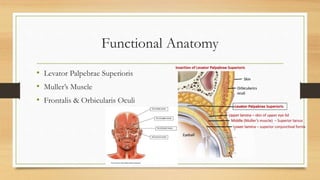
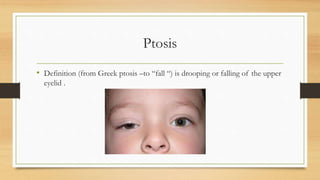
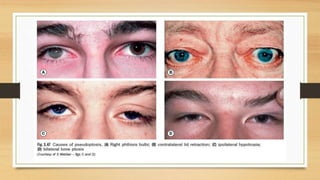
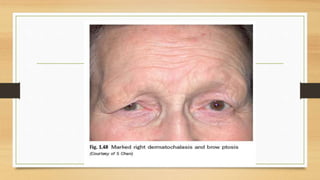
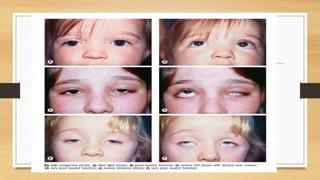
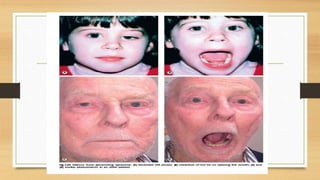
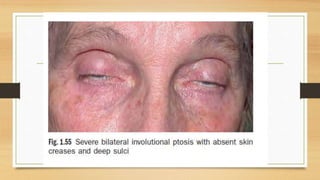
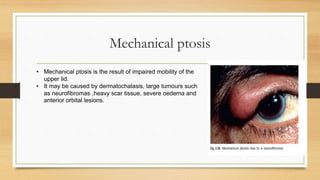
1. Ptosis, or drooping of the upper eyelid, can be congenital or acquired through various mechanisms including myogenic, neurogenic, mechanical, or aponeurotic causes.
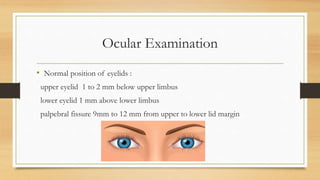
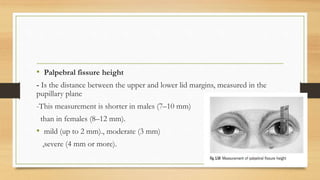
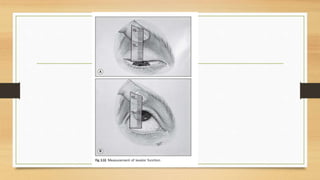
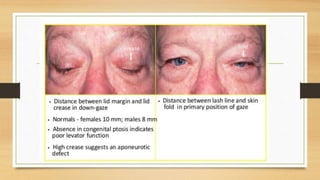
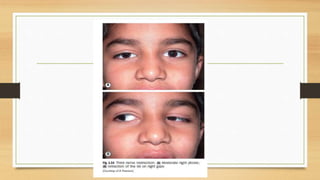
2. Clinical evaluation of ptosis involves measuring the margin-reflex distance, palpebral fissure height, and levator function to determine severity.
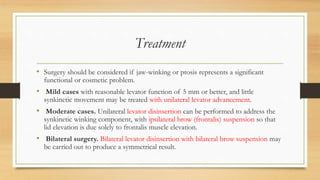
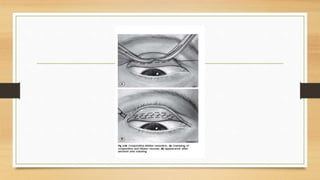
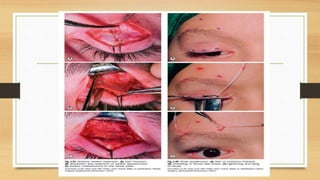
3. Simple congenital ptosis is usually treated through levator resection surgery during preschool years to prevent amblyopia, while Marcus Gunn jaw-winking syndrome may require levator disinsertion and brow suspension surgery.