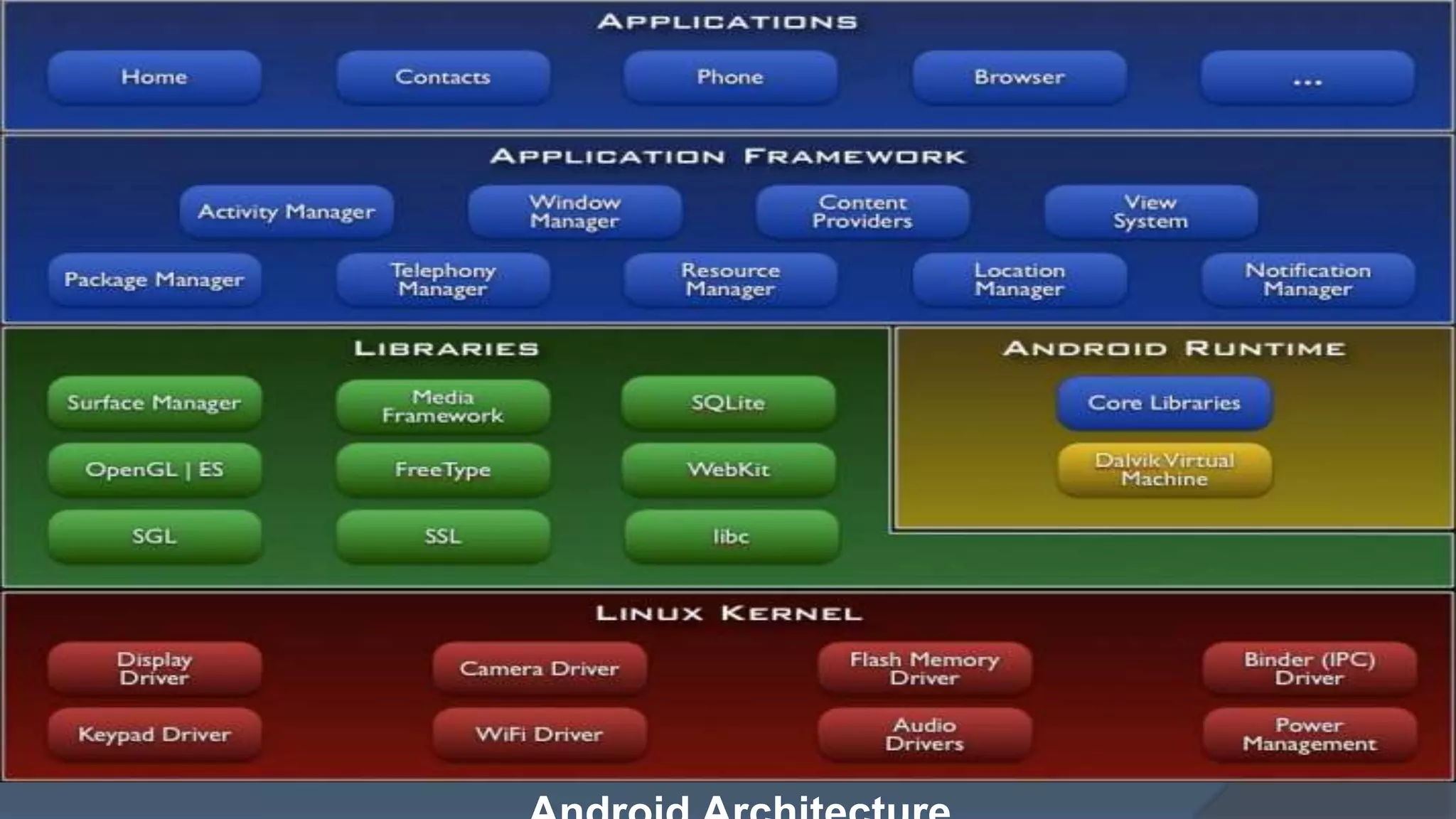
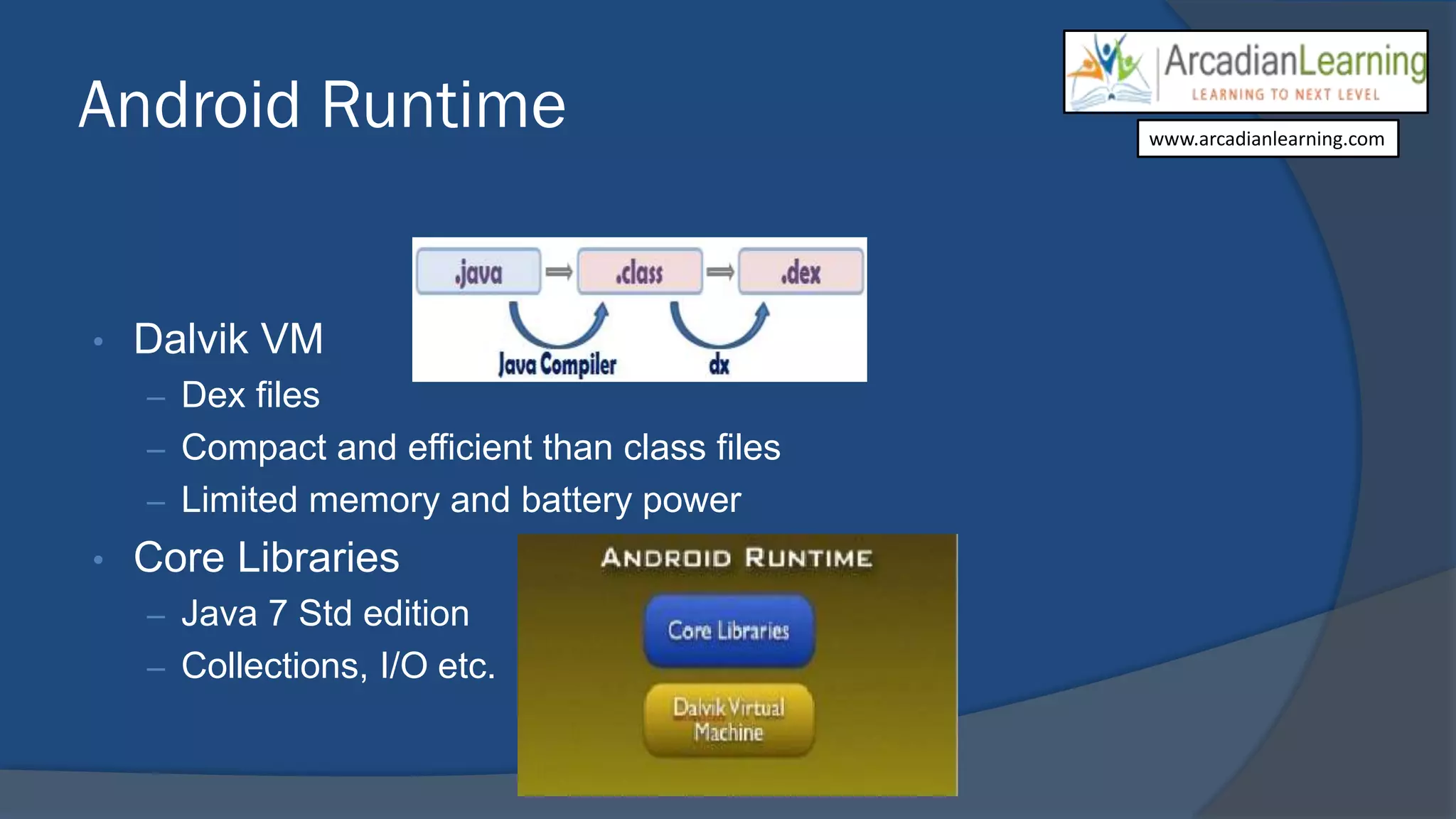
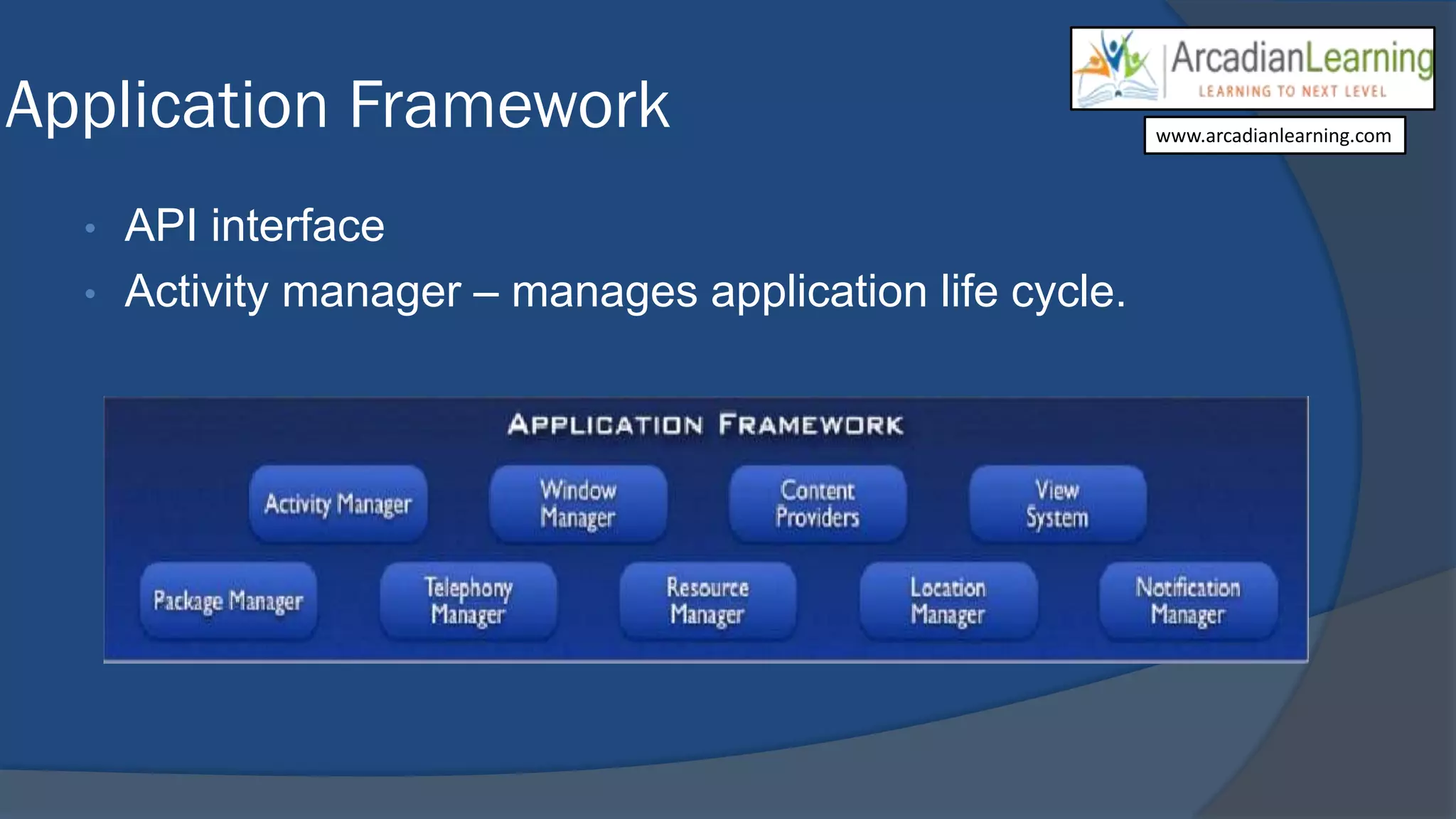
Android is a leading mobile operating system based on the Linux kernel, currently supporting over 200,000 applications developed primarily in Java. It features a robust application framework, including components such as activities, services, and content providers, while also facing challenges like limited hardware resources and UI design constraints. Despite these challenges, the platform presents significant opportunities for developers due to its extensive user base and rapid growth, particularly in Asia.