Embed presentation
Downloaded 17 times
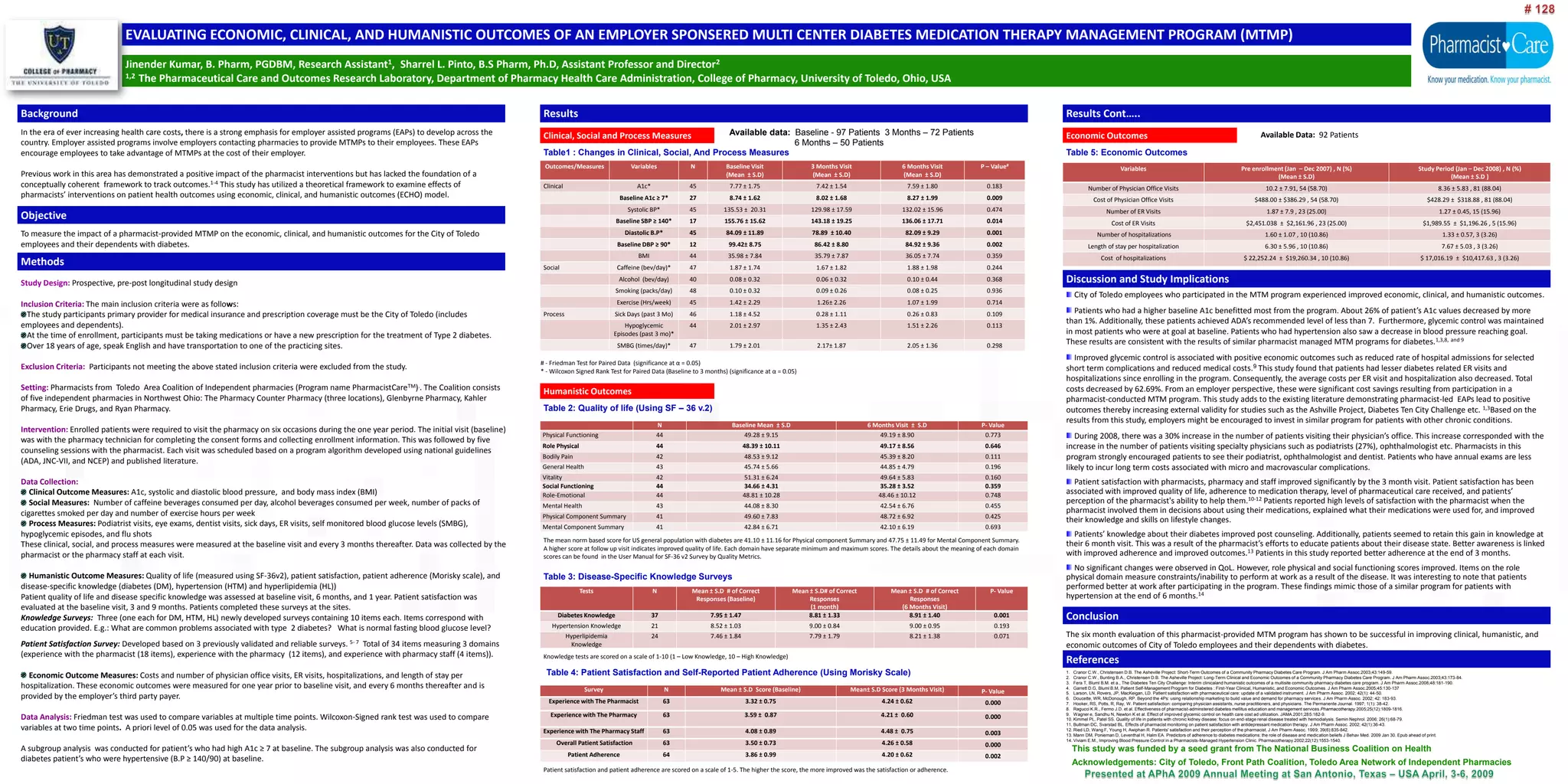
This study evaluated the outcomes of a pharmacist-provided diabetes medication therapy management program (MTMP) sponsored by an employer for its employees and dependents. The study found: 1) Patients experienced improved clinical outcomes including reductions in A1c, blood pressure, and hospitalizations/ER visits. 2) Economic outcomes improved with reductions in costs of physician visits, hospitalizations, and ER visits. 3) Humanistic outcomes were positive with high patient satisfaction and improved disease knowledge retention over 6 months. The MTMP resulted in overall improved health, quality of life and cost savings for participants.
