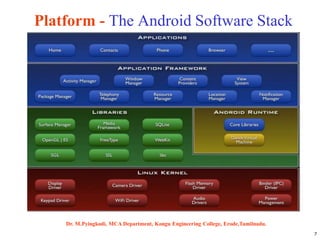
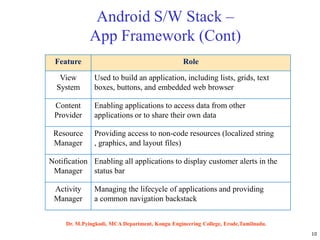
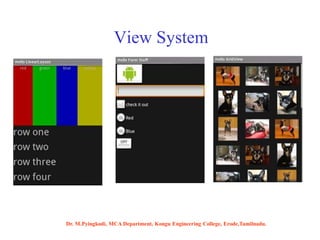
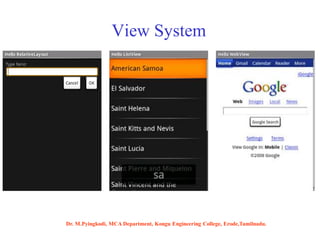
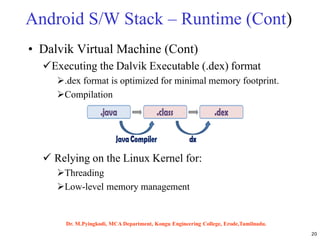
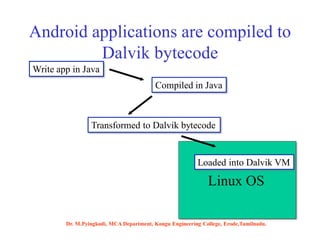
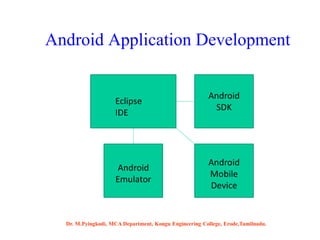
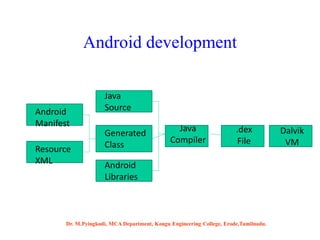
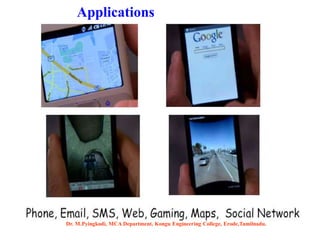
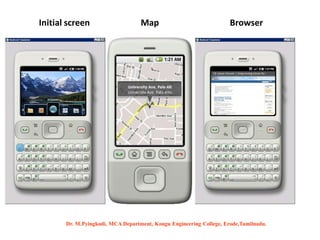
Android is an open-source software platform based on the Linux kernel that is used for mobile devices. It is developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance. The document discusses Android's architecture including its software stack from applications down to the Linux kernel. It also covers Android development tools and the building blocks of an Android application like activities, services, and content providers.