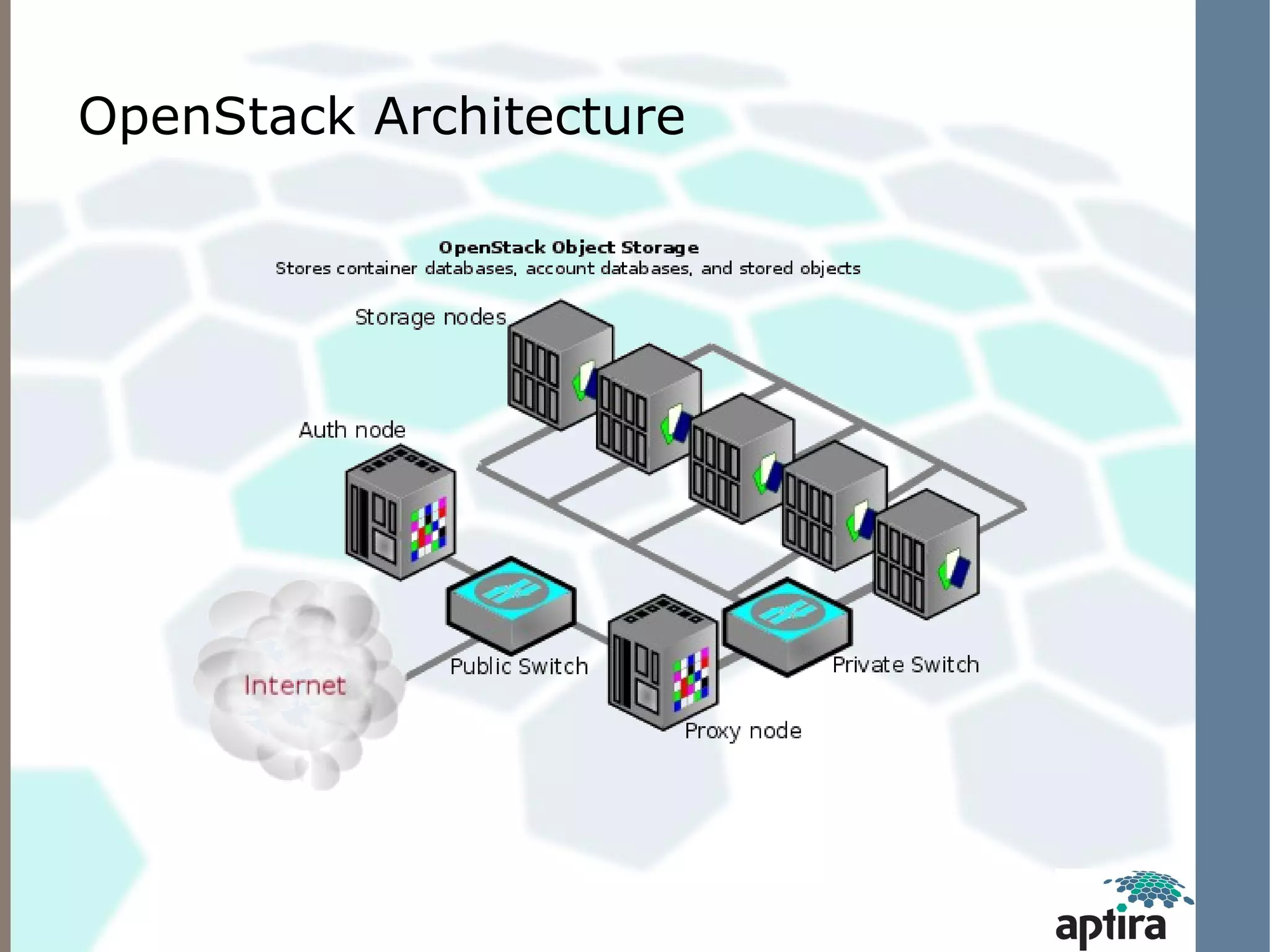
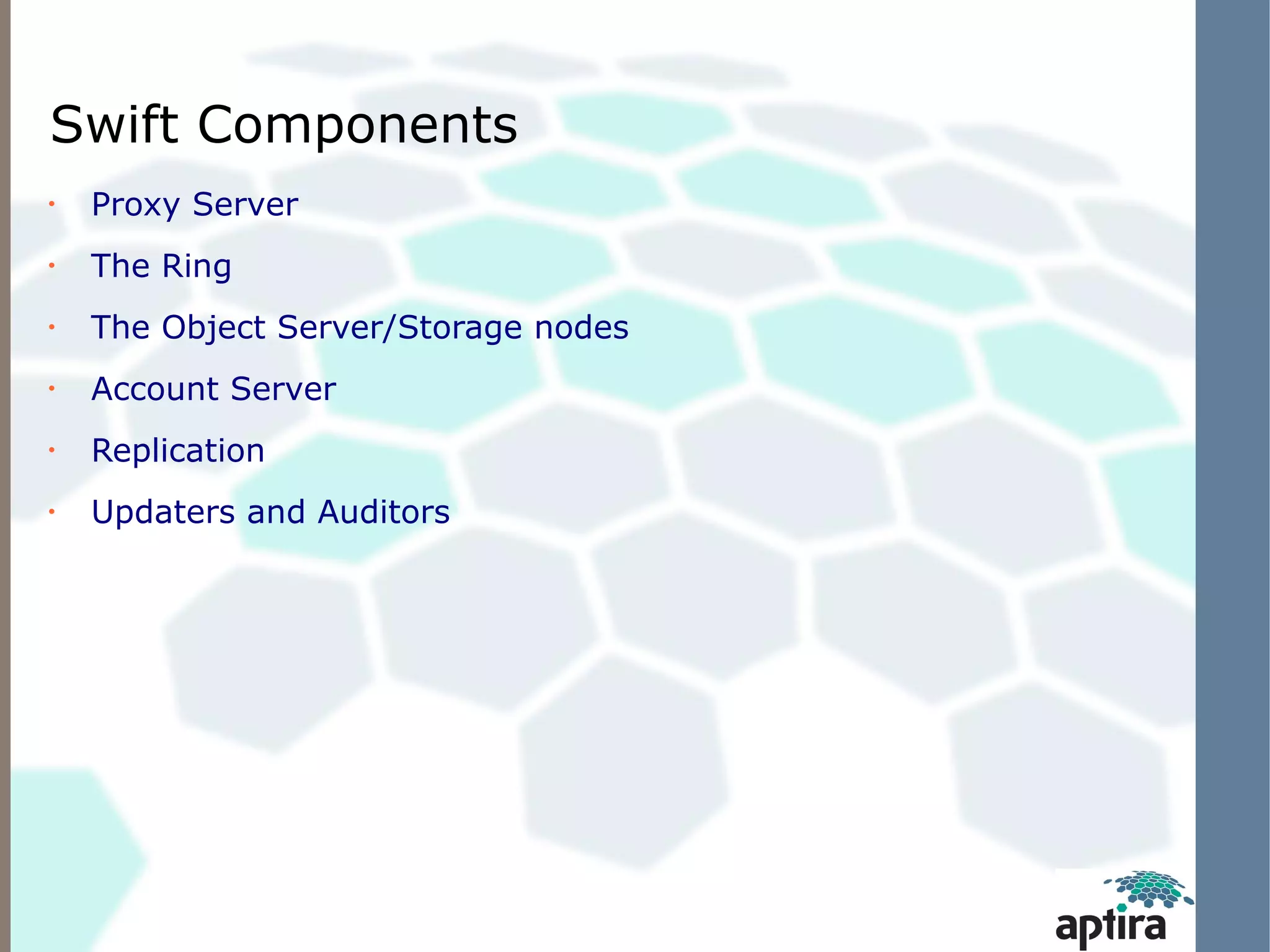
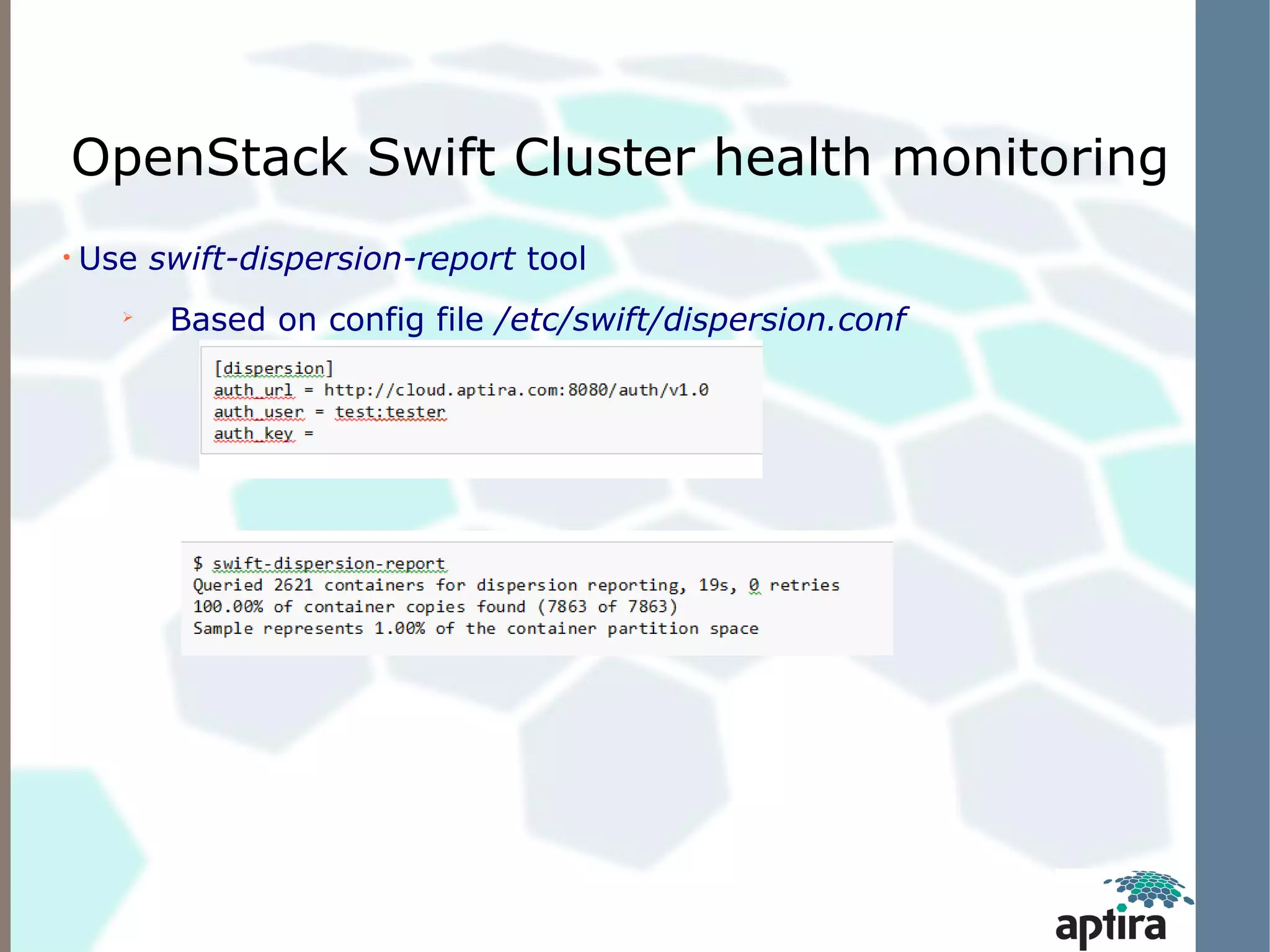
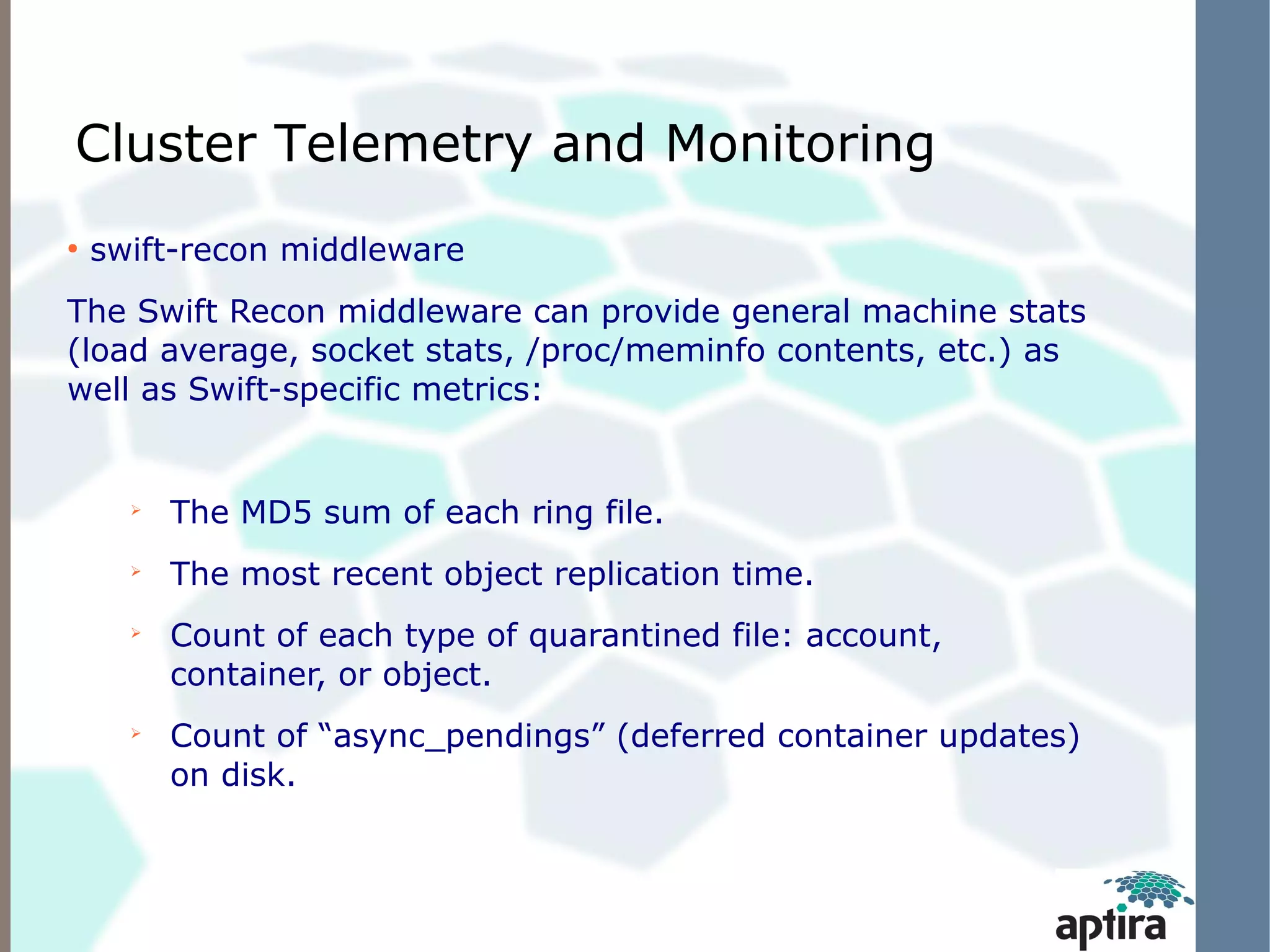
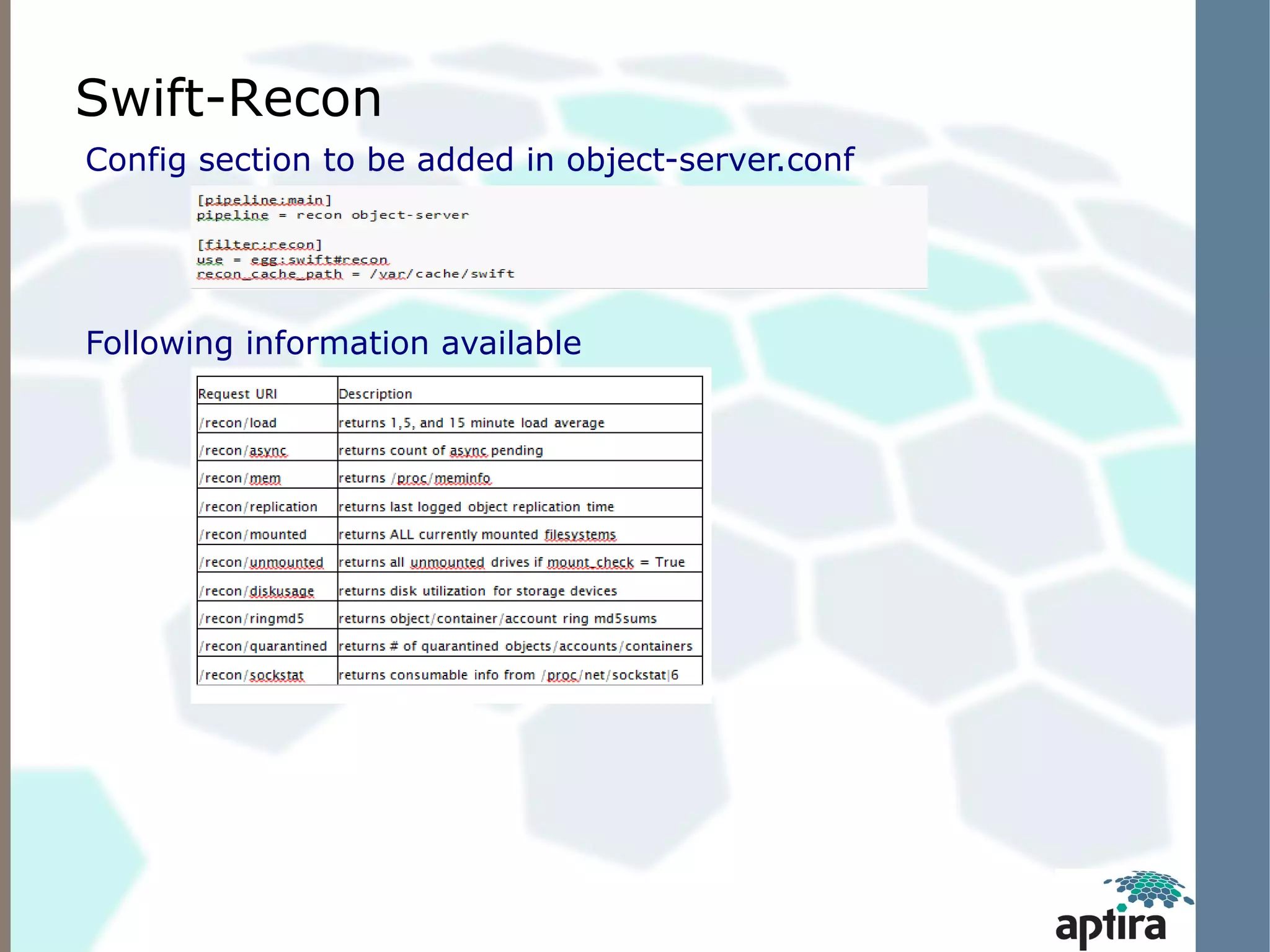
This document discusses OpenStack Swift architecture and monitoring options. It describes the key components of Swift including the proxy server, ring, object/storage nodes, account server, and replication. It recommends monitoring hardware/OS failures, cluster health using tools like swift-dispersion-report, and cluster telemetry using swift-recon. Existing monitoring options that can be used today include Nagios plugins for Swift and the Zenoss OpenStack Swift ZenPack, both of which retrieve metrics via the swift-recon API.