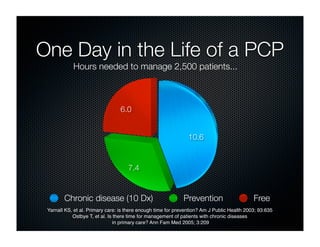
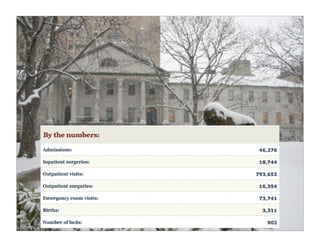
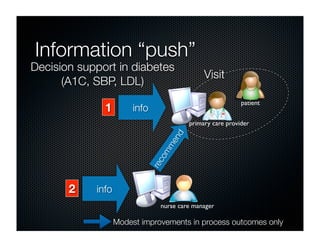
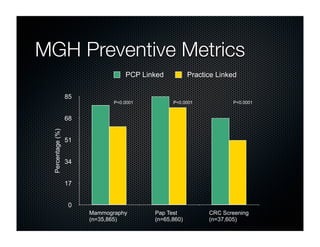
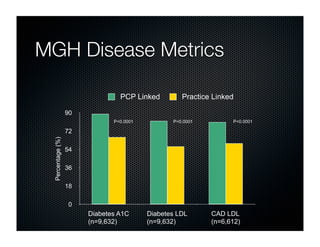
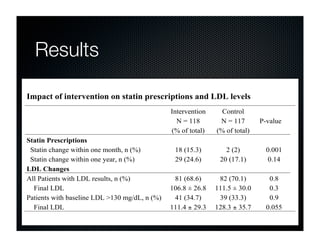
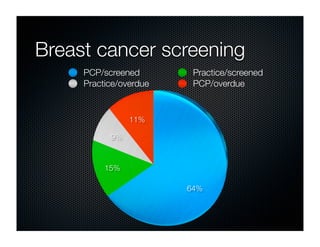
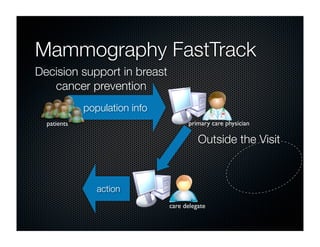
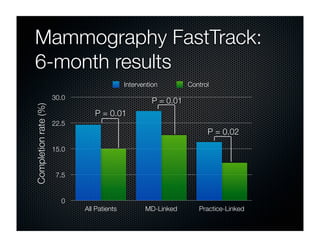
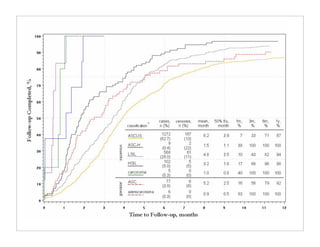
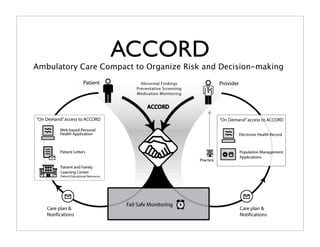
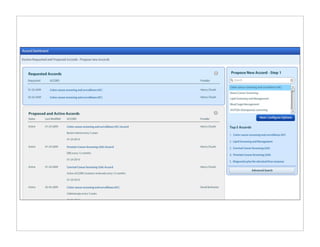
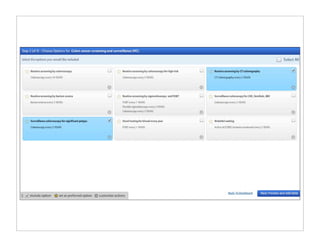
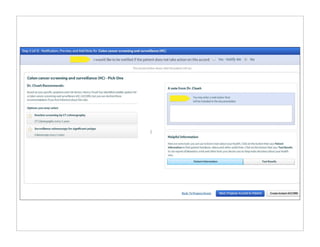
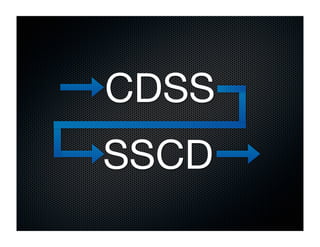
The document discusses transforming health care delivery through informatics using Massachusetts General Hospital as an example. It describes MGH's large primary care network and existing IT infrastructure. It then discusses challenges like lack of time and flawed care processes. Several tools are presented, including clinical decision support systems and same-day communication, to help close gaps outside of visits. Results show these tools improved preventative screening and disease metrics for connected patients. The document advocates for population-based, continuous approaches like ACCORD to strengthen fragile care loops through shared decision making and documentation.