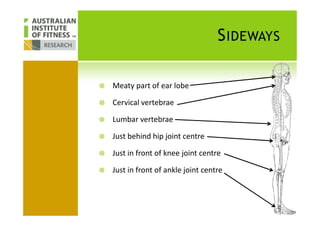
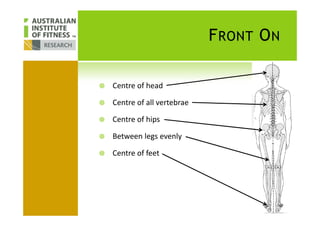
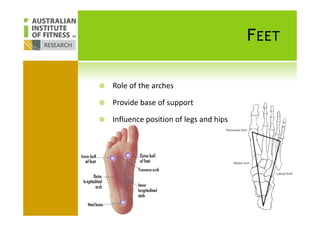
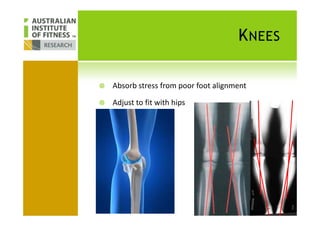
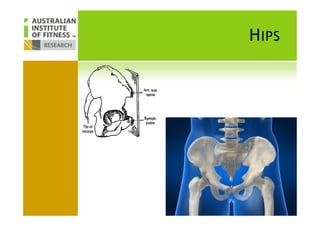
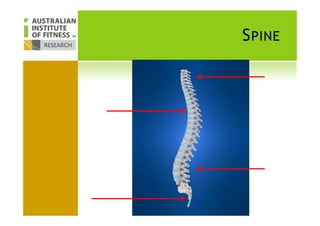
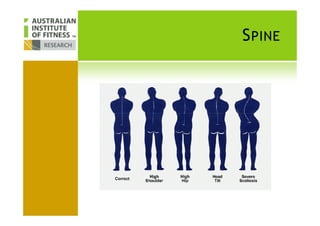
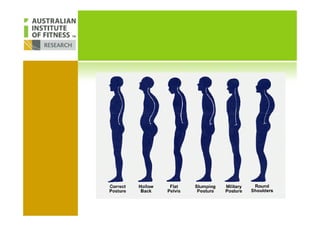
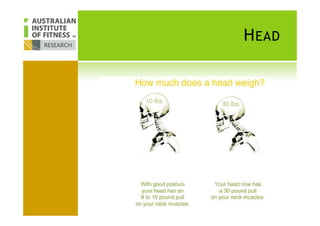
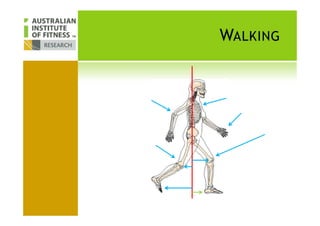
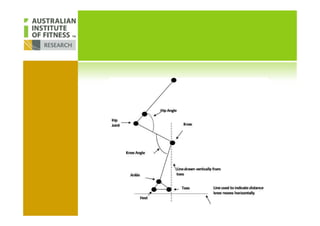
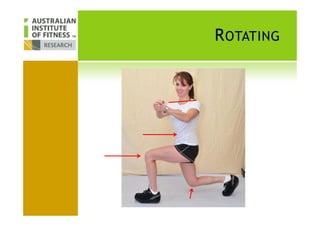
This document discusses human posture evolution from four-legged ancestors to modern two-legged humans. It covers how upright posture developed over millions of years, allowing for traits like throwing, carrying and an enlarged brain. While bipedalism provided advantages, it also introduced challenges like lower back problems. The document outlines ideal spinal and body alignment for good posture and how this impacts health, strength, flexibility and movement. It concludes by previewing a second session on observing common movement problems and examples of good and poor movements like walking, squatting and rotating.