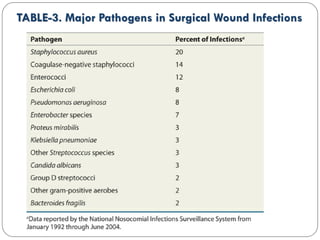
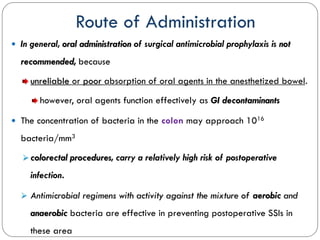
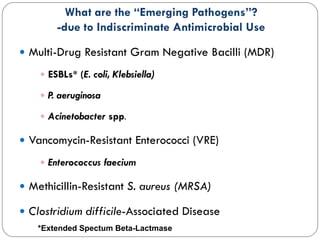
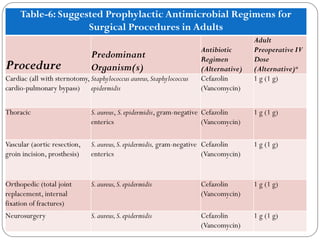
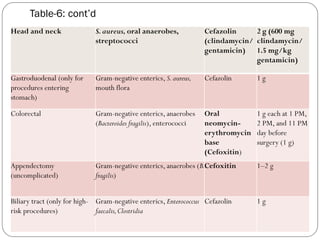
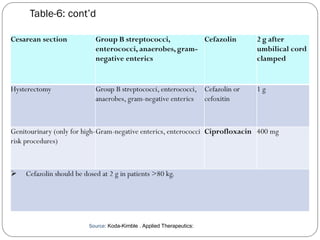
This document outlines guidelines for antimicrobial prophylaxis for surgical procedures. It discusses learning objectives, the epidemiology and etiology of surgical site infections, appropriate timing and selection of prophylactic antibiotics, and non-antimicrobial methods to reduce infection risk. Key points include that surgical site infections impact over 2 million patients annually in the US, common pathogens include Staphylococcus and streptococcus species, and cefazolin is recommended for most clean surgeries due to its efficacy against gram-positive organisms and favorable risk profile. Vancomycin may be used if MRSA rates are high. Proper administration and duration of prophylaxis is important to maintain bactericidal levels throughout the procedure.









































![Alternative Methods to Decrease SSI
Several non-antimicrobial methods have been studied for
reducing the risk of SSI.
providing supplemental warming(normothermia) to patients
(36.6°C -38°C) during the intraoperative period reduced
infection rates
use of warming blankets and IV fluid warmers
intensive glucose control [80 to 110 mg/dL (4.44 to 6.1
mmol/L)] versus conventional control [glucose less than 210
mg/dL (less than 11.7 mmol/L)] in reducing infections in
critically ill patients.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antimicrobialprophylaxisforsurgicalprocedures-230731152835-4507fcd5/85/Antimicrobial-Prophylaxis-for-Surgical-Procedures-pdf-52-320.jpg)







