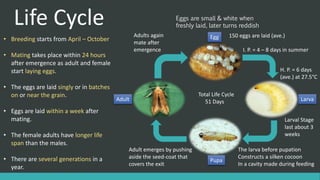
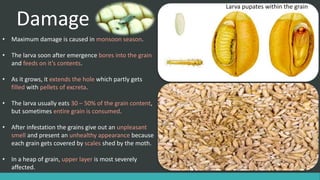
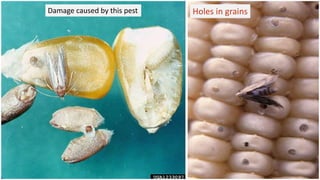
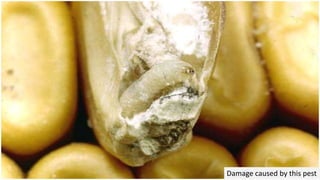
The Angoumois Grain Moth is a worldwide pest that attacks stored cereal grains like wheat, oats, barley, maize and sorghum. The larvae feed on and damage the grain kernels, while the adults feed on nectar and water. The larvae are white with a yellow-brown head, grow up to 5mm long, and cause the most damage by boring into and consuming 30-50% of grain contents. The moths have narrow pointed wings with long hairs and a 10-12mm wing span. There are multiple generations per year, with eggs hatching in 4-8 days and the full lifecycle taking 51 days from egg to adult.
![Angoumois Grain Moth
Sitotroga cerealella
ALL PRAISE IS DUE TO ALLAH , THE LORD OF THE WORLDS, THE [ONE WHO] SUSTAINS THE HEAVENS AND EARTHS
Made by:
Arslan Ahmad
University of Agriculture Faisalabad
Sub Campus Burewala, Pakistan
blackeagle94473@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angoumoisgrainmothpresentation-170402044923/85/Angoumois-Grain-Moth-1-320.jpg)