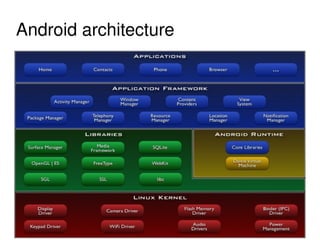
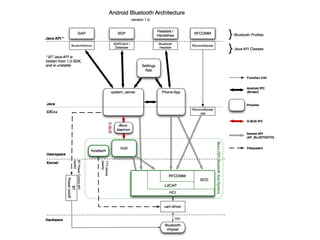
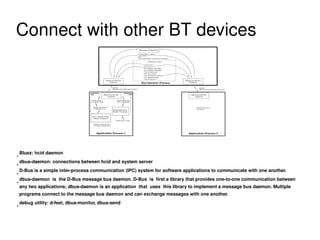
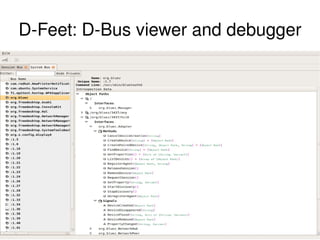
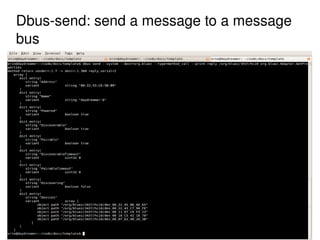
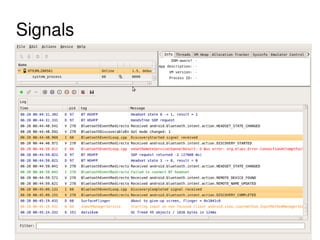
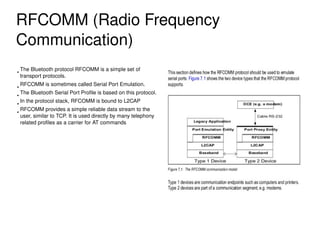
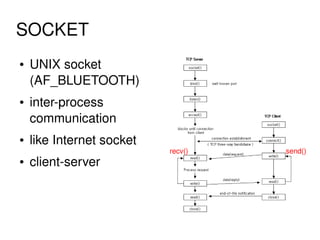
The document provides an overview of Bluetooth architecture and implementation in Android. It discusses the Bluetooth stack including BlueZ, related source code, initializing Bluetooth, connecting to other devices via D-Bus, using RFCOMM for serial communication, and exchanging objects with OBEX. Methods for pairing with devices, sending/receiving files, and using utilities like hcitool, rfcomm, and obexpushd are also summarized.