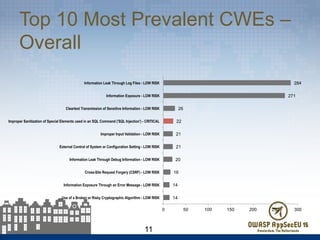
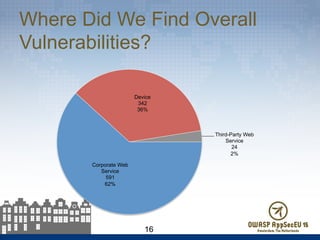
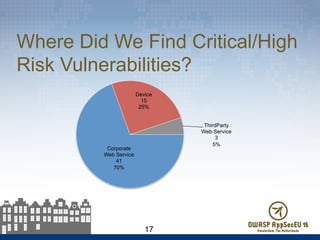
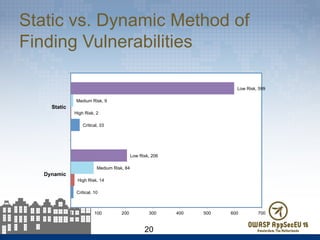
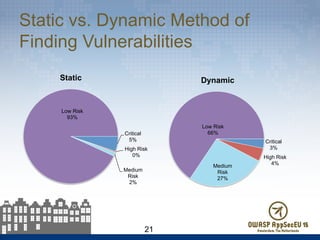
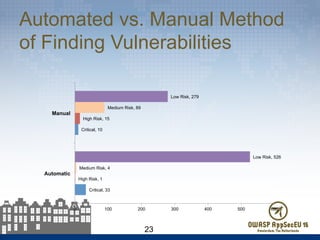
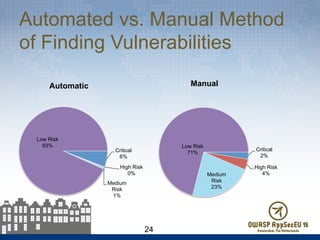
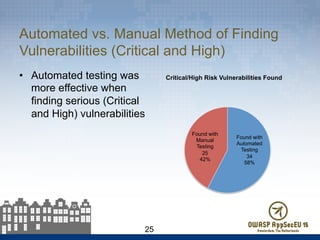
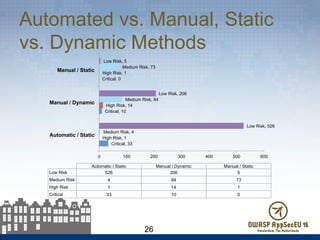
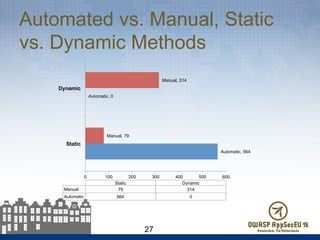
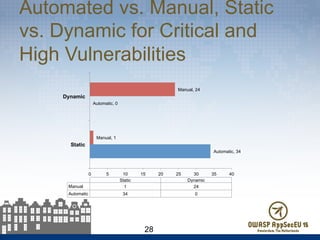
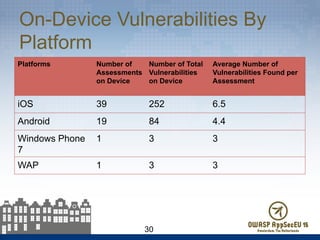
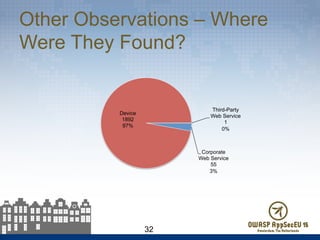
The document presents findings from 61 mobile application assessments, revealing 957 total vulnerabilities across 20 applications, with notable discrepancies between the number of vulnerabilities identified through static and dynamic testing methods. Key results highlight critical vulnerabilities commonly associated with corporate web services and emphasize the importance of both manual and automated testing approaches to enhance mobile application security. Recommendations for future assessments include a balanced strategy prioritizing comprehensive coverage and automation, while addressing the evolving landscape of mobile application vulnerabilities.