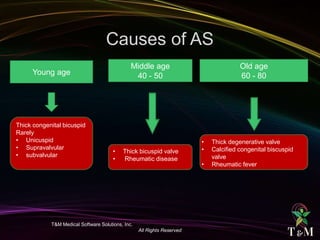
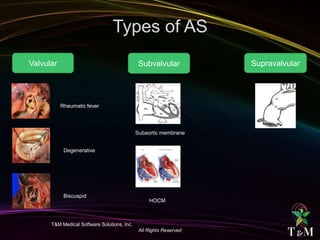
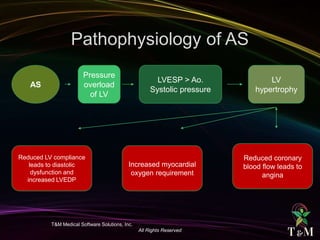
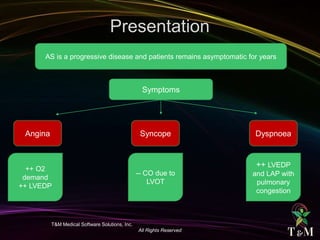
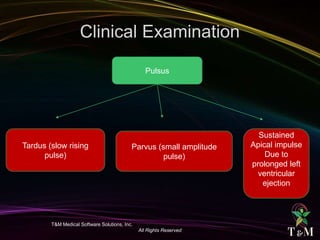
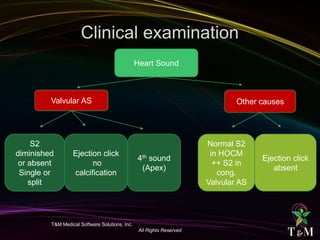
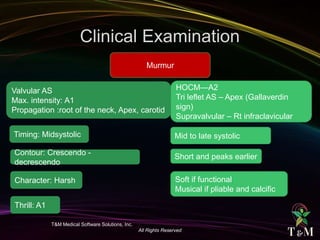
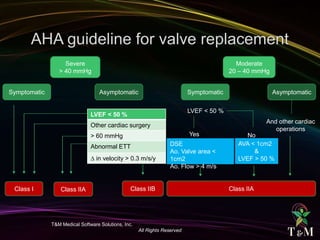
This document discusses aortic stenosis (AS) across different age groups and etiologies. It covers symptoms, physical exam findings, diagnostic criteria based on valve area and gradients, and indications for intervention. AS presents asymptomatically in early stages but can progress to cause angina, syncope and dyspnea from increased left ventricular pressure and reduced coronary flow. Physical exam may reveal delayed upstroke of the pulse and apical impulse. Diagnosis is made using echocardiography to measure valve area and gradients. Guidelines recommend intervention for severe AS or worsening symptoms.