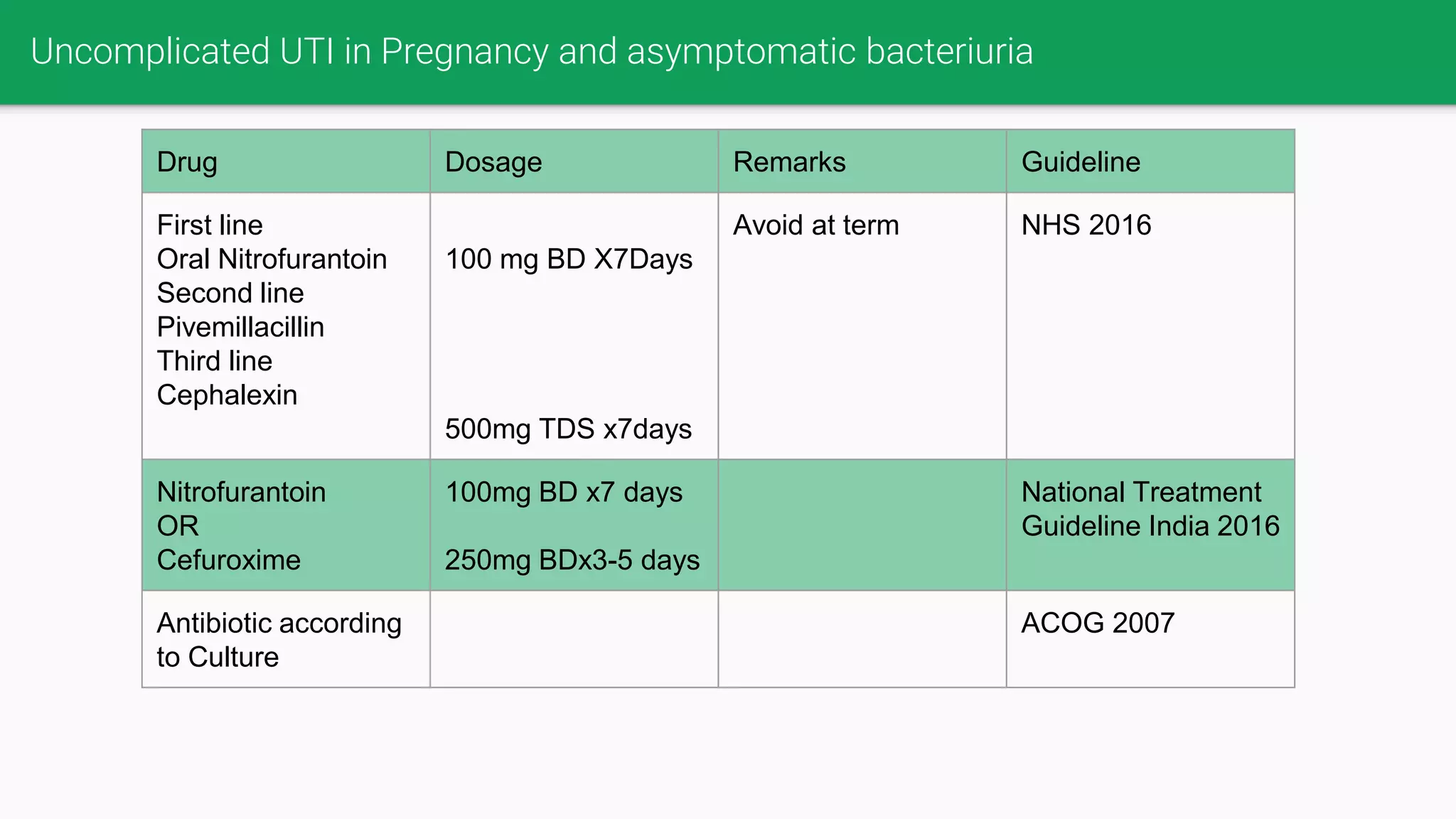
This document provides guidelines for the judicious use of antibiotics in obstetrics based on evidence. It discusses principles of surgical antibiotic prophylaxis and recommendations for cesarean sections, infectious endocarditis, GBS, operative vaginal deliveries, perineal lacerations, PPH, surgical abortions and therapeutic antibiotic usage in pregnancy. Guidelines are provided for appropriate antibiotic choice, dosage, and timing for various obstetric procedures based on levels of evidence from Cochrane reviews and randomized controlled trials. The document emphasizes using narrow spectrum antibiotics when possible to reduce antibiotic resistance.





























![Cephalosporin Antibiotics
Generati
on
Drug Sectrum
4 Cefepime inj (Cepime,
Micropime, Maxipime) 1-2
gm BD
Gram-positive: extended-spectrum agents with similar activity
against Gram-positive organisms as first-generation
cephalosporins.
Gram-negative: can penetrate the outer membrane of Gram-
negative bacteria.[19] They also have a greater resistance to β-
lactamases than the third-gen cephalosporins. can cross CNS.
They are also used against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Cefpirome inj (Cefor,
Bacirom) 1-2 gm BD
Ceflurepenam
5 Ceftobiprole Broad spectrum activity against MRSA and Pseudomonas
Ceftaroline
Ceftolozane](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antibioticusageinpregnancy-171122131006/75/Antibiotic-usage-in-pregnancy-32-2048.jpg)