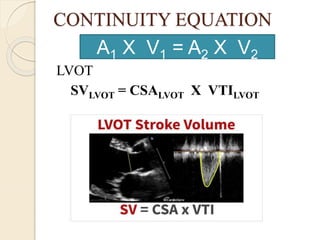
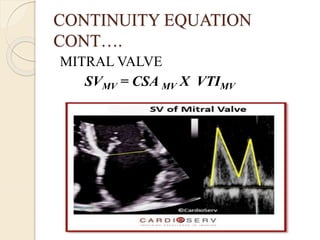
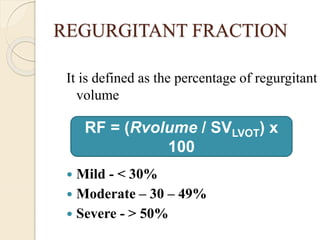
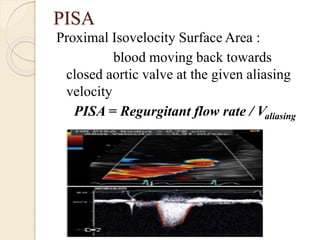
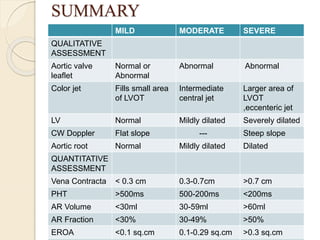
Aortic regurgitation is a heart valve disease characterized by improper closure of the aortic valve, leading to blood flow back into the left ventricle during diastole. Diagnosis involves echocardiographic evaluation, which reveals thickened valve leaflets and ventricular dilation, among other findings; severity is assessed through various measures, including vena contracta and Doppler studies. The document outlines diagnostic criteria, imaging techniques, and the classification of regurgitant severity into mild, moderate, and severe categories.