Anatomy of Ear | SurgicoMed.com
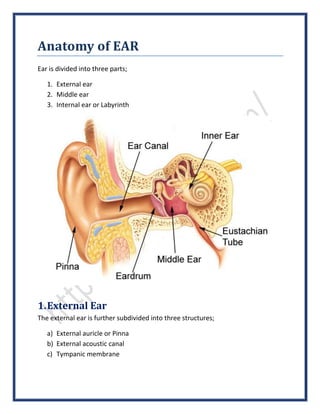
- 1. Anatomy of EAR Ear is divided into three parts; 1. External ear 2. Middle ear 3. Internal ear or Labyrinth 1.External Ear The external ear is further subdivided into three structures; a) External auricle or Pinna b) External acoustic canal c) Tympanic membrane
- 2. a)External Auricle Or Pinna The auricle or pinna forms the outer part of the external auditory canal and consists of a single piece of elastic cartilage covered with skin. Various elevations and depressions are present on the lateral aspect of the pinna. The deepest depression of the external ear is called Concha. The entire pinna (except its lobule & outer part of external acoustic canal) is made up of a cartilaginous framework which is a single piece of yellow elastic cartilage covered with skin. The skin is loosely attached to perichondrium on the medial aspect (cranial) of pinna while it is in close adherence to perichondrium on its lateral surface. Clinical: - The furuncles formed in ear are the most painful than any other site as the skin is closely adherent to perichondrium & little space is left. When a furuncle is formed in ear, high pressure is built which causes sensation of intense pain. Elevated outer margin of auricle or pinna is called Helix. Another smaller elevation opposite to it is called Anti-Helix. A large conical structure in the base of ear in front anti-helix is called Tragus. Behind the tragus & at the termination of anti- helix, a smaller conical structure is called Anti-Tragus. Above the tragus, the termination of elevated margin i-e helix is downward & backward which is called Curs of Helix. Curs of helix covers a space called Cymba Conchae, an important landmark used in mastoid surgery to reach mastoid antrum. The area between tragus and the crus of helix is called Incisura Terminalis, which lacks cartilage. An incision through the incisura terminalis does not cut through the cartilage and is done usually for endaural approach in surgery of external auditory canal or mastoid. b)External Acoustic Canal/External Auditory Canal The external auditory canal extends from the bottom of the concha to the tympanic membrane. It is about 24 mm in length along its posterior aspect. It is not a straight tube, its lateral part is directed upwards, backwards, forwards and
- 3. medially while its inner part is directed downwards, forwards and medially. Therefore, for the examination of the tympanic membrane the pinna is pulled upwards, backwards and laterally so as to form the External Auditory Canal a straight canal. The external auditory canal is divided into two parts; a) Outer part/cartilaginous part b) Inner part/bony part Outer or lateral one third is cartilaginous which forms almost 8 mm of the external auditory canal. The cartilage of the outer part is continuous with the cartilage of the pinna. The skin covering the cartilaginous part is covered with thick skin and contains ceruminous and pilosebaceous glands which secretes ear wax. Hair are present only in the outer cartilaginous part, therefore furuncles are seen only in the outer cartilaginous part. Inner or medial two third is bony in nature and forms 16 mm of the total auditory canal. Thin skin is present over the bony part. This part lacks the hair as well as ceruminous glands.
- 4. Relations Of External Acoustic Canal The relations of the external auditory canal are as followings, a) Anteriorly: - Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) b) Posteriorly: - Mastoid air cells and facial nerve c) Superiorly: - Middle cranial fossa d) Inferiorly: - Parotid gland c)Tympanic Membrane Tympanic membrane separates the external ear from the middle ear and it is set in oblique position therefore, its posterosuperior part is more lateral than the anteroinferior part. Tympanic membrane is almost 10 mm in length, 9 mm wide and 0.1 mm in thickness. Tympanic membrane can be divided into two parts; a) Pars Tensa b) Pars Flaccida Pars Tensa forms the major portion of the tympanic membrane. Its peripheral part is thickened to form a fibrocartilaginous ring called annulus tympanicus. The central part of the pars tensa is tented inwards at the level of tip of the malleus and is called Umbo.
- 5. Pars Flaccida forms the minor portion of the tympanic membrane and it is situated above the lateral process of the malleus. Tympanic membrane consists of three layers; a) Outer epithelial layer, which is continuous with the skin of the external auditory canal. b) Middle fibrous layer, which consists of three types of fibers-the radial, circular and parabolic fibers. c) Inner mucosal layer, which is continuous with the mucosa of the middle ear cavity. Nerve Supply of the External Ear i. Pinna a) Greater auricular nerve (C2, C3) supplies the most of the medial surface of the pinna and posterior part of lateral surface. b) Lesser occipital nerve (C2) supplies the upper part of the medial surface. c) Auriculotemporal nerve (V3) supplies the tragus and helix. d) Auricular branch of the Vagus nerve (CN X) supplies the concha. e) Facial nerve supplies the concha as well as retroauricular groove. ii. External Auditory Canal a) Auriculotemporal nerve (V3) supplies the anterior wall and roof of external auditory canal.
- 6. b) Auricular branch of Vagus nerve (CN X) supplies the posterior wall and floor of the external auditory canal. c) The sensory fibers of the CN VII through auricular branch of vagus nerve supply the posterior wall of the external auditory canal. iii. Tympanic Membrane a) Auriculotemporal nerve (V3) supplies the anterior aspect of the lateral surface of the tympanic membrane b) Auricular branch of the Vagus Nerve (CN X) supplies the posterior half of the lateral surface of the tympanic membrane c) Tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) supplies the medial aspect of the tympanic membrane 2.Middle Ear The middle ear cavity along with mastoid antrum, Eustachian tube, auditus and mastoid air cells is called Middle Ear Cleft. The middle ear is divided into; Mestotympanum Epitympanum Hypotympanum
- 7. The middle ear is like a six-sided box containing a roof, a floor, medial, lateral, anterior and posterior walls. a) The roof is formed by tegmen tympanic. b) The floor is formed by the thin plate of bone. c) The anterior wall is formed by the thin plate of bone which separates the internal carotid artery from the middle ear cavity. The anterior wall contains the opening of the Eustachian tube. d) The posterior wall lies close to the mastoid air cells. Facial nerve lies in the posterior wall of the middle ear. e) The lateral wall is formed by the tympanic membrane. f) The medial wall is formed by labyrinth. The medial wall presents a bulging surface called promontory which is due to the basal coil of the cochlea. i. Mastoid Antrum Mastoid antrum is a large, air containing space which is connected to the middle ear via auditus. Its roof is formed by tegmen antri, which is the continuation of the tegmen tympani and it separates the mastoid antrum from the middle cranial fossa. The lateral wall of the mastoid antrum is formed by thin plate of bone. ii. Auditus Auditus is an opening through which the mastoid antrum communicates with middle ear cavity. The facial nerve passes just below the auditus. iii. Mastoid Air Cells The mastoid consists of bone with a “honeycomb” appearance of the mastoid. The mastoid cells are well developed and pneumatized and their intervening septa are thin. Depending upon the location the mastoid air cells are divided into following types, a) Zygomatic cells b) Perisinus cells c) Perilabyrinth cells d) Tegmen cells
- 8. e) Peritubal cells f) Retrofacial cells g) Squamous cells h) Tip cells i) Marginal cells Ossicles of Middle Ear The Ossicles conduct sound waves from the tympanic membrane to the oval window and then into the inner ear. There are three Ossicles present in the middle ear cavity, a) Malleus b) Incus c) Stapes The malleus has a head, neck, handle, a lateral process and an anterior process. The handle of malleus is embedded in the fibrous layer of the tympanic membrane. The lateral process of the malleus makes the knob like projection of the ear-drum. The incus has a body and a short process as well as a long process. Both the body and short process of the incus lie in the attic of middle ear cavity. The long process is attached to the stapes.
- 9. The stapes has head, neck, anterior & posterior crura and footplate. The footplate of the stapes is attached to the oval window of the labyrinth by annular ligament Muscles of the Middle Ear There are two intra-tympanic muscles (muscles of the middle ear); a) Tensor tympani b) Stapedius
- 10. Tensor tympani muscle is attached to the malleus and creates tension in the tympanic membrane. Stapedius is attached to the neck of the stapes and prevent the inner air from noise pollution by dampening very loud sounds. Lining of Middle Ear The mucous membrane of the middle ear is continuous with the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx. The middle ear cavity is lined with ciliated columnar epithelium in the anterior wall while the epithelium changes to cuboidal epithelium in the posterior wall of middle ear cavity. Blood Supply of the Middle Ear Ear is supplied by six arteries, two are the major arteries while four are minor arteries. a) Anterior tympanic branch of the maxillary artery supplies the tympanic membrane b) Stylomastoid branch of auricular artery supplies the middle ear and mastoid air cells c) Tympanic branch of the internal carotid artery d) Superior branch of middle meningeal artery e) Branch from the artery of the pterygoid canal f) Petrosal branch of middle meningeal artery 3.Internal Ear The internal ear also called labyrinth is an important organ for hearing and maintaining balance of the body. The internal ear consists of bony labyrinth as well as Membranous Labyrinth. The membranous labyrinth is filled with fluid called Endolymph. Bony Labyrinth The bony labyrinth contains three parts;
- 11. a) Vestibule b) Semicircular canals c) Cochlea The vestibule is the main chamber of the labyrinth. The oval window lies in the lateral wall of the vestibule. In the posterosuperior part of the vestibule are the openings of the semicircular canals which are five in number. The semicircular canals are three in number, the lateral, superior and posterior. Each canal has an ampulla at its end which opens into vestibule. There are five openings of the three semicircular canals in the posterosuperior part of the vestibule. The bony cochlea makes 2.5 to 2.75 turns around the central pyramid of the bone called modiolus. The base of the modiolus is directed towards the internal acoustic meatus. The bony cochlea contains three compartments; i. Scala vestibuli ii. Scala tympani iii. Scala media The scala vestibuli and scala tympani are filled with perilymph and communicates with each other with an opening called Helicotrema. Membranous Labyrinth The membranous labyrinth consists of cochlear ducts, utericle and saccule, three semicircular ducts and endolymphatic duct. The cochlear duct also called Scala Media or Membranous Cochlea is a coiled tube. On cross-section it appears triangular in appearance. Its three walls are formed by a) The Basilar Membrane which provides support to the Organ of Corti. b) The Reissner’s Membrane which separates the scala media from scala vestibuli c) The Stria Vascularis which contains the vascular epithelium containing the secretory epithelium for secretion of the endolymph
- 12. The utericle is present in the posterior part of the bony vestibule and receives the five openings of the three semicircular ducts. Utericle is also connected to the saccule through utericulosaccular duct. The sensory epithelium of the utericle is called macula concerned with acceleration and deceleration. The saccule is also present in the bony vestibule. Its sensory epithelium is also called macula. It is also concerned with the acceleration and deceleration. Endolymphatic duct is formed by the union of two ducts, one from each utericle and saccule. Blood Supply of Labyrinth The entire labyrinth receives blood supply through labyrinthine artery, which is a branch of anterior-inferior cerebellar artery. Sometimes labyrinthine artery also originates from the basilar artery. The venous drainage is through three veins; a) Internal auditory vein b) Vein of cochlear duct c) Vein of vestibular duct Lymphatic Drainage Of Ear The lymph from concha, tragus, fossa triangularis and external auditory canal is drained into preauricular and parotid lymph nodes. The lymph from lymph and antitragus is drained into inferior auricular lymph nodes. The lymph from helix and antihelix is drained into posterior auricular and deep jugular lymph nodes Lymph from the middle ear is drained into the parotid and retropharyngeal lymph nodes. The lymph from Eustachian tube is drained into retropharyngeal lymph nodes. There are no more lymphatics and lymph nodes in the inner ear. Feedback us @ http://mukhdoom.com for more data & info. Like us @ https://www.facebook.com/StairsOfSuccess
