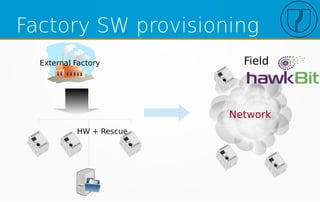
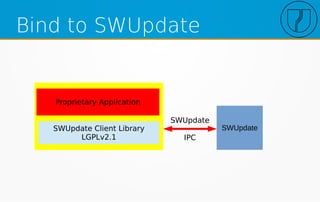
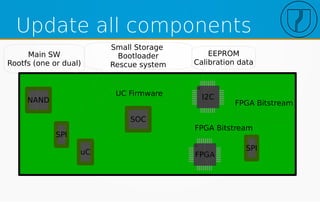
The document discusses the evolution of over-the-air (OTA) updates in the Internet of Things (IoT), emphasizing the role of hardware manufacturers and infrastructure in facilitating these updates. It outlines key features for update agents, security measures, and challenges in managing updates across different versions and devices. Additionally, it covers requirements for effective software updates in a private network, including streamlined deployment and the need for a robust update process for various system components.










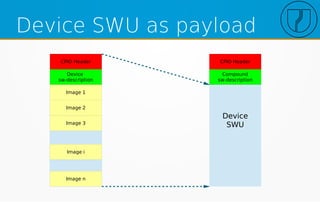
![Device SWU
software = {
device-controller = {
hardware-compatibility: [ "1.0"];
rescue : {
partitions: ( /* ubi volumes */ );
images: ( {…..});
uboot: ( {…..} );
};
};
production : {
copy1 : {
images: (...)
uboot: (...)
};
copy2 : {
images: (...)
uboot: (...)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evolutionofotaupdateintheiotworld-190918071826/85/Evolution-of-ota_update_in_the_io_t_world-15-320.jpg)
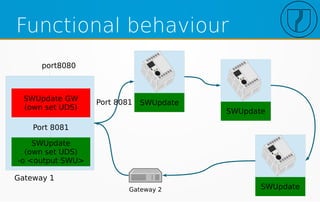
![Compound image
software = {
gateway-controller = {
embedded-script = „
function detect_topology(image)
……………………..
end
hardware-compatibility: [ "1.0"];
images: (
{
filename = "<SWU Image for each device>";
type = "swuforwarder“;
sha256 = "<hash 256 of SWU>“;
hook = "detect_topology“
properties {
}; // this will be filles by the embedded script
};
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evolutionofotaupdateintheiotworld-190918071826/85/Evolution-of-ota_update_in_the_io_t_world-18-320.jpg)
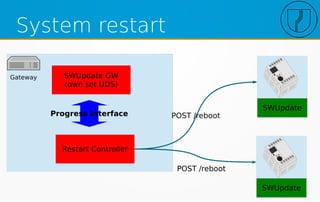


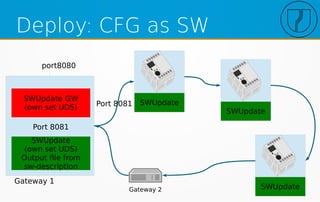
![Configuration SWU
software = {
device-controller = {
output = „config.swu“
hardware-compatibility: [ "1.0"];
production : {
copy1 : {
files: (
filename = „configuration.tar.gz“
type = „archive“;
compressed = true;
path = „/etc/application“;
);
};
copy2 : {
ref = „ ../copy1“;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evolutionofotaupdateintheiotworld-190918071826/85/Evolution-of-ota_update_in_the_io_t_world-24-320.jpg)