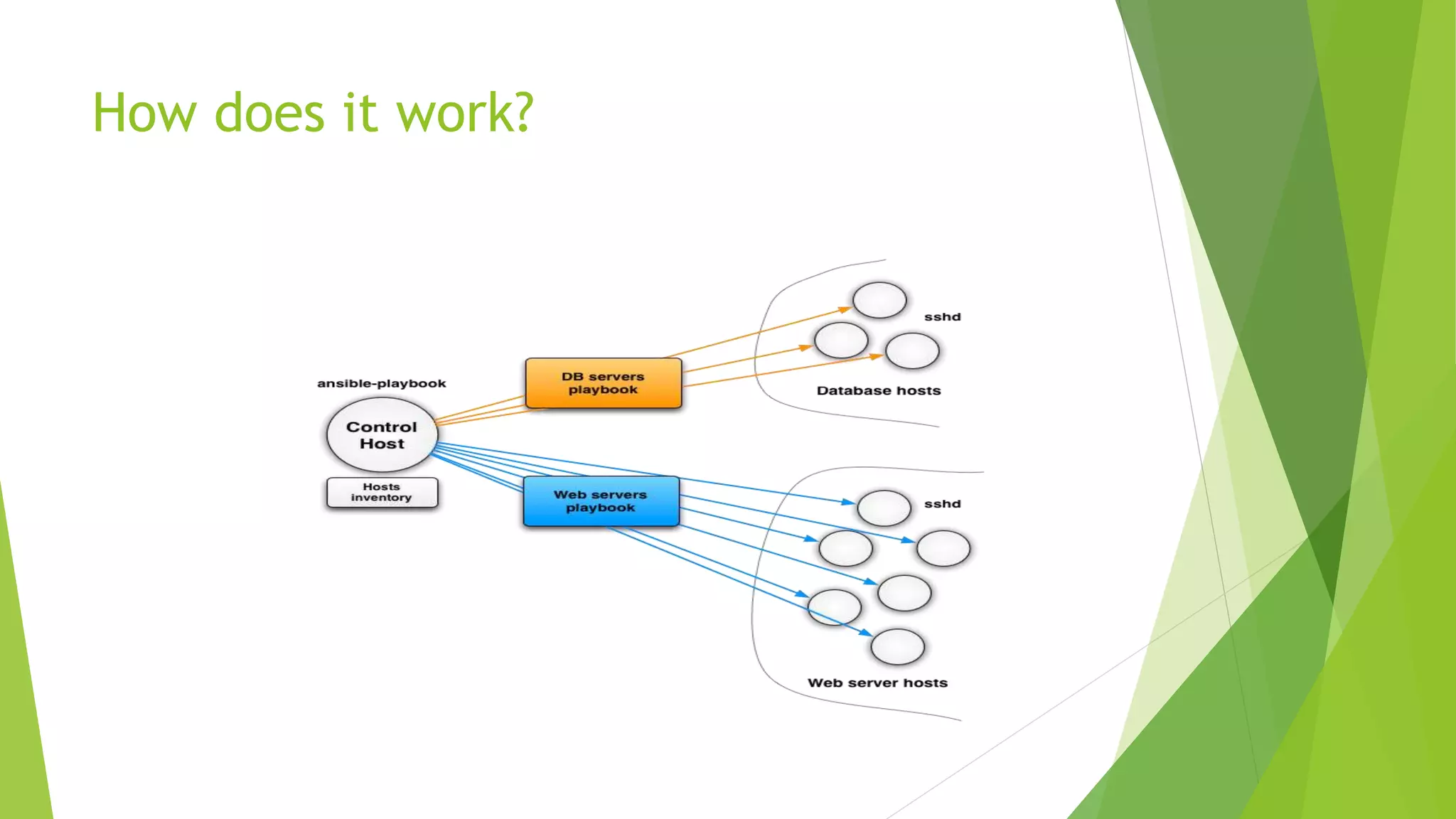
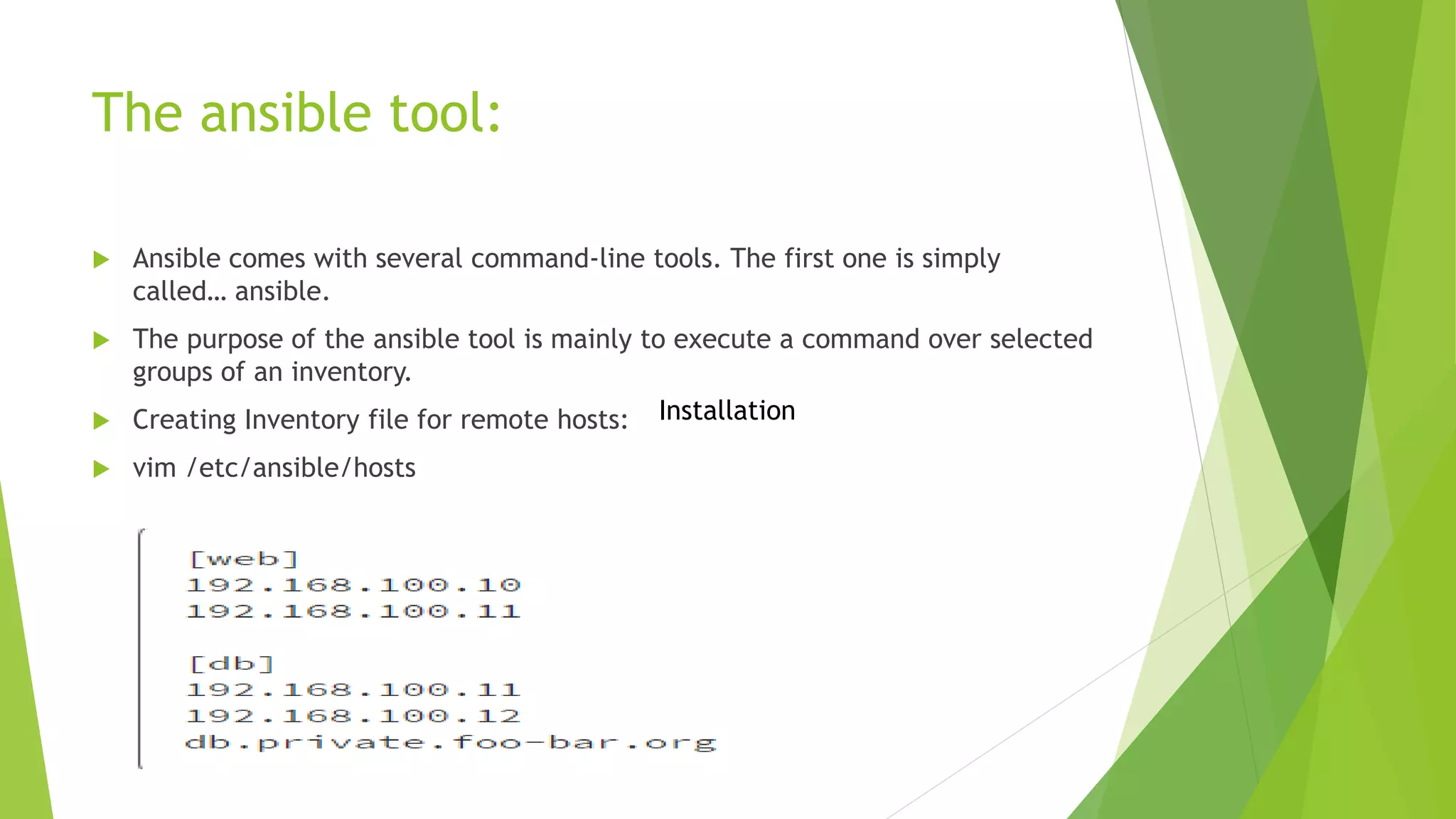
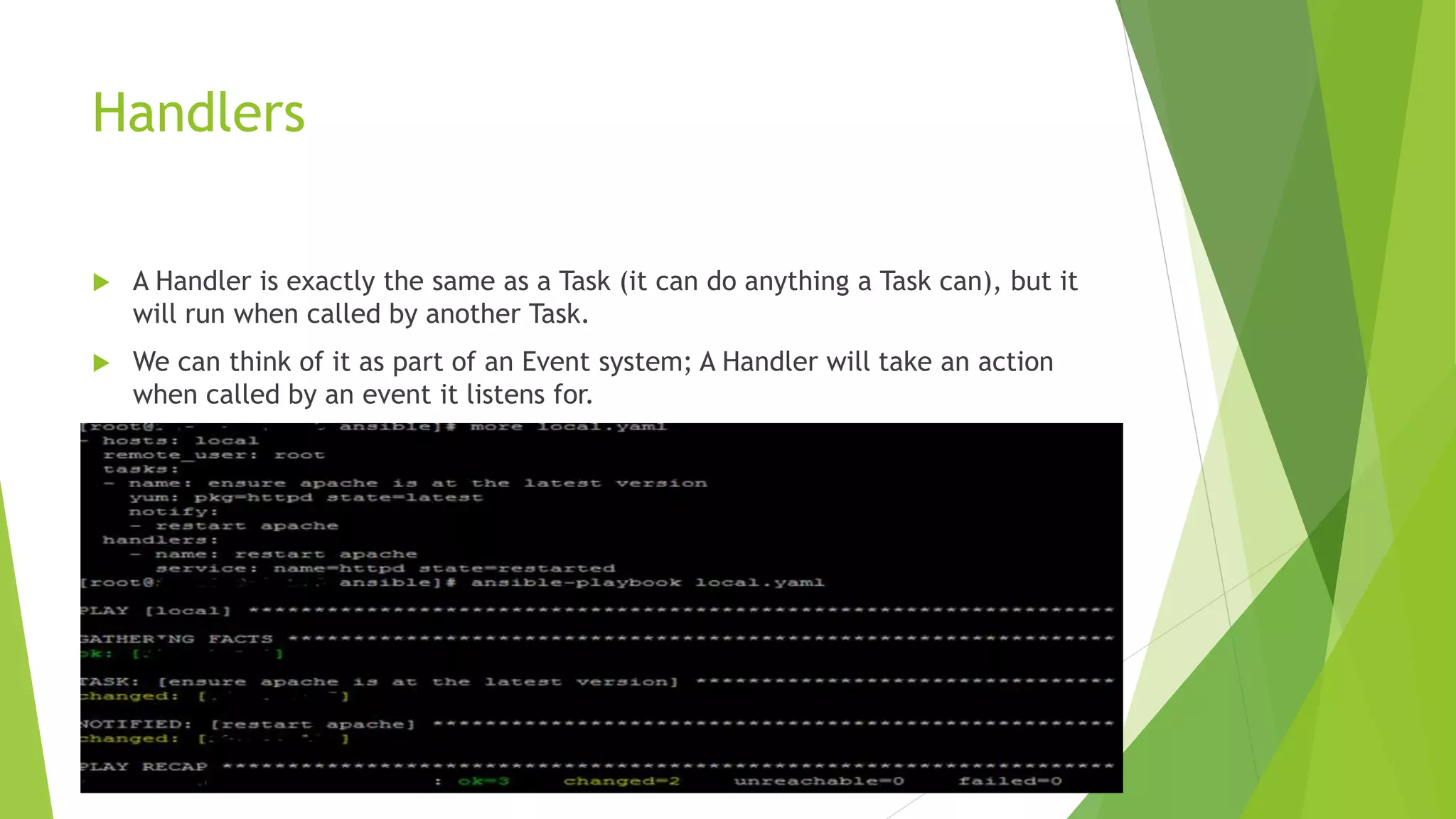
This document discusses Ansible configuration management. It begins with an agenda that includes what Ansible is, how it differs from other tools, how it works, installation, available tools, running ad hoc commands, playbooks, handlers, roles, and a demo playbook for Apache. Ansible is an agentless automation tool that uses YAML playbooks to describe configuration and deployment jobs in a way that is human-readable. It has many built-in modules and can be used for configuration management, orchestration, and deployment.