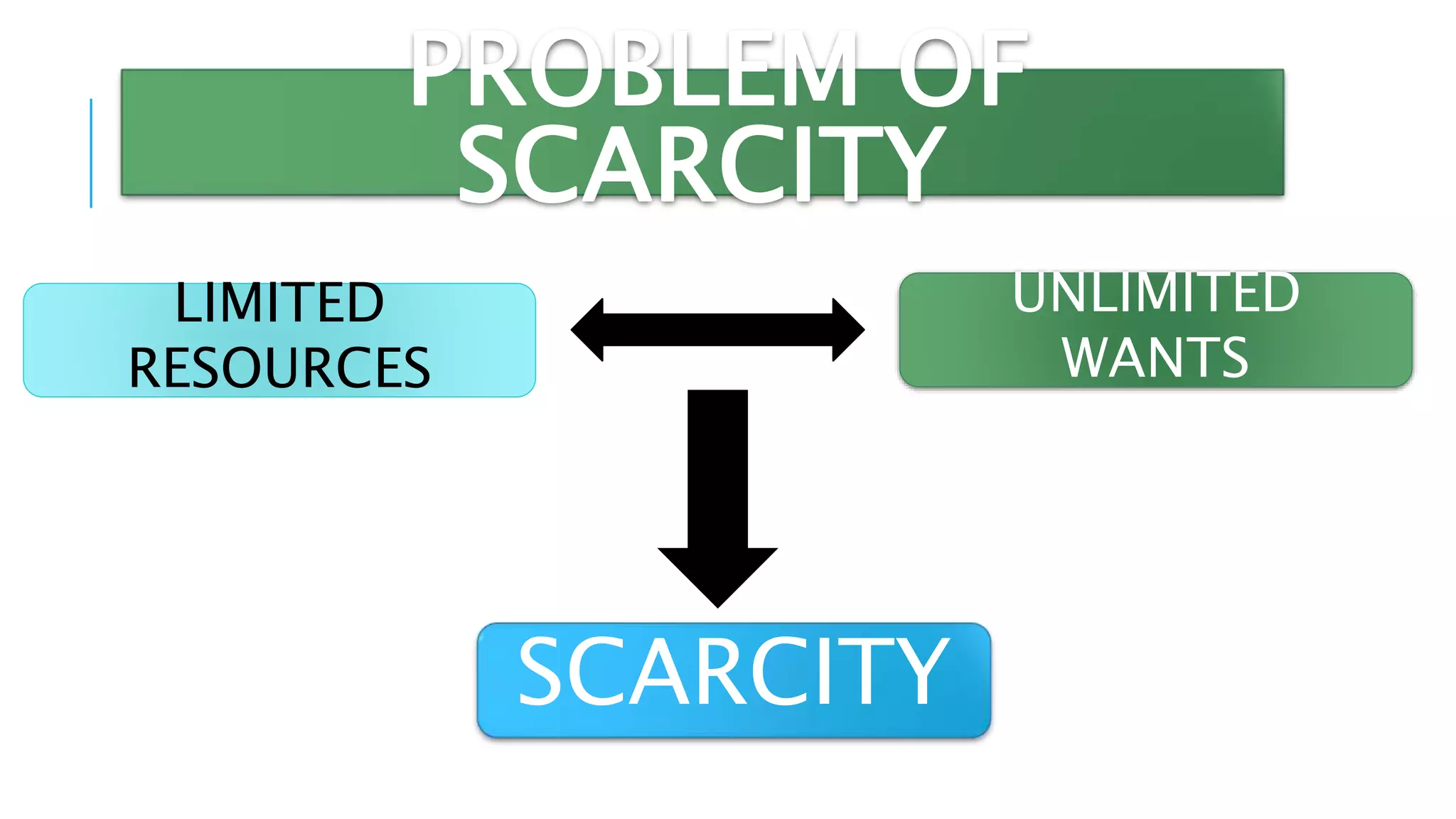
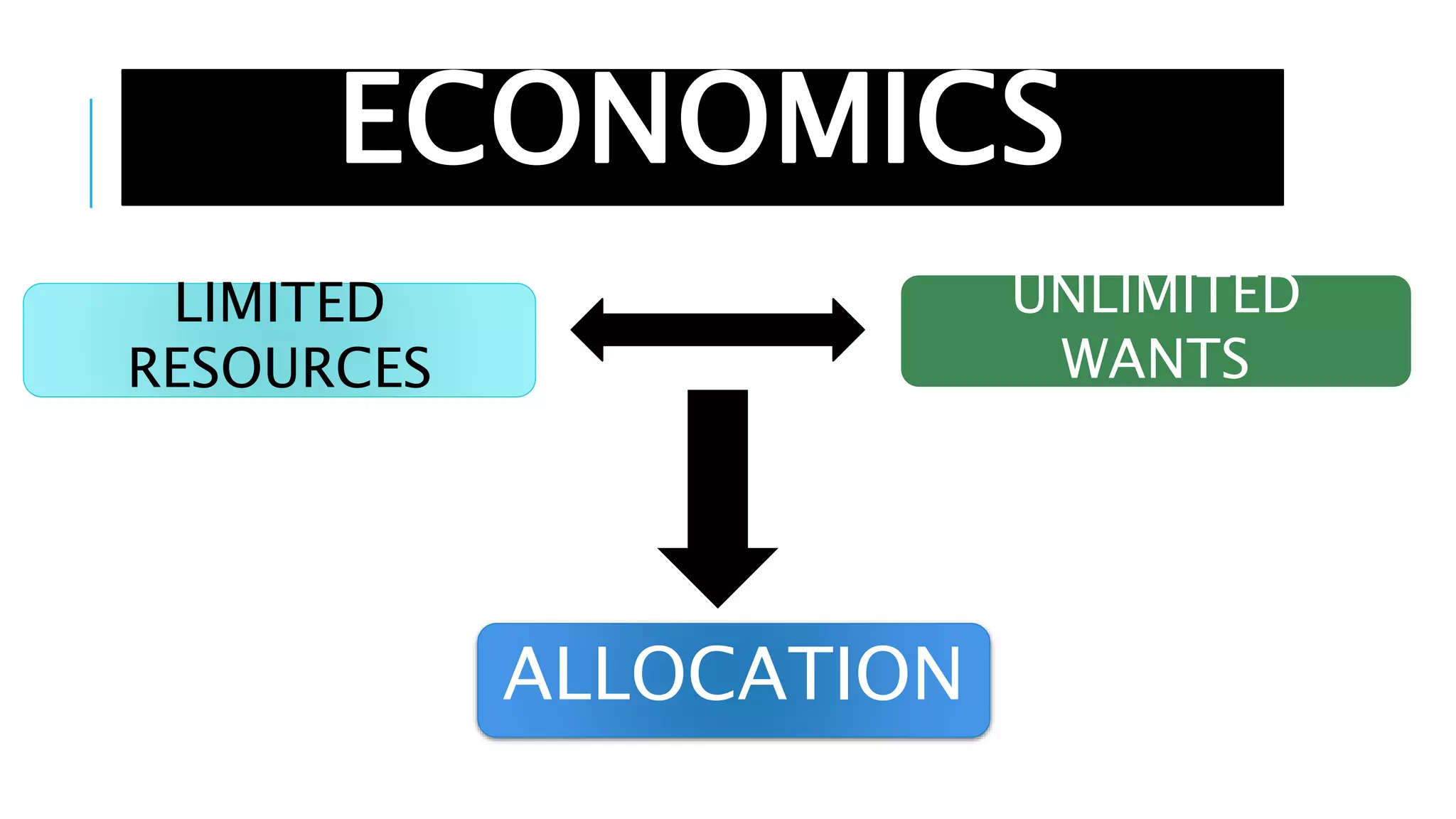
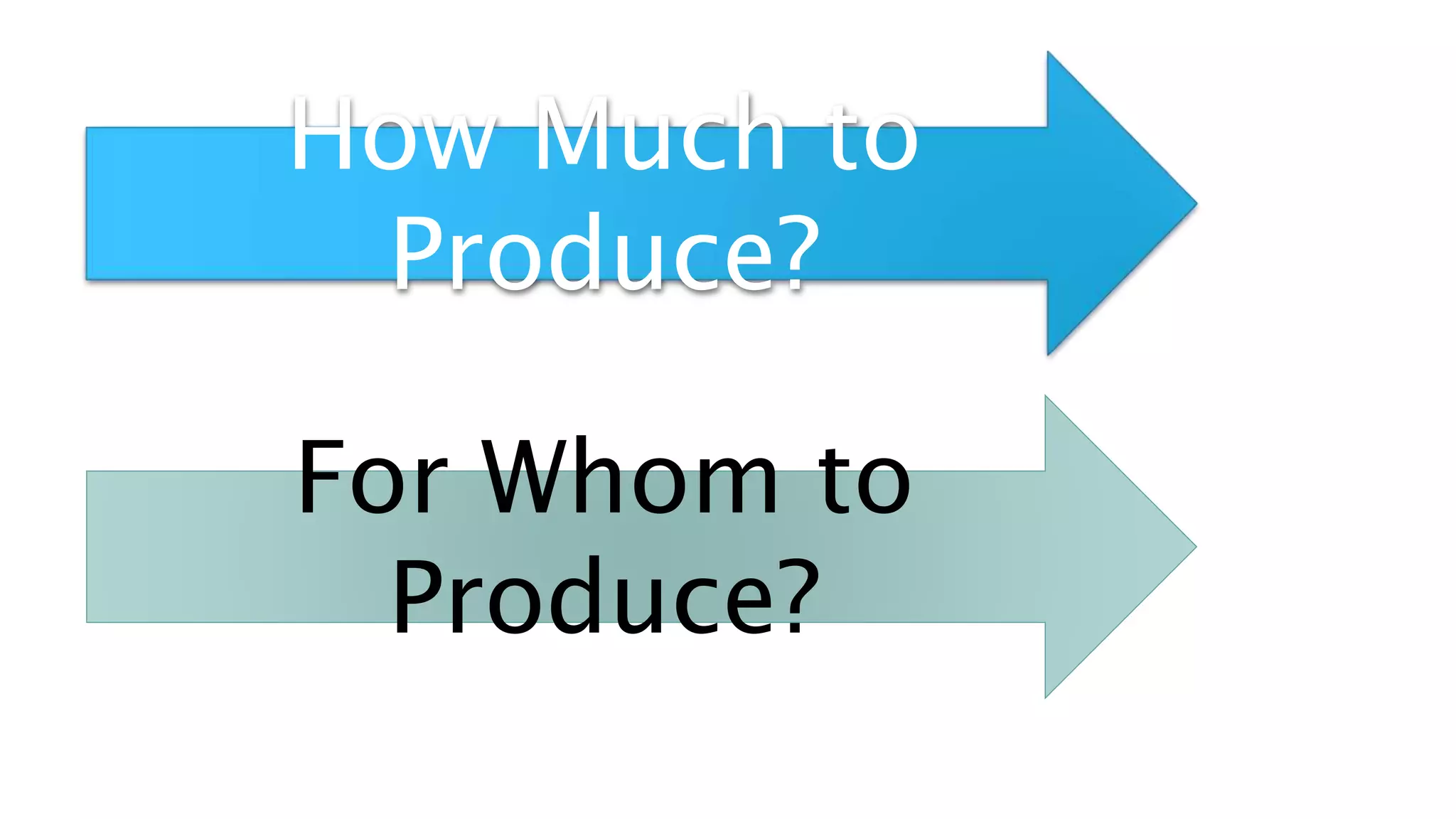
The document outlines key learning objectives for Grade 11 Applied Economics, defining economics as an applied social science that addresses scarcity, resource allocation, and the factors of production. It distinguishes between microeconomics and macroeconomics, detailing their scopes and goals while emphasizing the relationships between economics and other fields such as business management, history, finance, sociology, and psychology. Essential economic questions regarding production and distribution are also introduced.