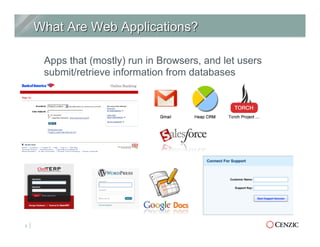
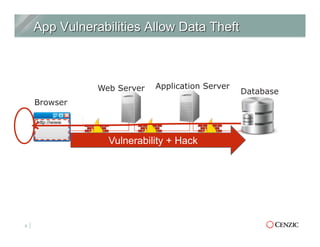
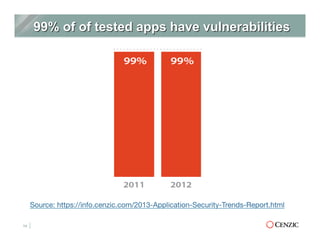
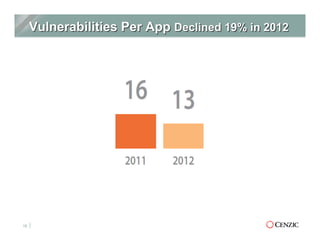
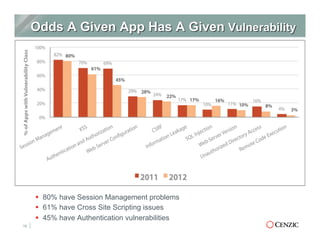
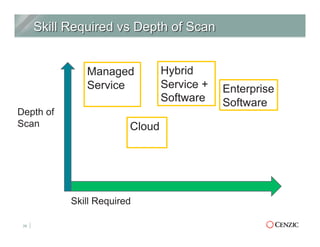
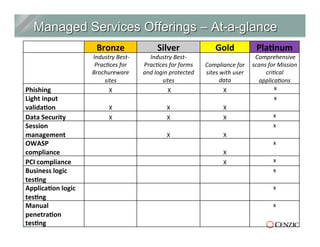
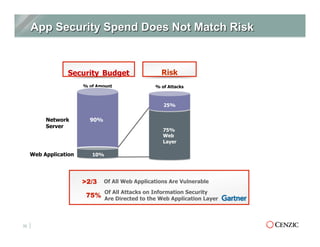
The document outlines the essentials of web application security, explaining its importance in protecting critical data from various vulnerabilities such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting. It emphasizes the need for proactive scanning, remediation, and the adoption of security best practices to safeguard applications. Additionally, it highlights different types of security services available, including managed services and hybrid solutions, tailored for various organizational needs.