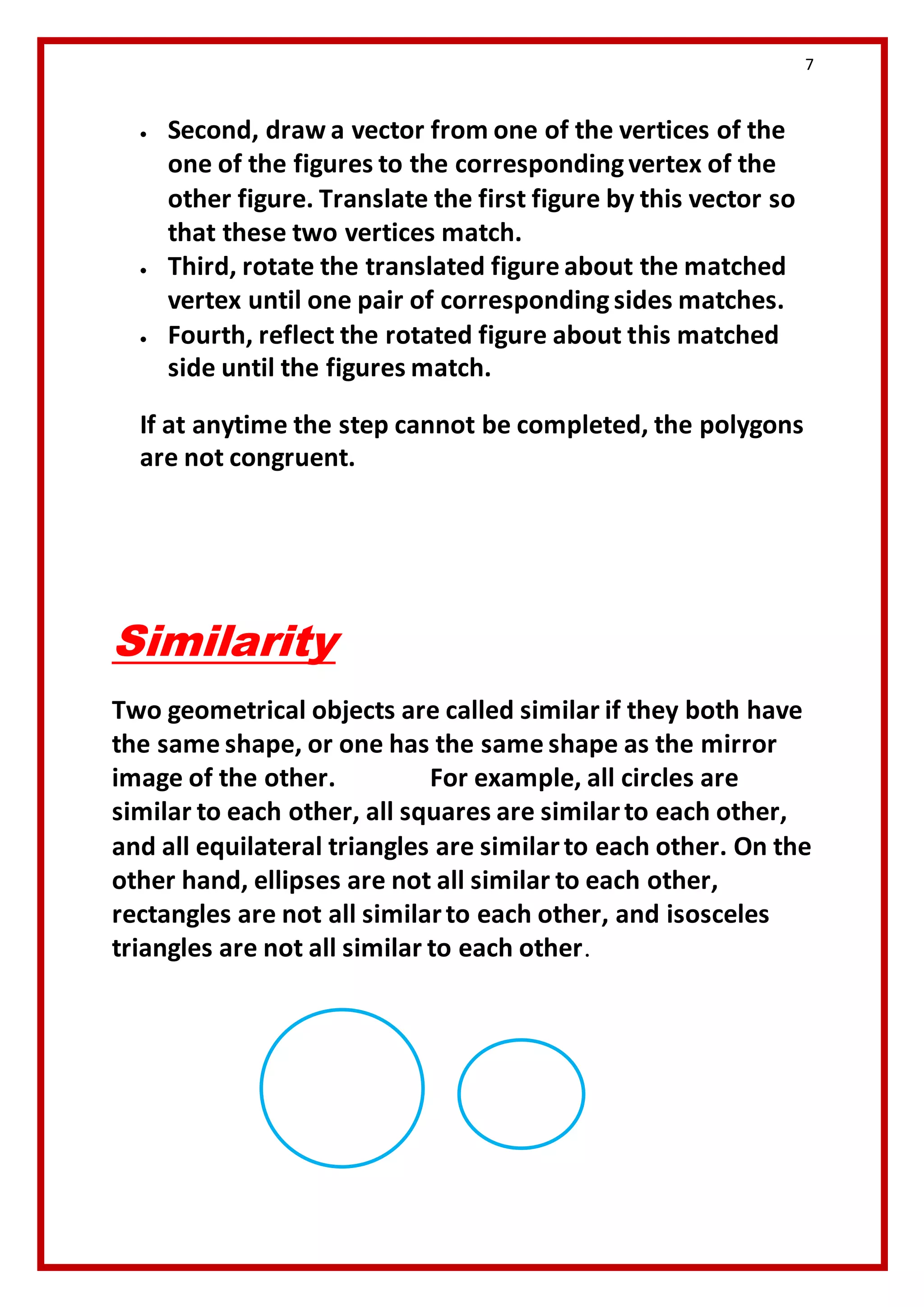
The document discusses congruence and similarity in geometry. Congruence refers to two objects having the same shape and size. Similarity refers to two objects having the same shape, though not necessarily the same size. Specific examples are provided of congruent and similar line segments, angles, circles, polygons, and triangles. The concepts of uniform scaling, matching corresponding sides and angles, and proportional sides are also covered.