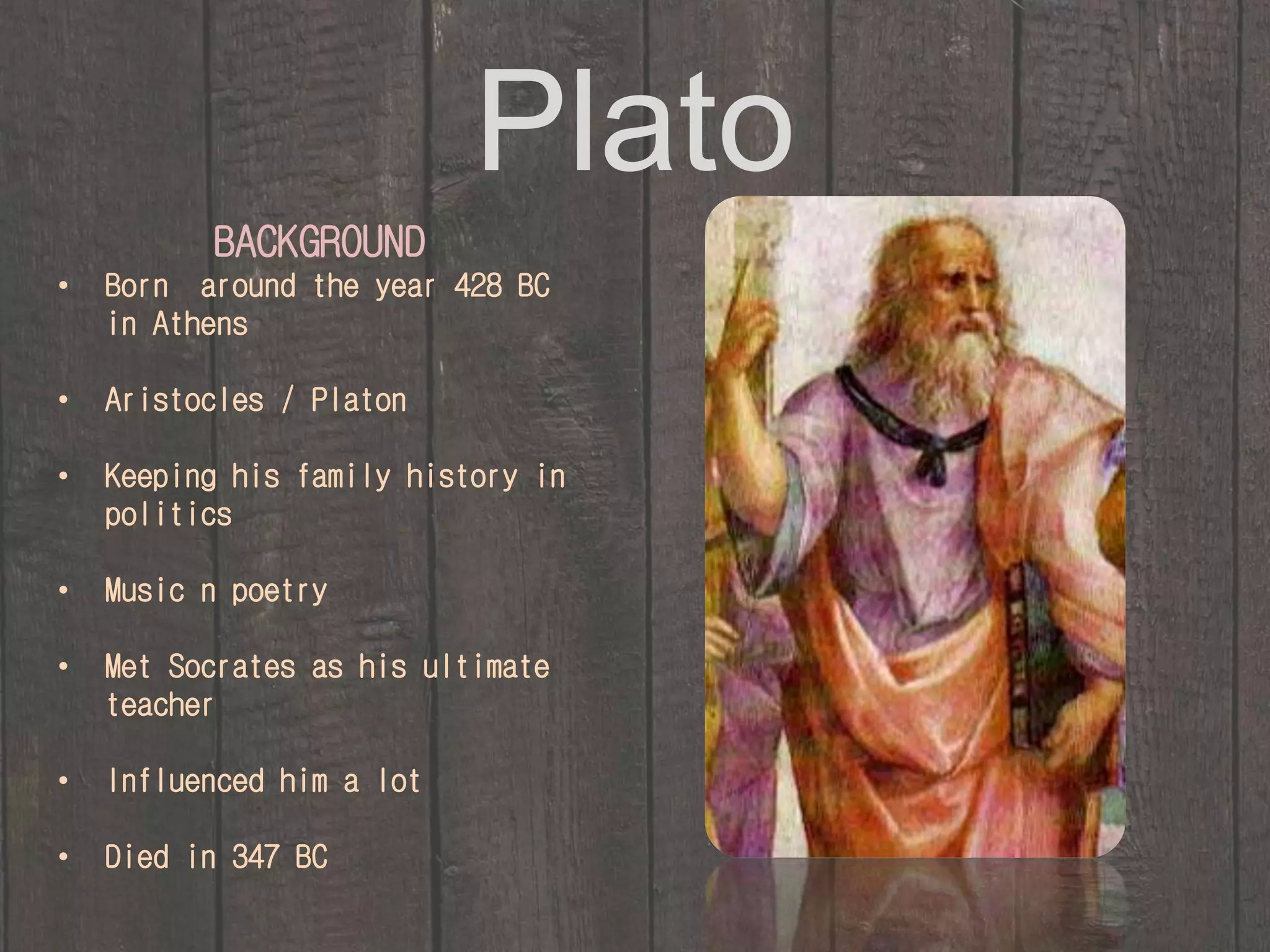
This document discusses three ancient Greek philosophers - Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle - and their contributions to philosophy and education. Socrates established the Socratic method of questioning beliefs and examining one's own knowledge. Plato introduced discussion as a teaching method and advocated for co-education. Aristotle studied different customs and literature, established principles in physics, and defined branches of knowledge. He influenced Western philosophy, science, and Islamic thought.