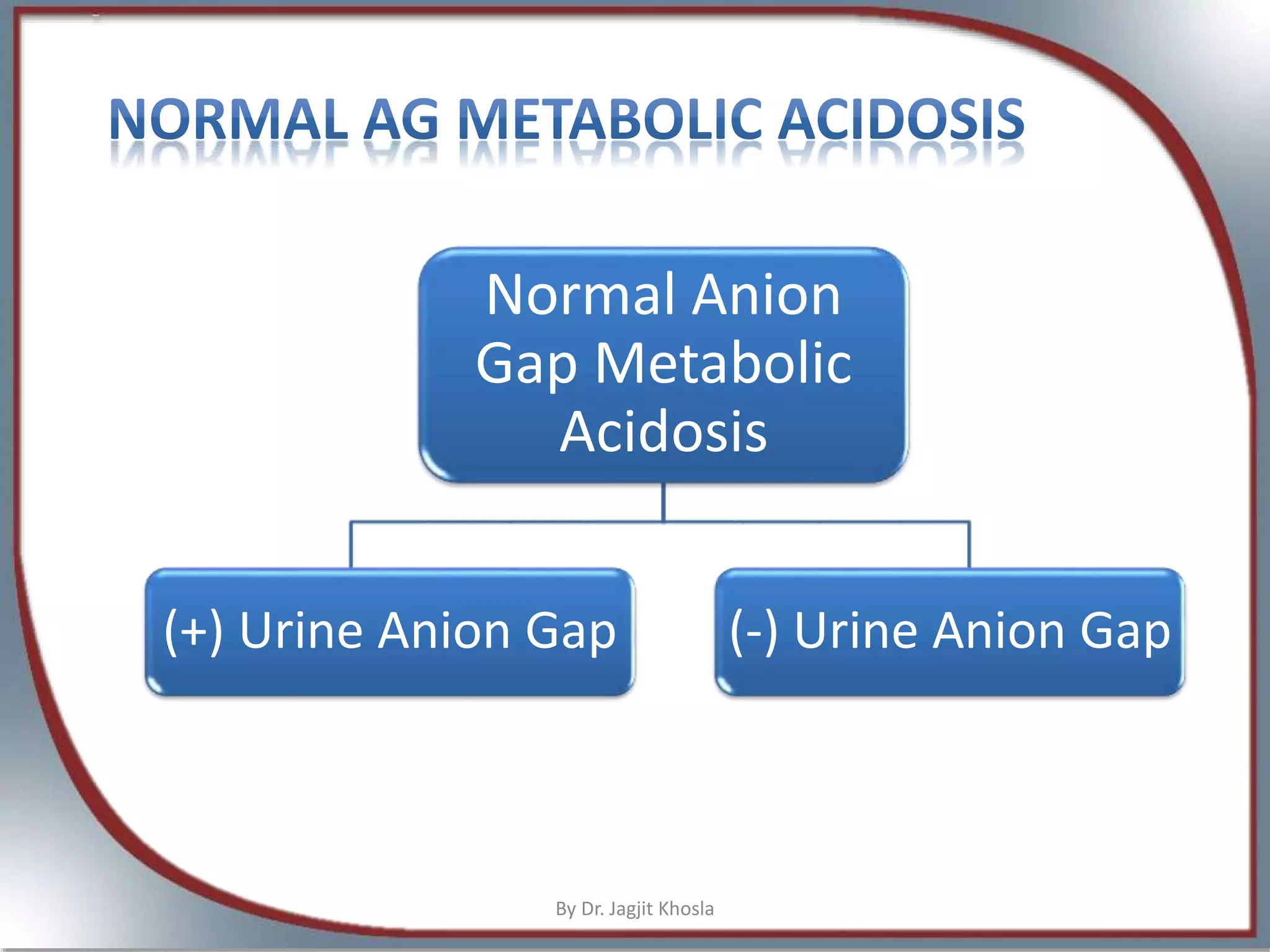
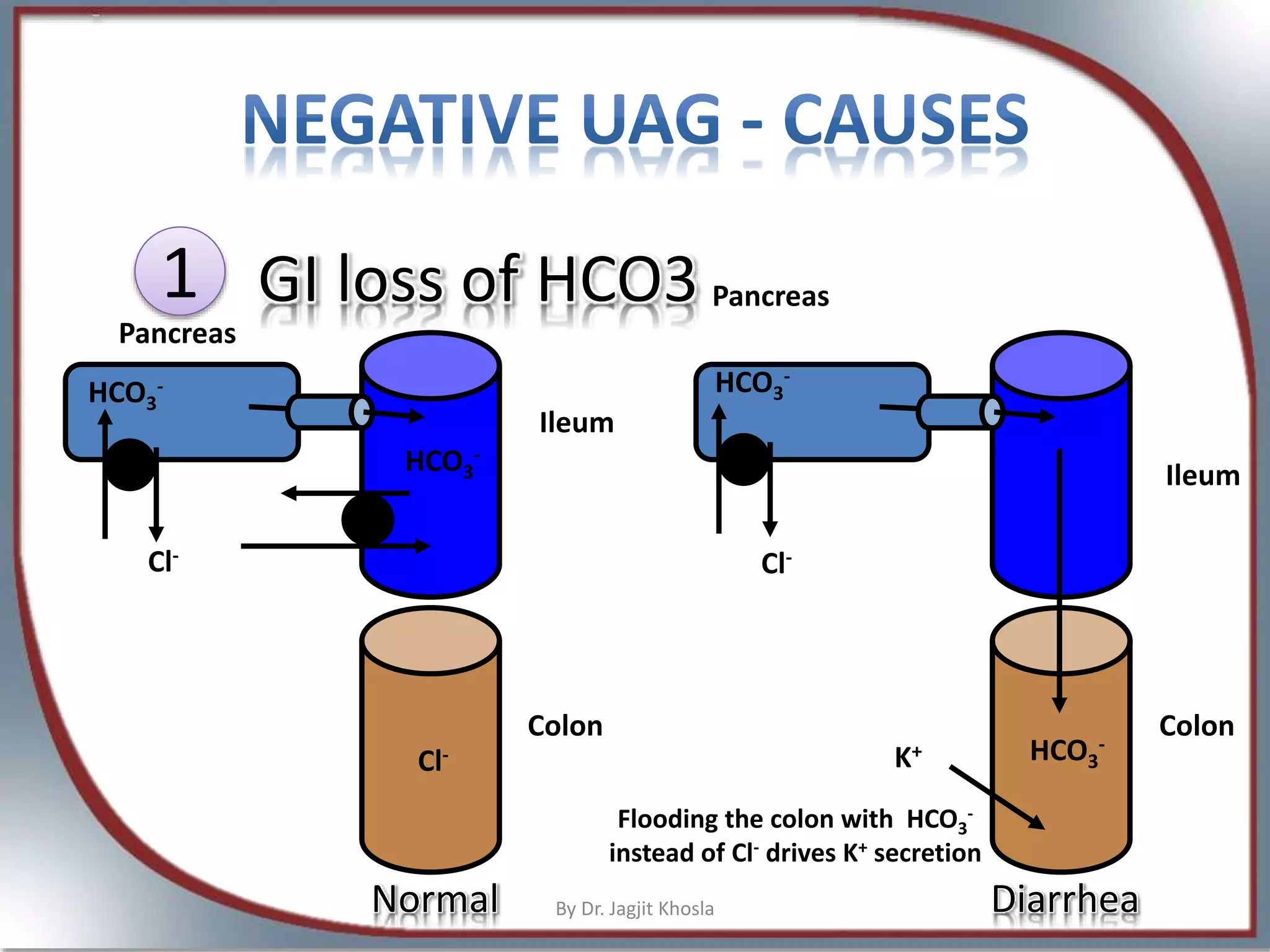
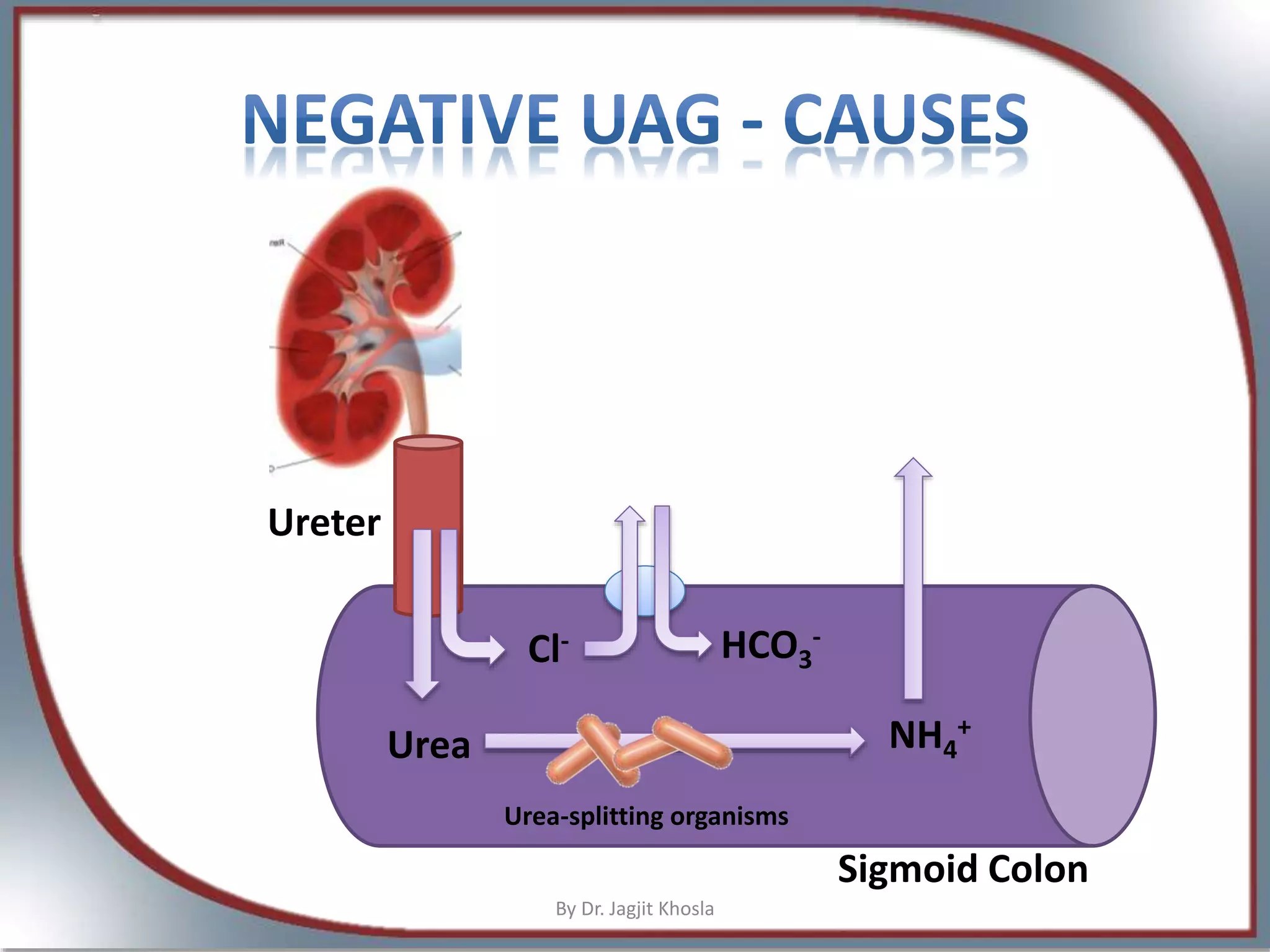
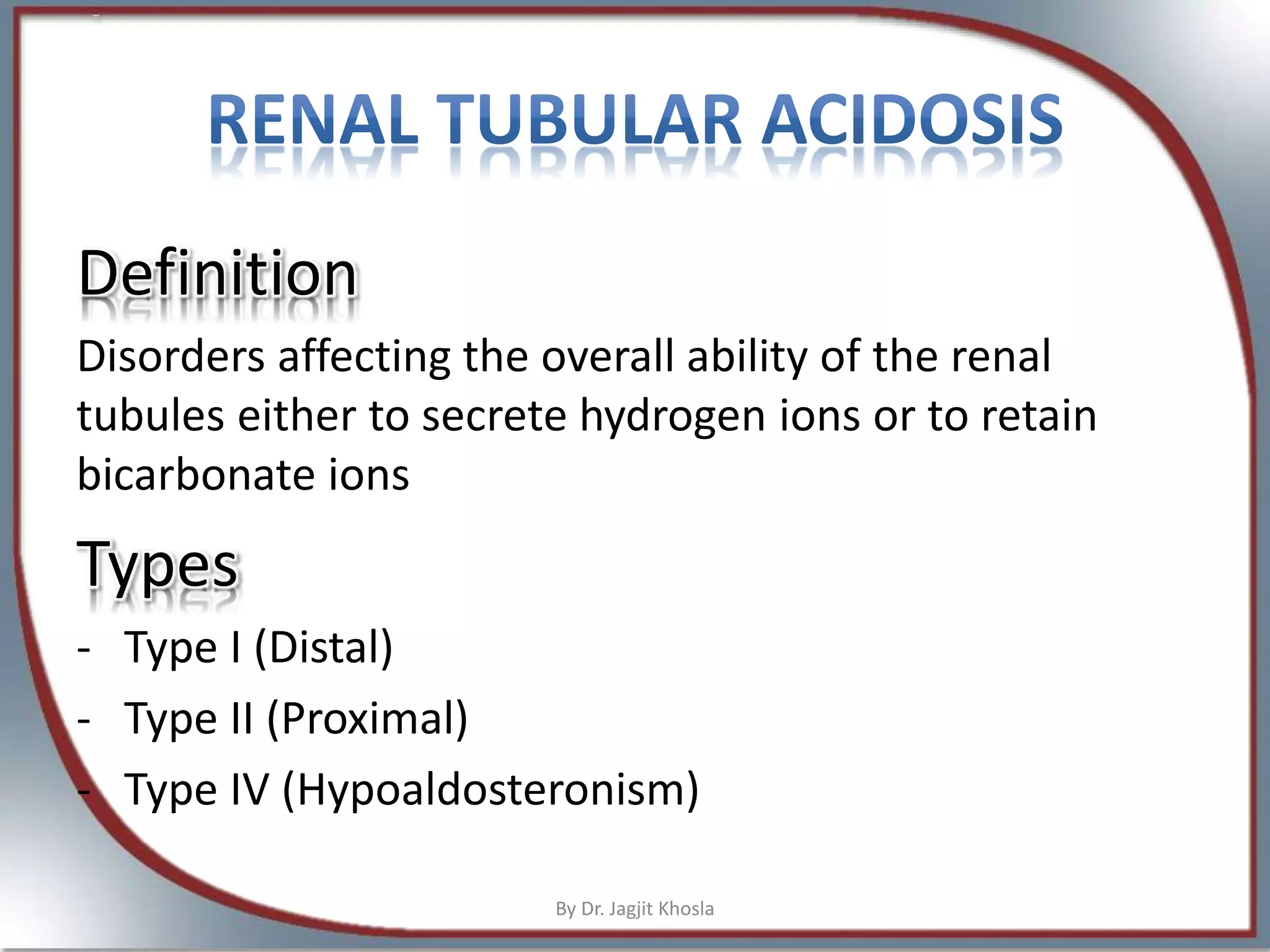
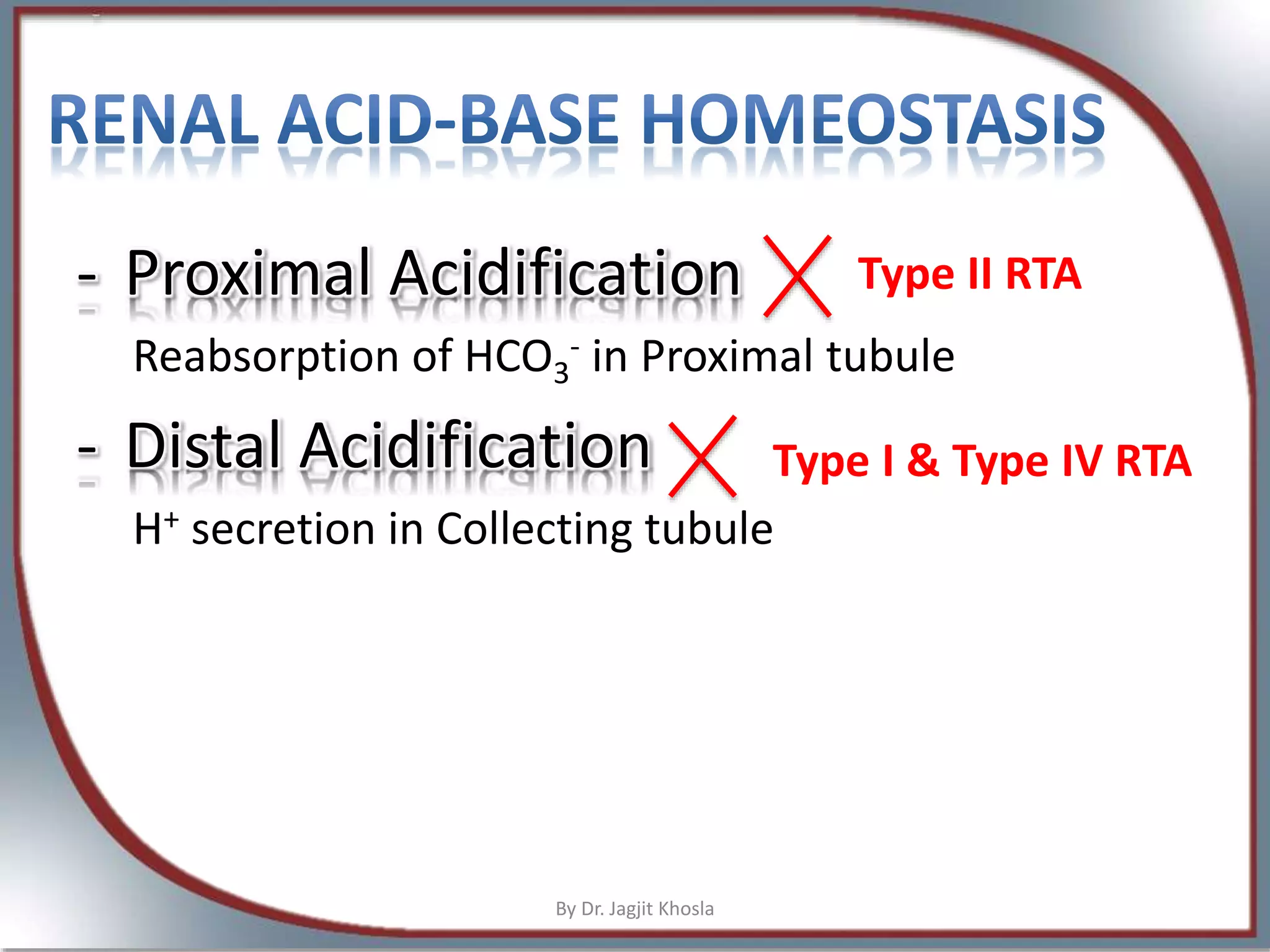
The document discusses metabolic acidosis, detailing definitions, types (high and normal anion gap), and underlying causes such as renal tubule disorders and gastrointestinal losses. It elaborates on anion gap equations, urine anion gap implications, and the mechanisms of renal acid-base regulation, including renal tubular acidosis (RTA) types. The document further explores the intricacies of bicarbonate reabsorption and potassium excretion related to proximal and distal tubular functions.

![Definition
- Blood pH <7.35 (Acidemia)
- [HCO3
-]
- [PaCO2]
(1.2 mm Hg fall in [PaCO2] for every 1 meq/L reduction in [HCO3
-])
By Dr. Jagjit Khosla](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rta-150721181157-lva1-app6891/75/Renal-tubular-acidosis-and-other-causes-of-Normal-anion-gap-Metabolic-acidosis-2-2048.jpg)

















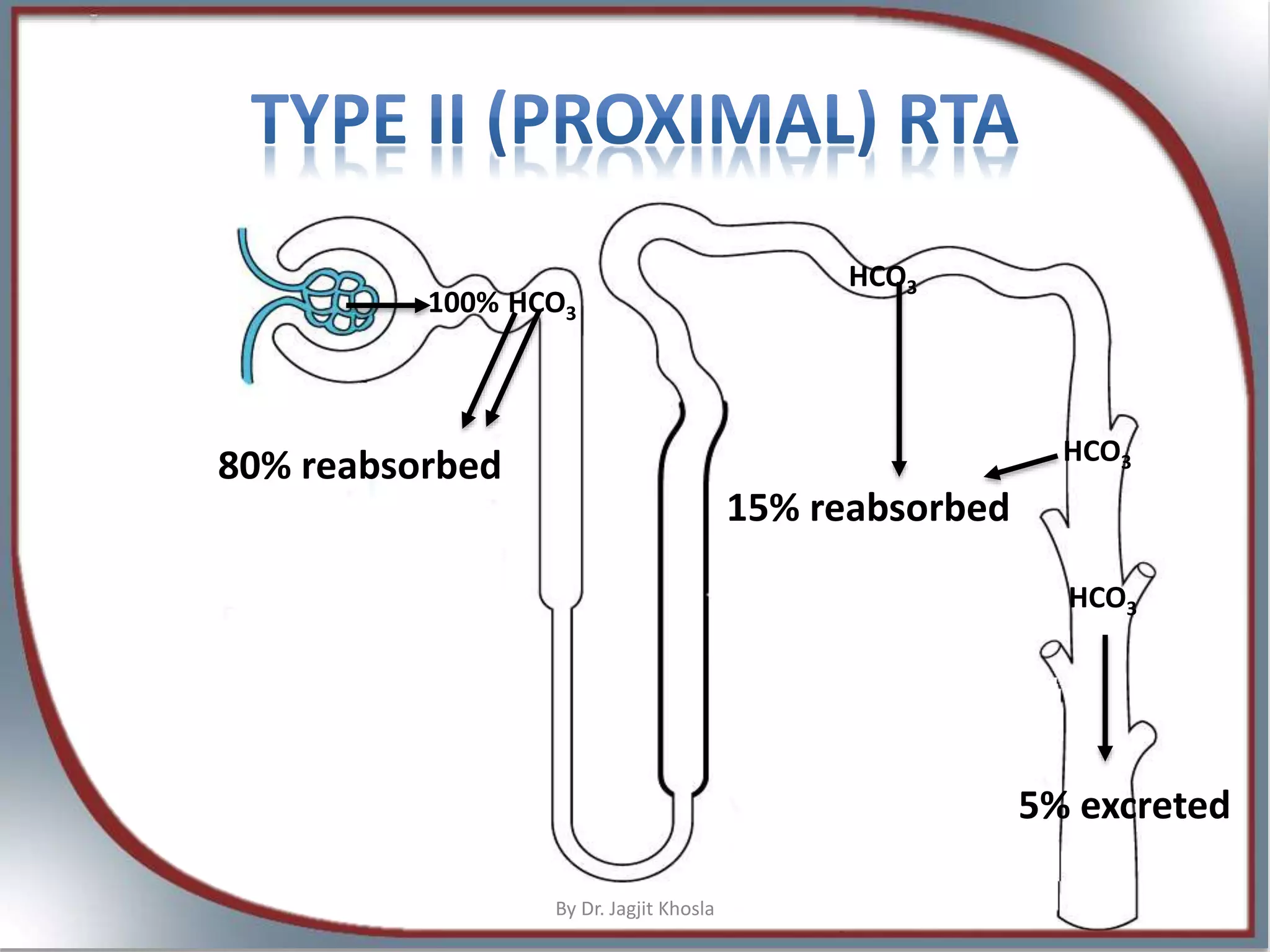

![Features
• U. HCO3- (FeHCO3 > 15%)
• U. pH <5.5,
• S. [HCO3
-] 12-20
• U. Na+
• U. K+ - Hypokalemia
Mechanism of enhanced K+ excretion
- Increased distal Na+ delivery
- Sodium wasting induced secondary hyperaldosteronism
By Dr. Jagjit Khosla](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rta-150721181157-lva1-app6891/75/Renal-tubular-acidosis-and-other-causes-of-Normal-anion-gap-Metabolic-acidosis-30-2048.jpg)

![Effect on Potassium excretion
With alkali therapy
Increased S. [HCO3
-]
Increased filtered load above proximal reabsorptive capacity
Increased distal sodium and water delivery
Enhanced distal potassium excretion
Note : Alkali therapy in proximal RTA should be accompanied with potassium
to prevent hypokalemia
By Dr. Jagjit Khosla](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rta-150721181157-lva1-app6891/75/Renal-tubular-acidosis-and-other-causes-of-Normal-anion-gap-Metabolic-acidosis-32-2048.jpg)