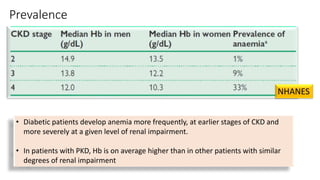
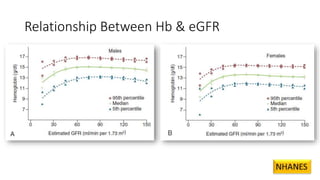
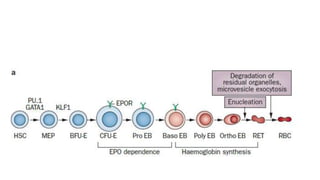
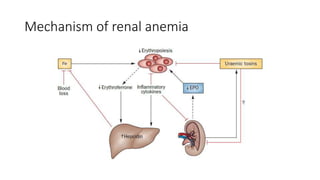
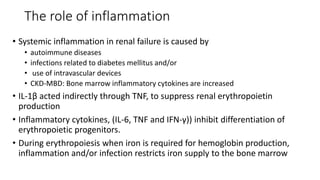
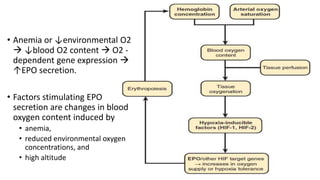
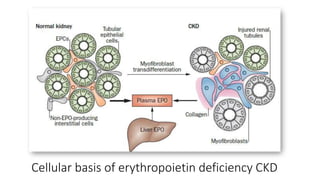
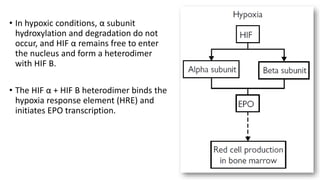
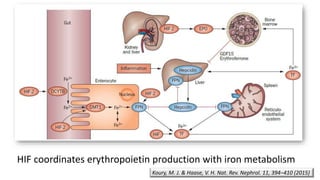
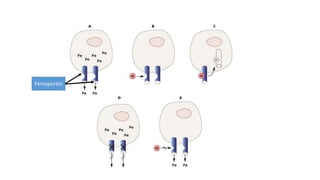
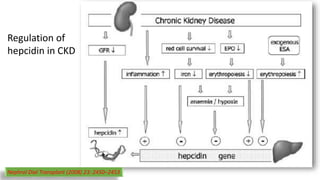
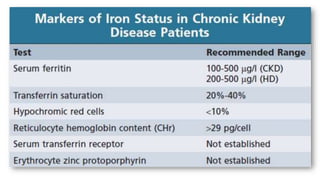
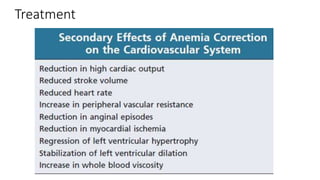
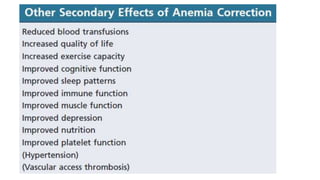
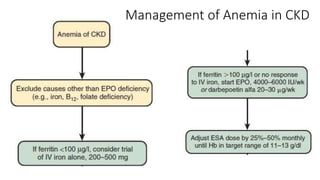
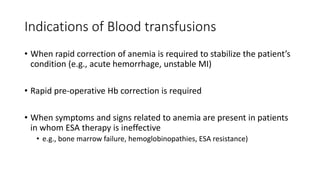
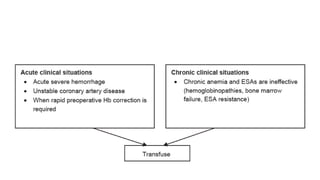
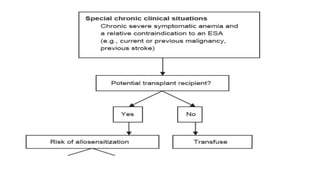
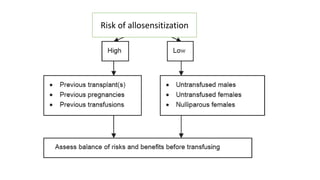
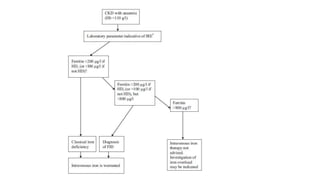
This document discusses anemia in chronic kidney disease (CKD). It notes that anemia is a clinical hallmark of advanced CKD, characterized by decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. Around 90% of patients with a GFR below 25-30 mL/min develop anemia, many with hemoglobin levels below 10 g/dL. The main causes of renal anemia are erythropoietin deficiency and reduced red blood cell lifespan and production. Inflammation and uremic toxins also contribute by suppressing erythropoiesis and erythropoietin production. Treatment involves iron supplementation and administration of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents to compensate for reduced endogenous erythropoietin levels