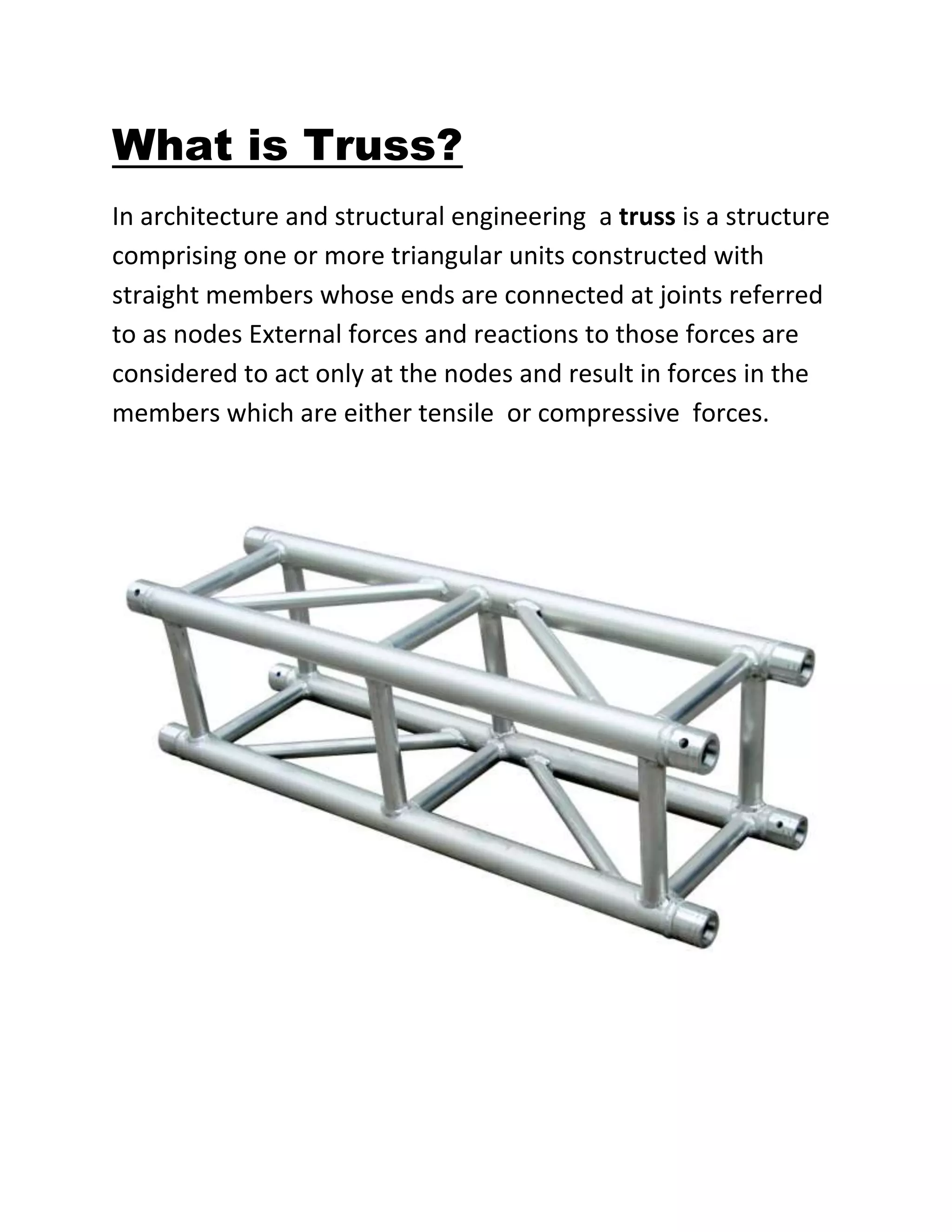
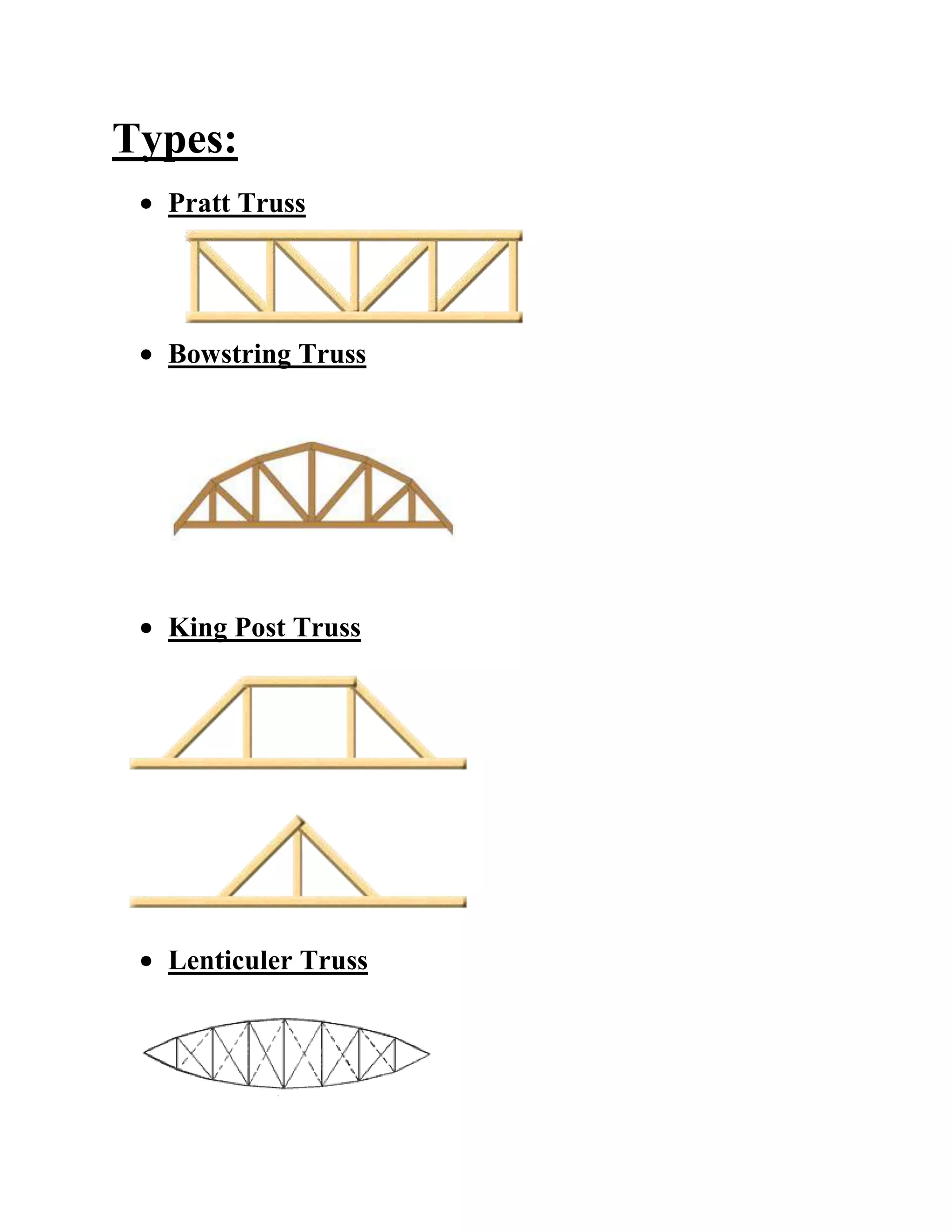
This document provides information about trusses and their application. It discusses two basic types of trusses - pitched trusses and parallel chord trusses. It describes various truss configurations including Pratt trusses, Bowstring trusses, King post trusses, and Lenticuler trusses. It also discusses how critical component connections are for structural integrity, specifically connections between trusses and their supports that must resist forces like shear, uplift, and bending moment. Wood posts are described as enabling strong, direct connections between large trusses and walls.