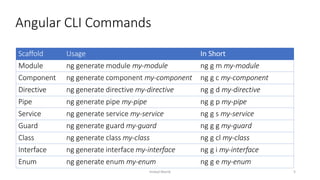
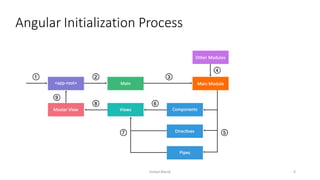
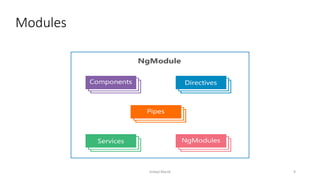
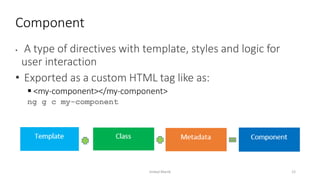
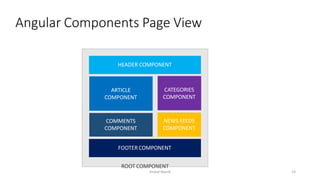
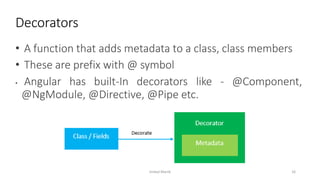
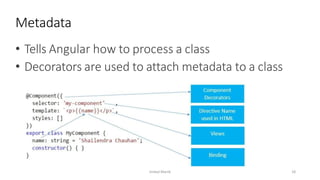
This document provides an introduction to Angular, a framework built with TypeScript, detailing its architecture, environment setup, and basic building blocks like components and modules. It explains key concepts such as services, dependency injection, directives, and data binding while offering commands for Angular CLI usage. Additionally, it discusses routing, templates, and decorators, essential for Angular application development.