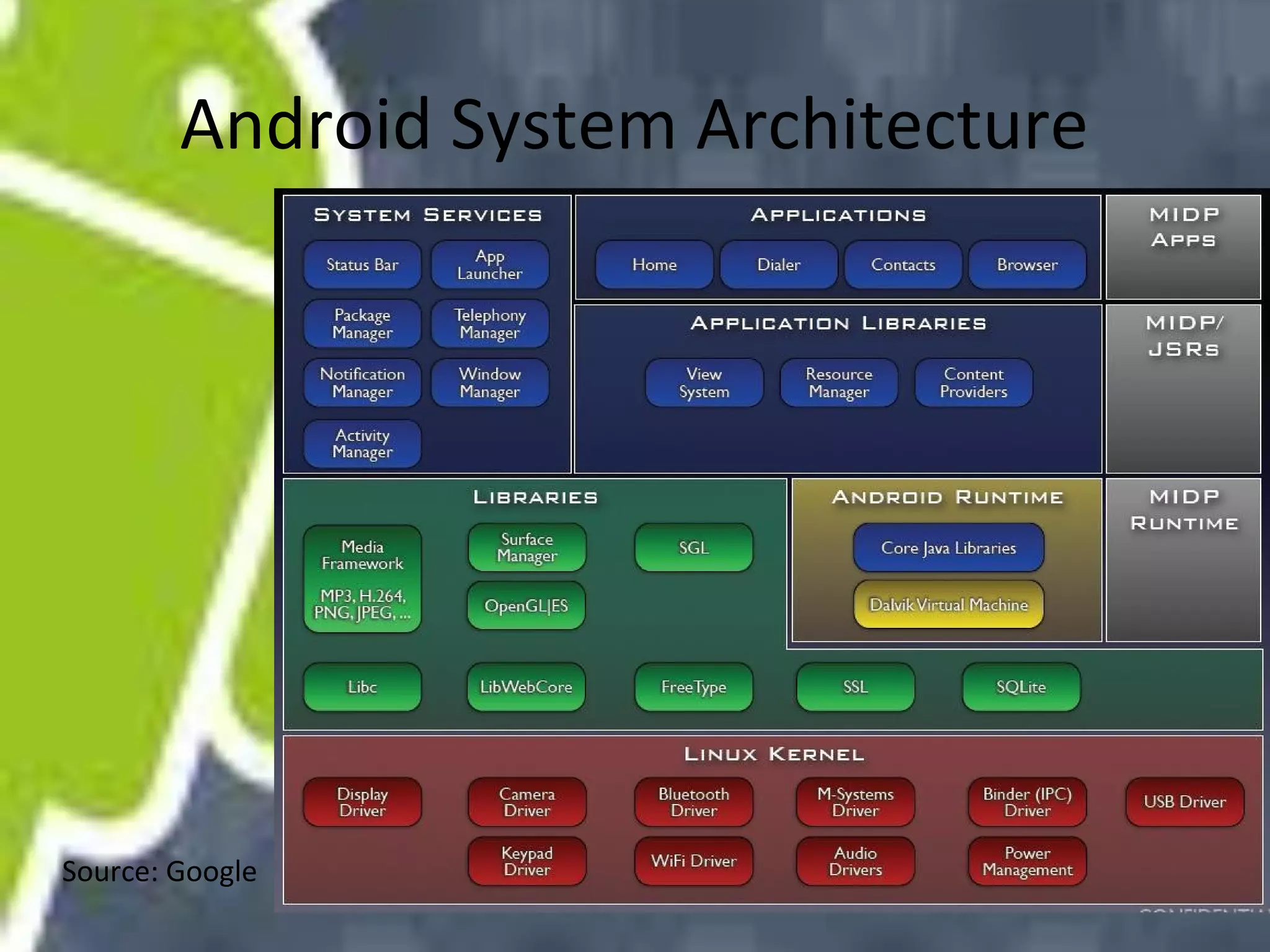
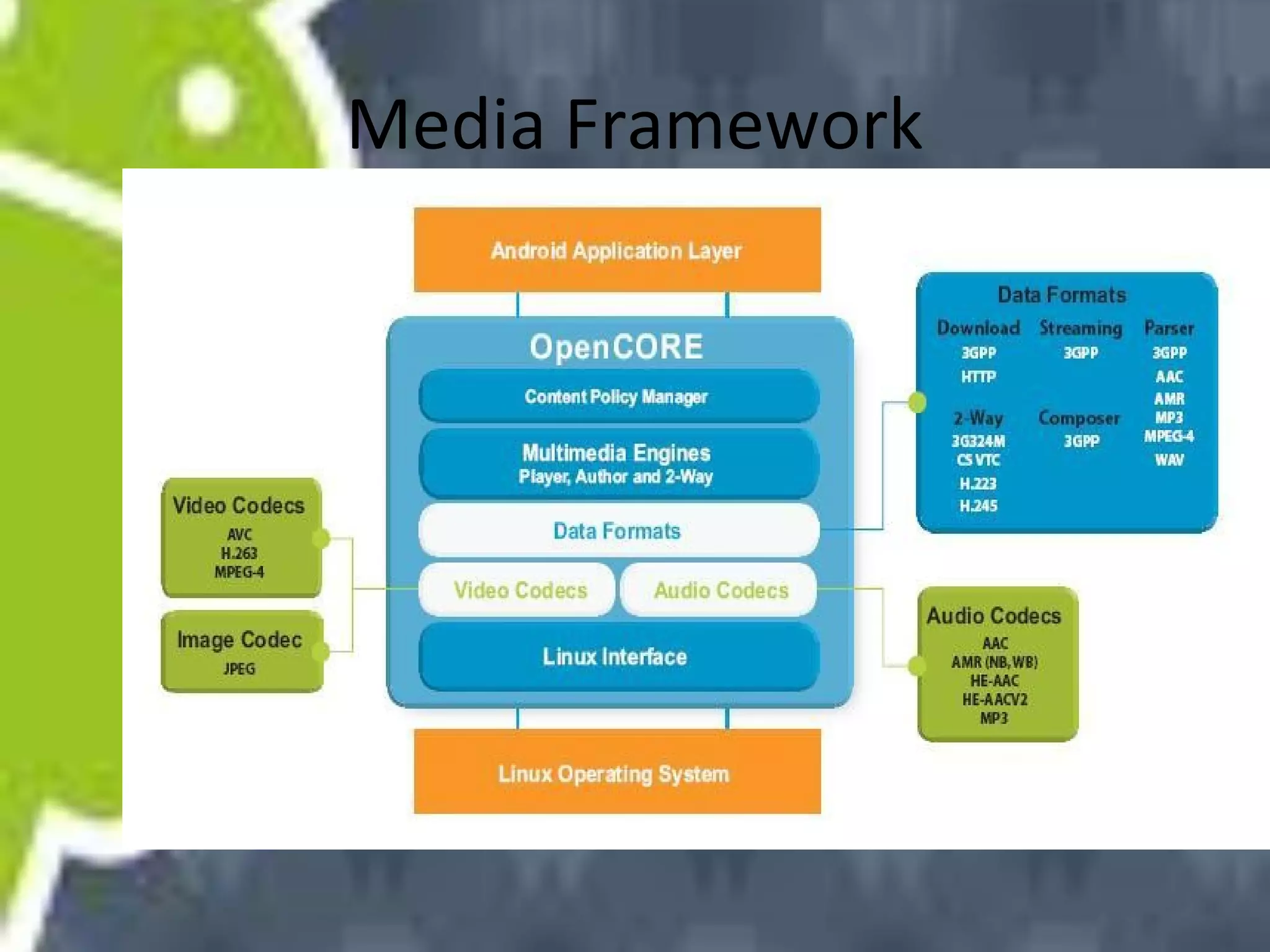
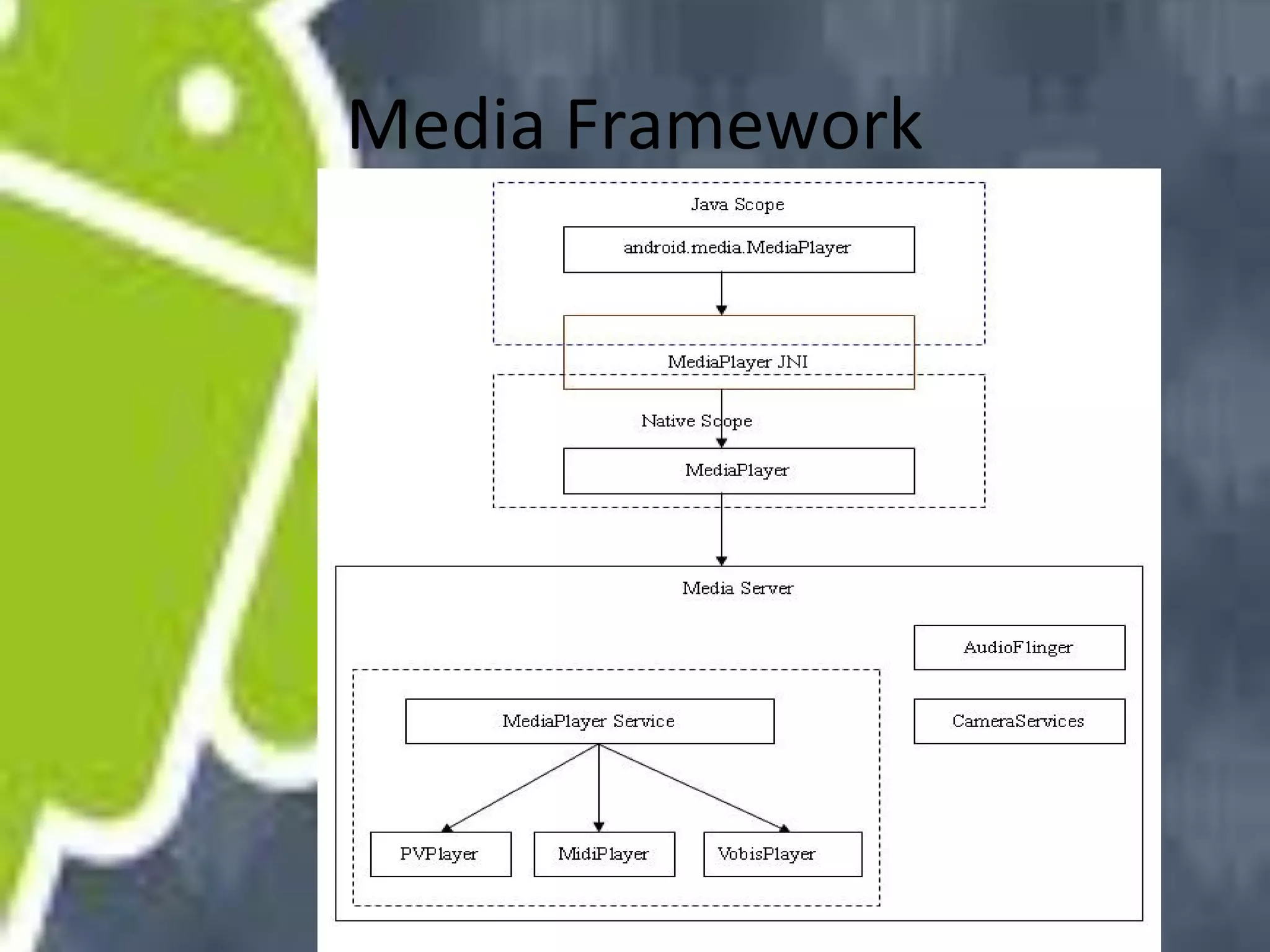
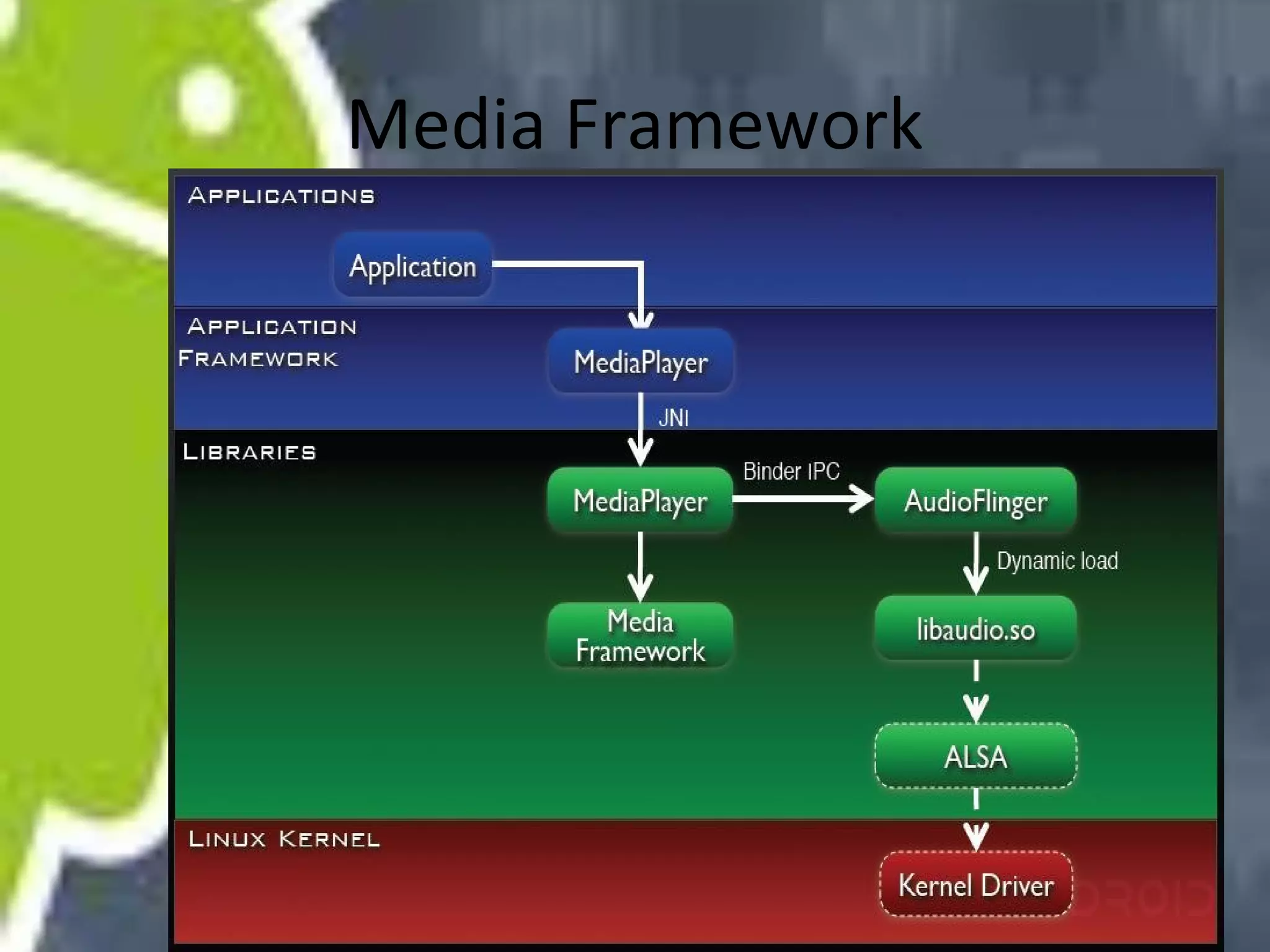
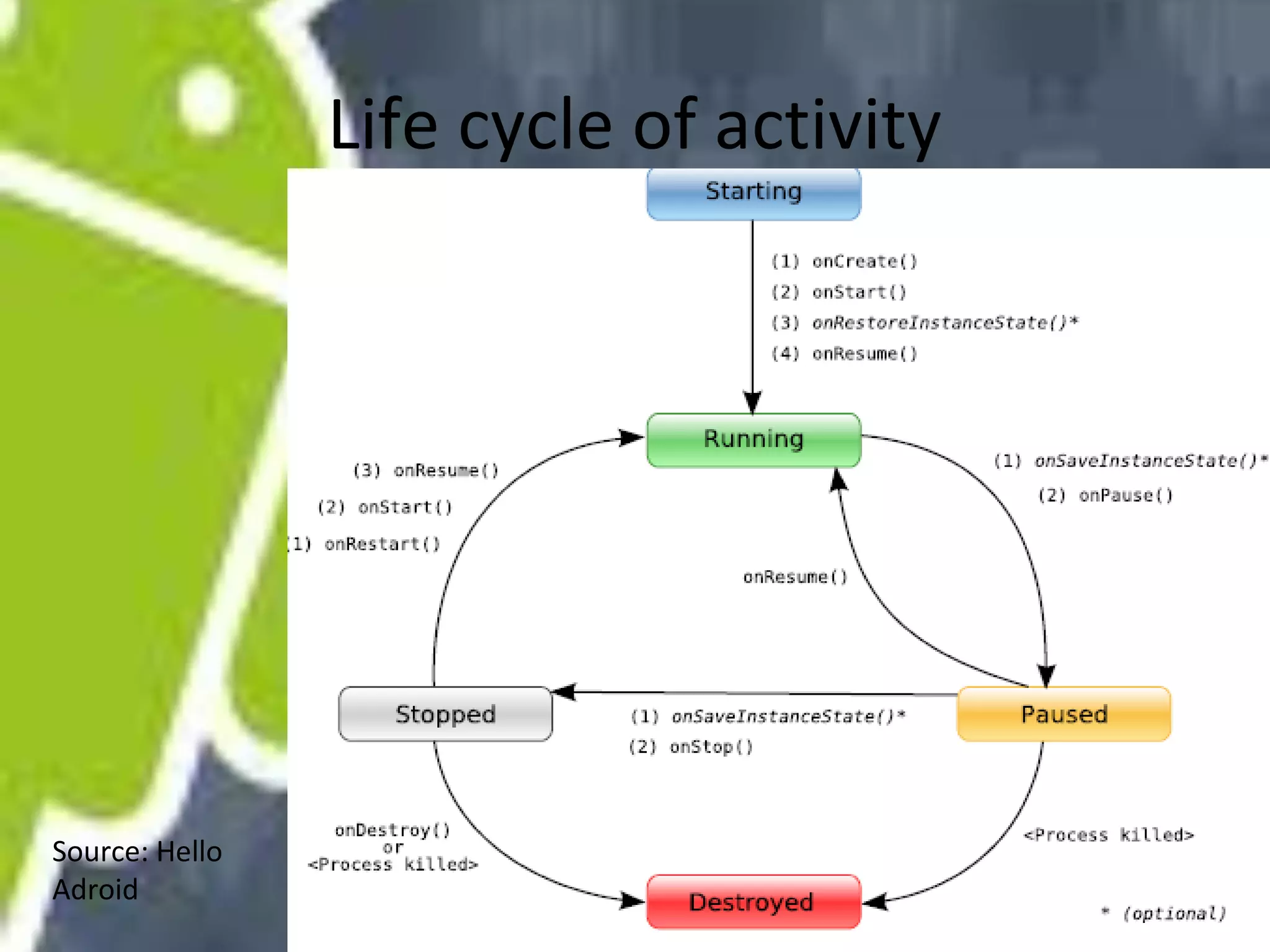
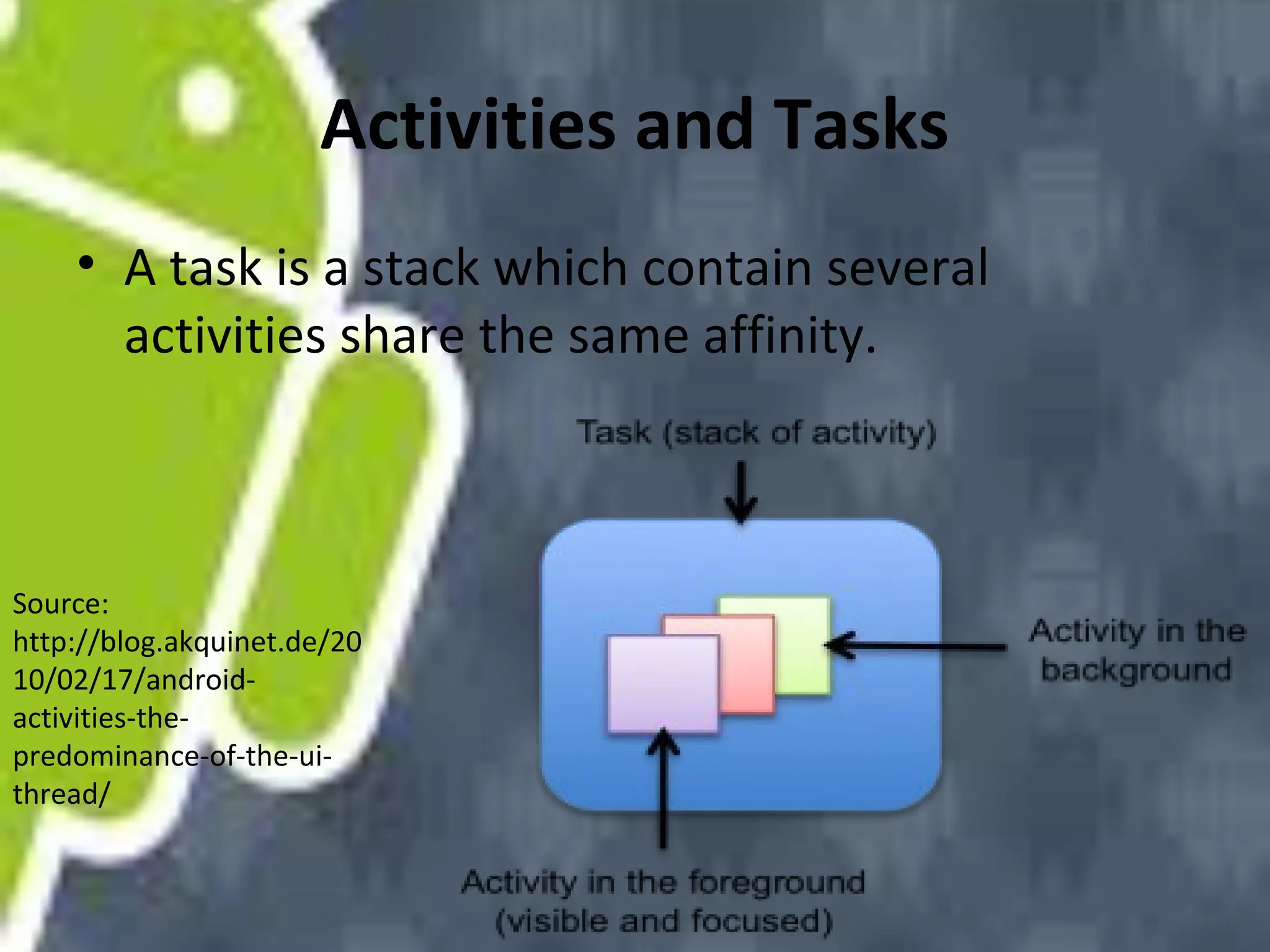
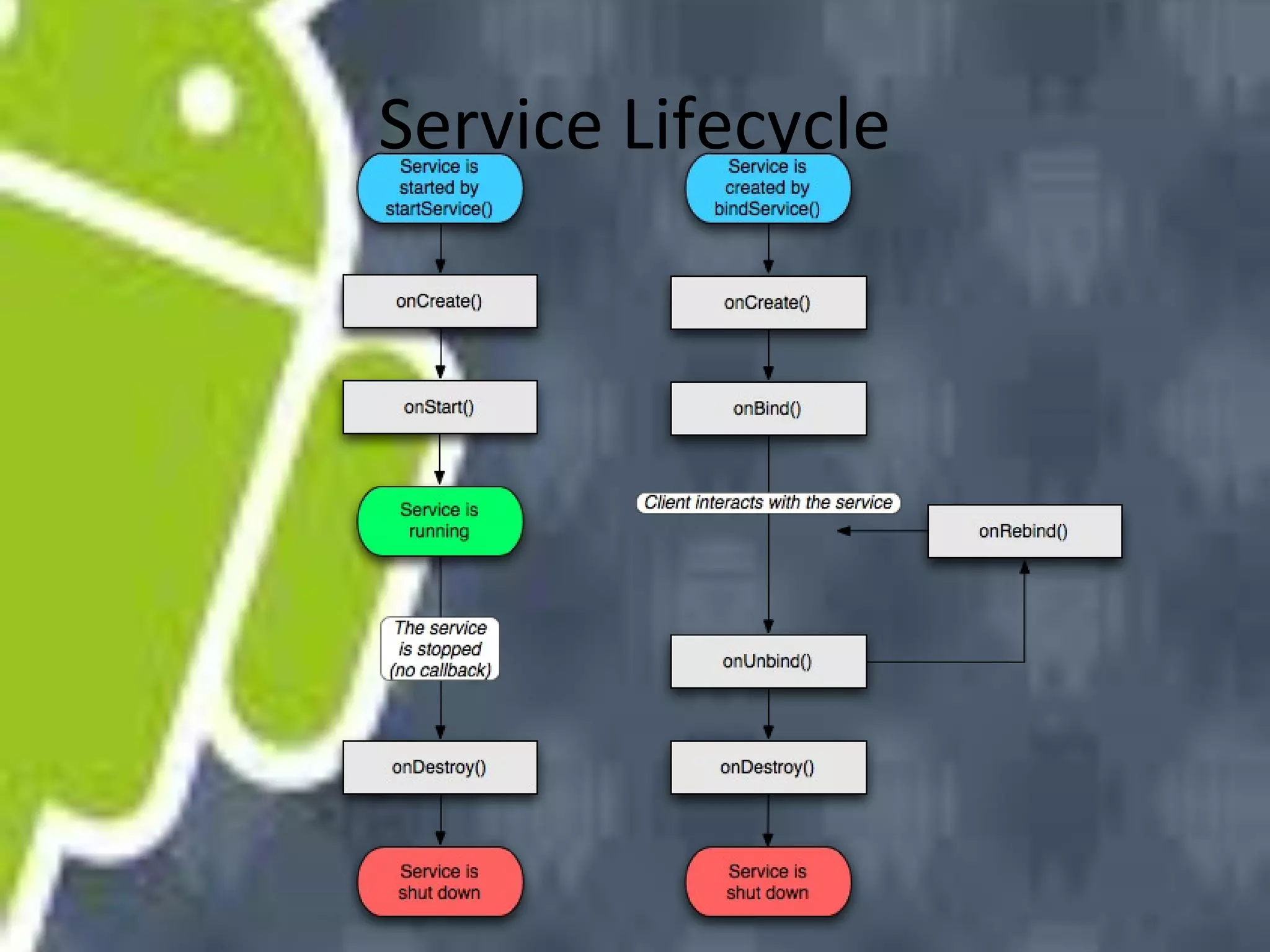
Android uses a Linux kernel for core system services. It includes native libraries for graphics, media playback, and databases. The Android runtime includes the Dalvik VM and Java core libraries. The application framework manages activities, content providers, notifications and resources. Activities display user interfaces. The media framework uses OpenCore for formats like MP3 and MPEG-4. It has a client-server architecture with MediaPlayer as the client. Activities have a lifecycle managed by the activity manager using intents. Content providers manage shared data through a client-server model using URIs. Permissions control access between apps and the system.