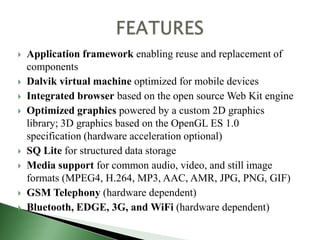
Android is an open source operating system used primarily for mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. It uses a modified Linux kernel and includes key applications and middleware written in C/C++. Java is used for application development. Android provides basic OS services, messaging, and allows inter-process communication. It has a large developer community and supports many hardware manufacturers.





![ Android is a mobile operating system which is
becoming a major competitor to iPhone OS in
terms of openness.I am beginning the android
series which will be helpful for developers who
wish to develop android apps.
Android was initially developed by Android Inc.
Later acquired by Google to form open Headset
alliance [ a group of 65 hardware, software, and
telecom companies ].Applications for android
devices are written in Java language.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-111121031806-phpapp01/85/Android-6-320.jpg)

![v 3.0 Honeycomb
Designed especially for Tablet PC’s
Android 3.0[Honeycomb] is dedicated for tablet PCs hence the design change primarily focuses in tablet optimization with updated UI.
Honeycomb is the next version of the Android platform, designed from the ground up for devices with larger screen sizes, particularly tablets
Icecream Sandwich
The next version composing of both
gingerbread and honeycomb into unified
OS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-111121031806-phpapp01/85/Android-8-320.jpg)