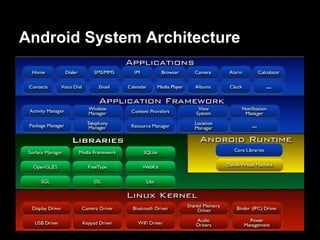
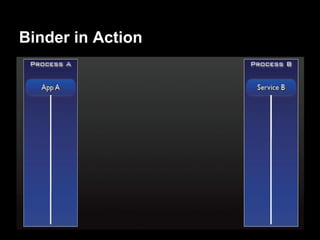
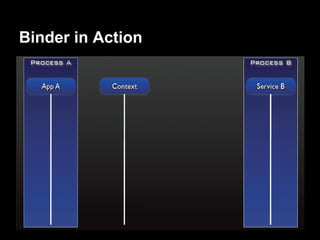
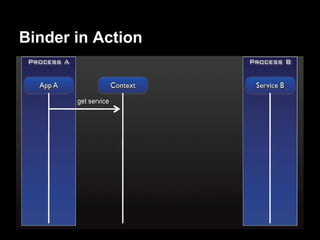
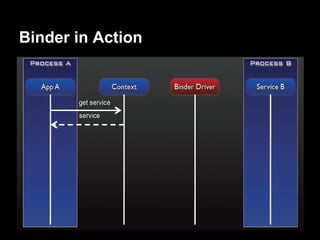
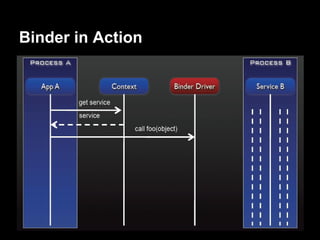
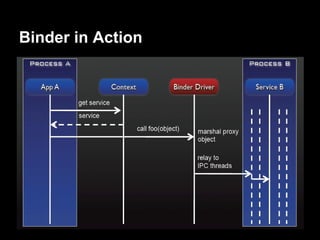
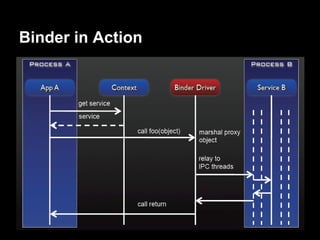
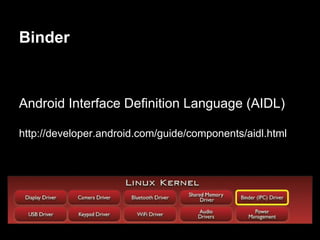
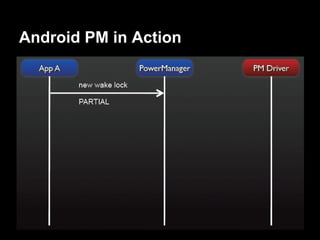
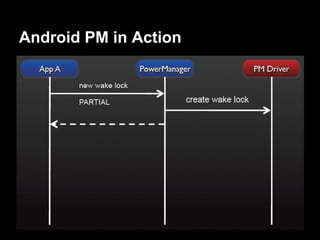
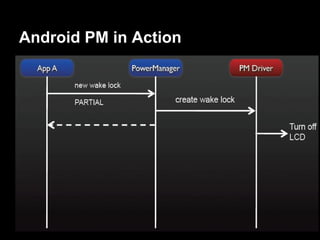
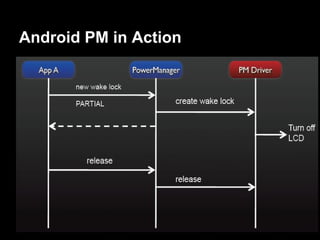
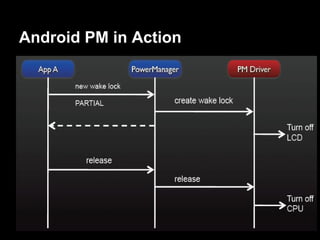
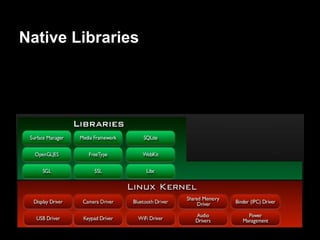
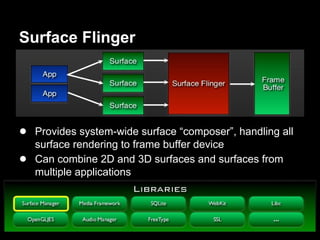
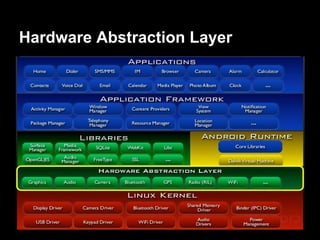
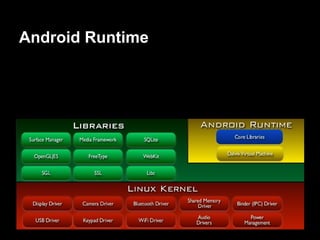
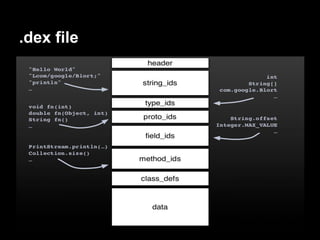
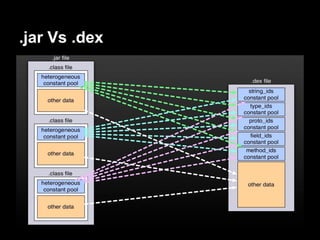
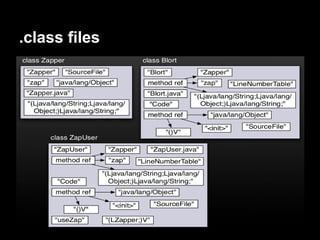
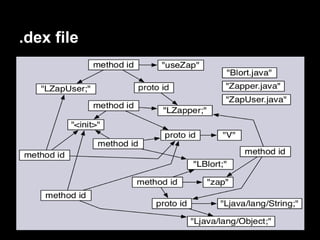
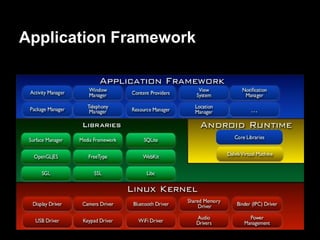
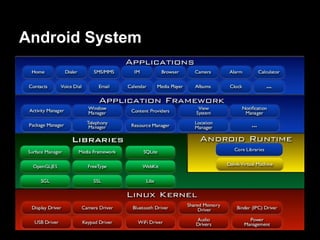
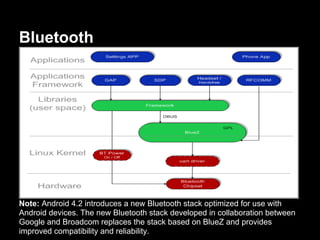
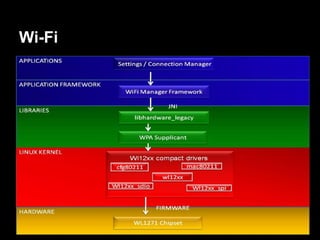
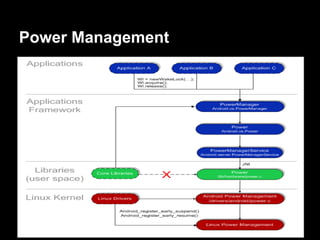
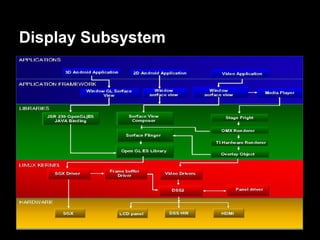
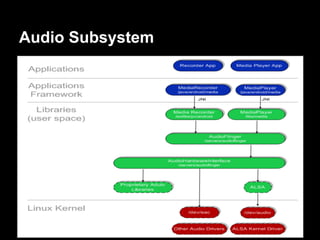
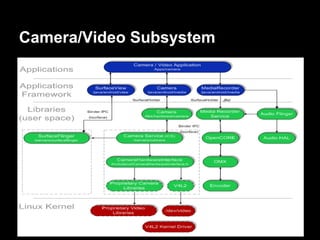
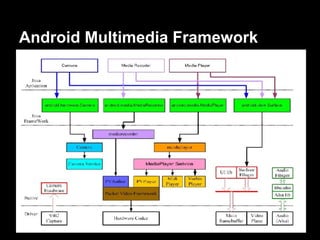
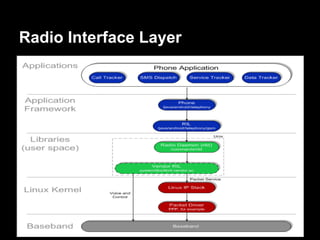
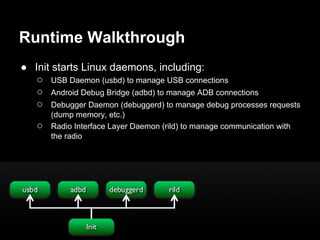
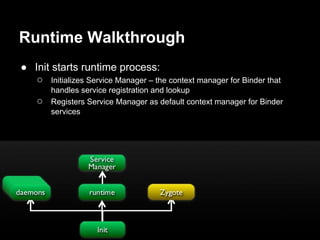
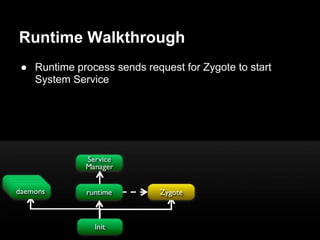
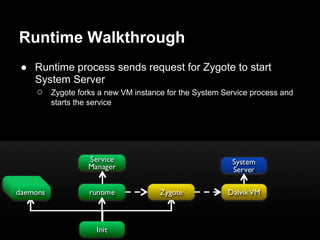
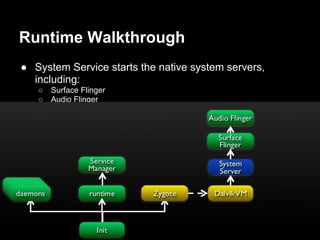
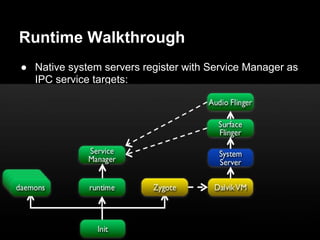
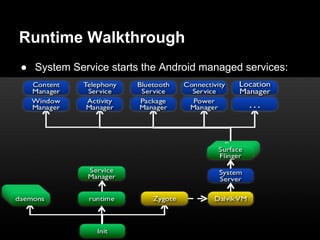
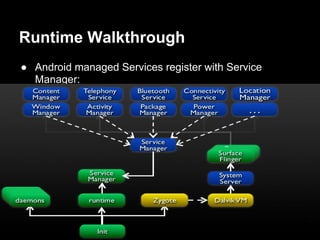
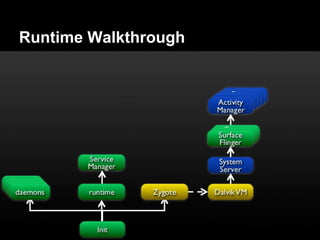
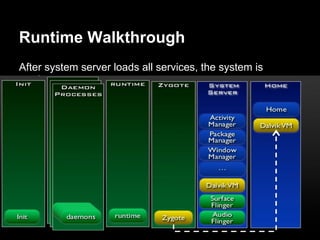
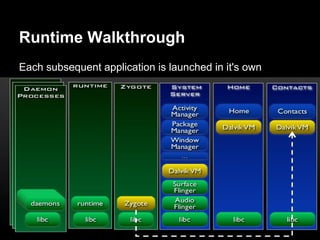
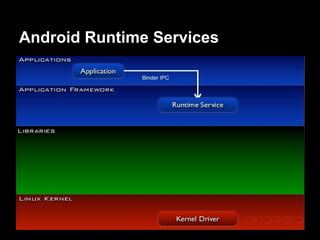
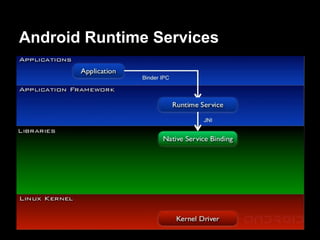
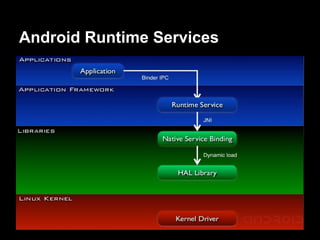
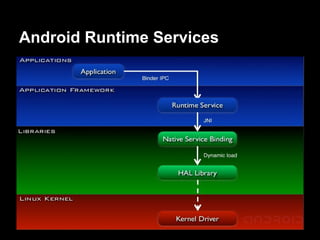
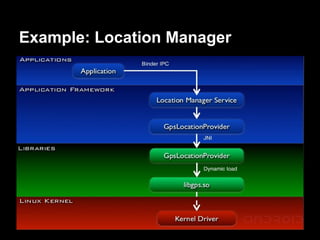
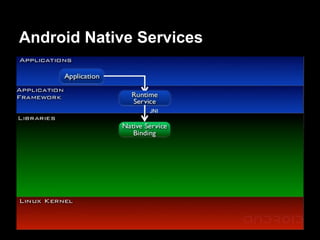
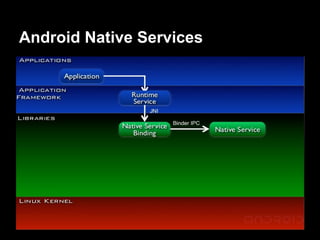
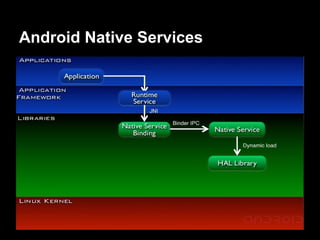
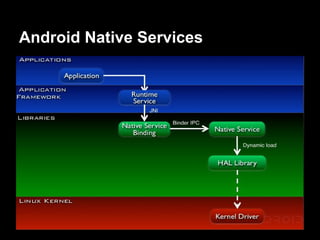
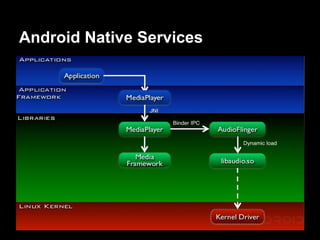
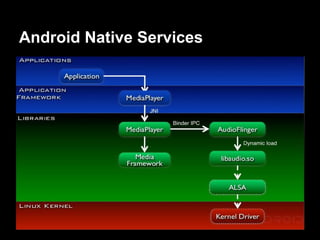
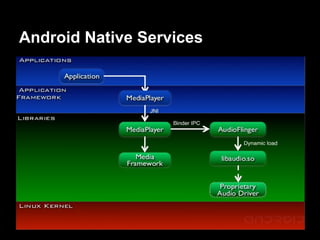
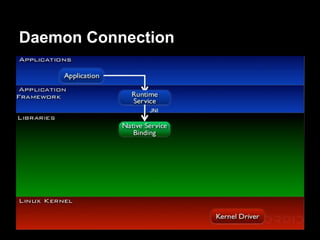
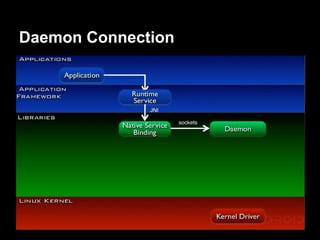
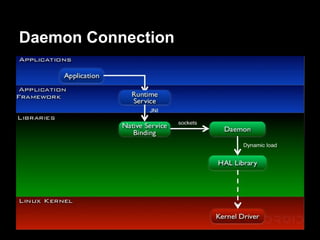
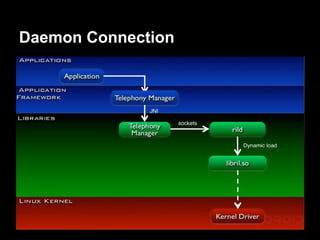
This document provides an overview of the Android system architecture. It describes the key components including the Linux kernel, native libraries like Bionic and SQLite, the Android runtime using the Dalvik VM, and the application framework. It also covers core platform services, hardware services, and internal system components for connectivity, power management, display/multimedia, and telephony. The document outlines how these layers interact and provides technical details on implementations like Binder IPC and the SurfaceFlinger compositor.