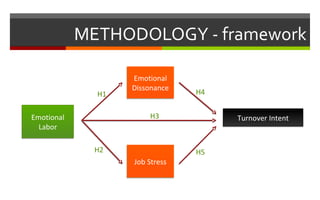
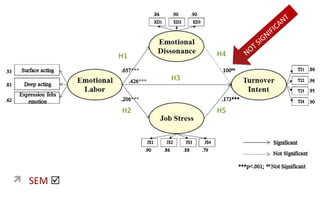
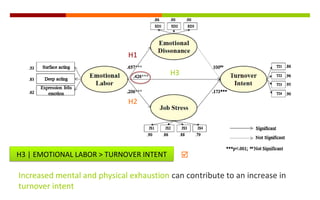
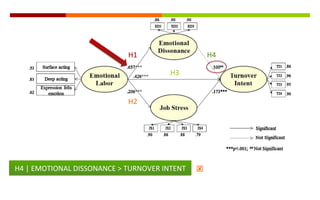
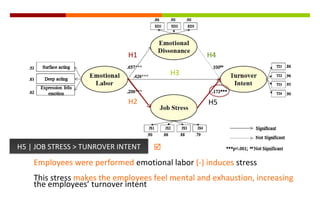
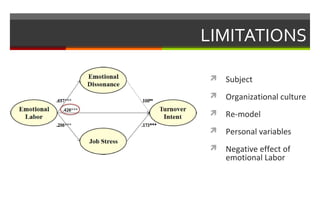
1) The document discusses a study on the antecedents (emotional labor) and consequences (turnover intent) of job stress in the foodservice industry, with emotional dissonance and job stress as mediating factors.
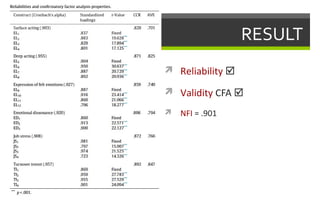
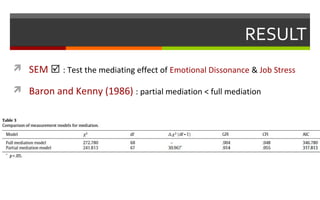
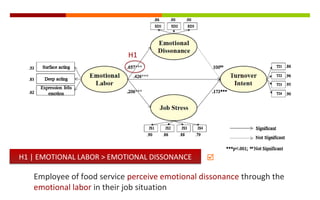
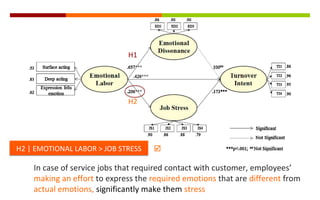
2) The study found that emotional labor leads to increased emotional dissonance and job stress. Job stress was also found to increase turnover intent. However, emotional dissonance was not found to increase turnover intent.
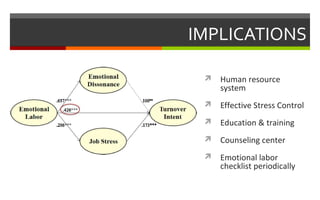
3) The implications discussed include implementing human resource programs like stress control training, counseling, and periodic emotional labor assessments to help mitigate the negative impacts of emotional labor.