The document presents an analytical model for predicting the relationship between operating speed and shaft power output of Stirling engines. The model uses a lumped mass approach to analyze transient temperature variations in the expansion and compression spaces. Results show that shaft power output initially increases with operating speed, reaches a maximum at a critical speed, and then decreases at higher speeds as temperature differences are reduced. Power output is also affected by parameters like air mass, thermal resistances, and regenerator effectiveness.
![Energy 36 (2011) 5899e5908
Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect
Energy
journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/energy
Analytical model for predicting the effect of operating speed on shaft power
output of Stirling engines
Chin-Hsiang Cheng*, Hang-Suin Yang
Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, National Cheng Kung University, No.1, Ta-Shieh Road, Tainan 70101, Taiwan, ROC
a r t i c l e i n f o a b s t r a c t
Article history: This paper is concerned with numerical predictions of relationship between operating speed and shaft
Received 23 February 2011 power output of Stirling engines. Temperature variations in expansion and compression spaces as well as
Received in revised form the shaft power output corresponding to different operating speeds were investigated by using a lum-
16 August 2011
ped-mass transient model. Effects of major operating parameters on power output were studied.
Accepted 19 August 2011
Results show that as the operating speed increased, temperature difference between the expansion and
Available online 21 September 2011
compression spaces was reduced and as a result, the shaft work output decreased. However, the shaft
power output is determined in terms of the shaft work output and the operating speed. When the
Keywords:
Analytical model
operating speed was elevated, the shaft power output reached a maximum at a critical operating speed.
Stirling engine Over the critical operating speed, the shaft power output decreased in high-speed regime. In addition, as
Mechanism effectiveness air mass was reduced, either a decrease in thermal resistances or an increase in effectivenesses of the
Shaft power output regenerator leads to an increase in the engine power.
Ó 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
1. Introduction is equal to the Carnot cycle efficiency under the same thermal
reservoirs temperatures. As compared with other alternative power
Owing to rapid depletion of fossil fuels and threat of global generation methods, the CSP-Stirling system features high effi-
warming, environmental problems have received great attention in ciency and modular construction. Therefore, cost of these systems is
recent years. A large number of researchers concentrate their focus expected to become more competitive in the distributed markets in
on the electricity generation from solar energy which is treated as near future. However, it is noted that performance of the CSP-
one of potential energy sources in near future. Practically, there are Stirling system for generating electrical power is dependent on
two major effects to convert the solar energy into electricity: energy conversion and mechanical efficiencies of the Stirling engine.
photovoltaic and thermodynamic. The photovoltaic (PV) effect is Therefore, predictions and improvement in the performance of the
used to produce electricity when sunlight hits a PV panel and Stirling engine are of major concerns to related investigators.
releases electrons from special layers of silicon and pushes them An ideal regenerative Stirling cycle consists of four processes in
across an electric field. On the other hand, the thermodynamic a cycle. Firstly, working fluid absorbs heat from high temperature
effect is used in devices like concentrating solar power systems reservoir and experiences an isothermal expansion (1/2).
with Stirling engines (CSP-Stirling) [1]. The CSP-Stirling system is Secondly, the hot working fluid flows through a regenerator, and the
typically equipped with a solar energy receiver to absorb the solar regenerator absorbs heat from the hot working fluid. Thus,
radiation and the Stirling engine to convert the absorbed solar temperature of the working fluid decreases in an isochoric process
energy to mechanical energy and then electricity [2,3]. In addition, (2/3). Thirdly, the working fluid rejects heat to a low temperature
the Stirling engines can also be applied in automobiles and reservoir and experiences an isothermal compression (3/4).
submarines as power resources [4,5]. Finally, the cold working fluid flows back through the regenerator,
The Stirling engines are referred to as external combustion heat and the regenerator rejects heat to the working fluid. The temper-
engines that are operated based on a regenerative closed power ature of work fluid increases in the second isochoric process (4/1).
cycle using air, nitrogen, helium, or hydrogen as working fluid [6]. In The p-V diagram of the ideal Stirling cycle (1/2/3/4/1) is
theory, the thermal efficiency of an ideal regenerative Stirling cycle plotted in Fig. 1.
As mentioned in Ref. [7], the Stirling engine was invented by
* Corresponding author. Tel.: þ886 6 2757575x63627; fax: þ886 6 2389940. Robert Stirling in 1816, which was called ‘hot-air engine’ originally,
E-mail address: chcheng@mail.ncku.edu.tw (C.-H. Cheng). and the first successful reversible model for analysis of the Stirling
0360-5442/$ e see front matter Ó 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
doi:10.1016/j.energy.2011.08.033](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmodelforpredictingtheeffectofoperatingspeedonshaftpower-121028104508-phpapp02/75/Analytical-model-for-predicting-the-effect-of-operating-speed-on-shaft-power-1-2048.jpg)
![5900 C.-H. Cheng, H.-S. Yang / Energy 36 (2011) 5899e5908
Nomenclature t time (sec)
U gas velocity through regenerator (m/s)
Cp specific heat (J=kg,K) Vc volume of compression chamber (m3 )
E mechanism effectiveness Vd dead volume (m3 )
eC effectiveness of regenerator in cooling process Ve volume of expansion chamber (m3 )
eH effectiveness of regenerator in heating process Vr volume of regenerator (m3 )
Lr length of regenerator (m) V total volume (m3 )
M molecular weight of working fluid (kg/mol) W indicated work (J)
m mass of working fluid (kg) Ws shaft work (J)
N number of moles WÀ forced work (J)
Ps shaft power output (W)
p pressure of work space (N=m2 ) Greek symbols
Dp pressure difference between expansion and q crank angle (deg)
compression spaces (N=m2 ) r density of working fluid (kg=m3 )
Qgen:absorb heat absorbed by regenerator from working fluid (J) s operating temperature ratio
Qgen:reject heat rejected by regenerator to working fluid (J) u operating speed (rad/s)
R gas constant (J=K,mol) uo operating speed (rpm)
RC thermal resistance of cold side (K=W)
RH thermal resistance of hot side (K=W) Subscripts
rh hydraulic radius of regenerator (m) C cold side
TC cold side reservoir temperature (K) c compression space
TRm mean fluid temperature in regenerator channel (K) d dead space
TH hot side reservoir temperature (K) e expansion space
TL fluid temperature in compression space (K) ex experimental
TLm mean fluid temperature in compression space (K) th theoretical
TU fluid temperature in expansion space (K) H hot side
TUm mean temperature in expansion space (K) m mean
TL0 initial temperature of cooling process (K) r regenerator
TU0 initial temperature of heating process (K)
engine was presented by Schmidt [8] in 1871. In the reversible to replace the isothermal processes and introduced a realistic
model, a closed-form solution for indicted work output of the regenerator into the model. Wu et al. [11] also studied the irre-
engine was obtained by assuming that the pressure of the working versible model of the Stirling engine with an imperfect regenerator.
fluid is uniform throughout the working space of the engine and The authors presented a criterion for optimizing the dead volume
that the variation in the pressure with time follows sinusoidal and studied the relationship between net power output and
function. In the past several decades, the analysis has been thermal efficiency. Kaushik and Kumar [12,13] performed a finite
extended to irreversible models. For examples, Blank and Wu [9] time thermodynamic analysis of the power output and the thermal
optimized the power of solar-radiant Stirling engine by using efficiency for the Stirling engine with internal heat loss in the
finite-time analysis. Erbay and Yavuz [10] used polytropic processes regenerator and with finite-heat-capacity external reservoirs. Senft
[14,15] took into account internal heat losses and mechanical fric-
tion losses and determined theoretical limits on the performance of
Stirling engines as well as the maximum value of the mechanical
p
efficiency. Petrescu et al. [16] used a direct method to investigate
the irreversible Stirling cycle model with finite speed. In this report,
effects of the regenerator loss on the power output and the thermal
TH
1 efficiency of the engines were evaluated. Recently, Kongtragool and
Wongwises [17] extended the thermodynamic model to include the
TU (t ) dead volumes inside the working spaces. Qin et al. [18] used a linear
phenomenological heat-transfer law to analyze an ‘endoreversible’
Carnot heat engine. The authors found that the power output, the
TU′ 2
thermal efficiency and the heat-conduction losses are dependent
4 on frequency and heat transfer time ratio. Karabulut et al. [19]
TL′ compared different kinds of b-type Stirling engines and studied
the effect of convective heat transfer coefficient on the power
3′ output at different operating speeds. Meanwhile, experiments were
TL (t )
3 conducted by Kongtragool and Wongwises [20] for the low
temperature differential g-type Stirling engines. In this study,
TC
engine torque, shaft work, and thermal efficiency of the engines
were measured at different engine speeds.
Most recently, Cheng and Yu [21] proposed an irreversible
V thermodynamic model for the b-type Stirling engines. Periodic
variation of pressures, volumes, temperatures, masses, and heat
Fig. 1. p-V diagram of Stirling cycle with imperfect regenerator. transfers in expansion and compression chambers of the engines](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmodelforpredictingtheeffectofoperatingspeedonshaftpower-121028104508-phpapp02/75/Analytical-model-for-predicting-the-effect-of-operating-speed-on-shaft-power-2-2048.jpg)
![C.-H. Cheng, H.-S. Yang / Energy 36 (2011) 5899e5908 5901
are predicted by taking into account heat transfer effectiveness of
regenerative channels as well as thermal resistances of heating and
cooling heads. Lately, Cheng and Yu [22] first performed a dynamic
simulation of the b-type Stirling engines with a cam-drive mech-
anism by combining dynamic and thermodynamic models. Tran-
sient variation in rotational speed of the engines during start-up
period can then be predicted.
Performance curves showing the shaft power output at different
operating speeds of the Stirling engines may be obtained by
analytical or experimental methods based on the above literature
survey. However, unfortunately, in spite of the valuable analytical
and experimental studies performed in Refs. [19,20,23], so far only
a limited number of analytical models were presented that are
capable of predicting the dependence of the shaft power output on
the operating speed. In consequence, the effects of operating
parameters such as the operating temperature ratio, the mass of
working fluid, the thermal resistances of the heater and the cooler,
the effectiveness of the regenerator, and the properties of working
fluids on the performance curves of the Stirling engines are not
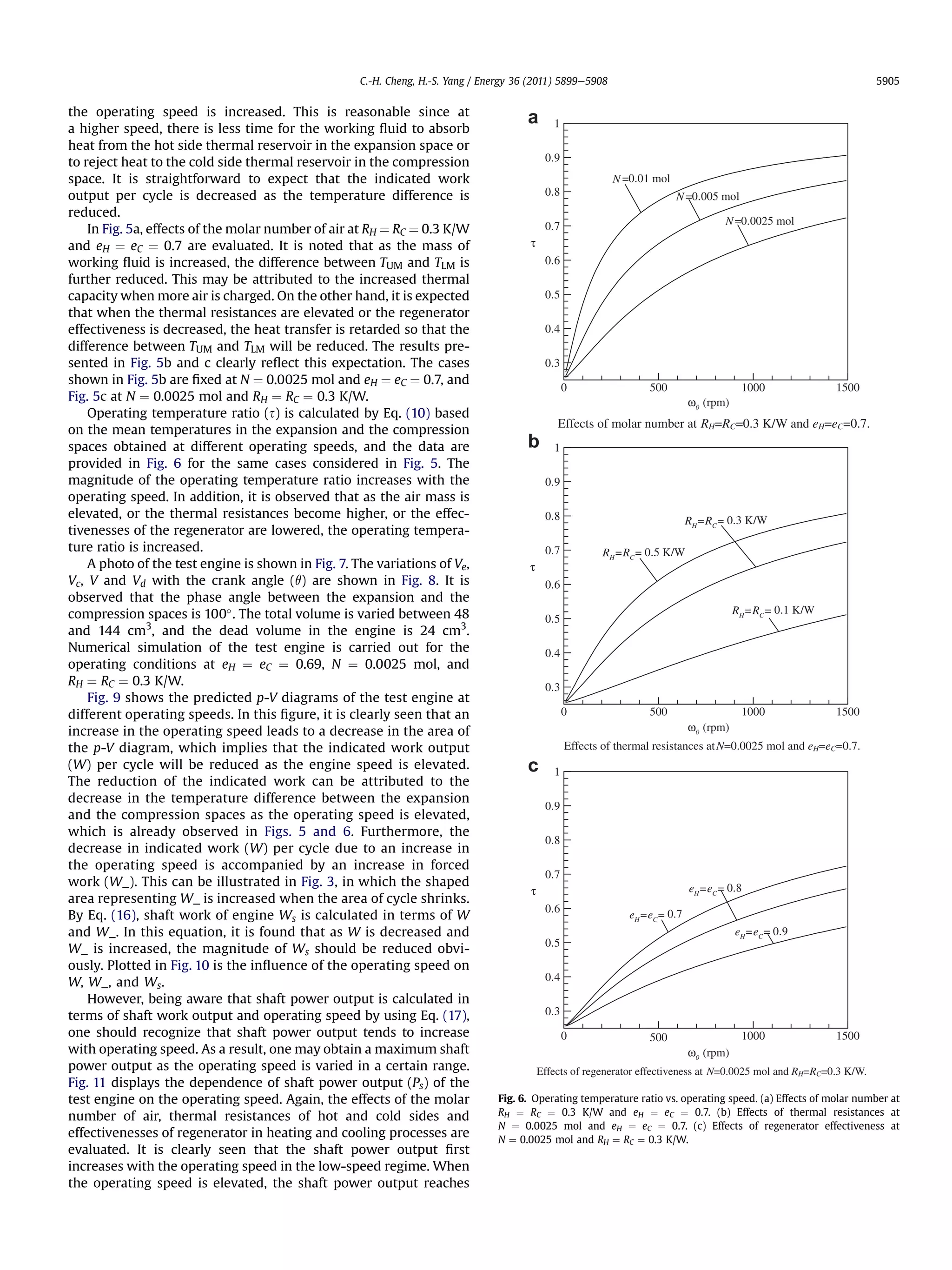
sufficiently understood. Fig. 2. Temperature changes of lumped mass in the processes.
Under these circumstances, this study is aimed to develop an
analytical model that can be used to yield the relationship between
the shaft power output and the operating speed of the Stirling _
where qin denotes the rate of heat absorbed by the working fluid,
engines with imperfect regenerators. The analytical model includes andRH is the thermal resistance of the hot side. Magnitude of RH is
a lumped-mass concept such that transient variation of the ther- dependent on the operating speed, properties of working fluid,
modynamic properties of the working fluid in each process of the operating temperature, design of heater, and the heating method,
cycle can be predicted. This approach first allows the effects of the which can be determined by experiments. To simplify the analysis,
operating parameters on the performance curve to be evaluated. here the value ofRH is fixed. Based on the energy conservation law,
_
qin is approximately equal to rate of change in enthalpy of the
2. Analytical model working fluid. That is,
Let TH and TC represent the temperatures of the hot side and the dTU ðT À TU Þ
cold-side reservoirs, respectively, and TU and TL represent the fluid mCp ¼ H (1)
dt RH
temperatures in the expansion and the compression spaces,
respectively. Note that TU < TH and TL > TC . Heat transfer between where m is the mass of the working fluid, which is the product of
the working fluid and the thermal reservoirs is strongly dependent the molecular weight (M) and the molar number of working fluid
on the temperature differences, TH À TU and TL À TC , and time for (N) contained in the working space. Eq. (1) is a first-order ordinary
heat transfer. Furthermore, because the time for heating in the differential equation. Thus, one can carry out the solution of the
expansion space and that for cooling in the compression space in equation as
a cycle are decreased as the operating engine speed is increased;
therefore, TU is reduced and TL is elevated by increasing the oper- t
TU ðtÞ ¼ TH À C1 exp À (2)
ating speed. As a result, the differences TH À TU and TL À TC both mCp RH
increase with the operating engine speed. It is noticed that in spite
of the constant thermal reservoirs temperatures, the working fluid where C1 is a constant to determine. The working fluid enters the
temperatures in the working spaces are varied with time in the expansion space at TU and there it is heated in process 10 -2.
0
respective processes, which may be denoted by TU (t) and TL (t). 0
Therefore, introducing the initial condition TU(0) ¼ TU yields
Temperature changes in the processes of the cycle must be 0
C1 ¼ TH À TU . The solution can be rewritten as
examined. Notice that due to the imperfection of the regenerator,
0
the working fluid enters the expansion space at TU , not TU , at state
À 0 Á t
1 0 after passing through the regenerator. Meanwhile, it enters the TU ðtÞ ¼ TH À TH À TU exp À (3)
mCp RH
compression space at TL , not TL , at state 30 after flowing back
0
through the regenerator. The real cycle with an imperfect regen-
erator is illustrated in Fig. 1. 2.2. Compression space
In this study, a lumped-mass transient model is developed. The
working fluid of mass m is regarded as a lumped mass that travels Similarly, in the compression space, rate of heat rejected by the
through four working spaces (expansion space, regenerator chan- working fluid to the cold side reservoir is expressed as
nels, compression space, and regenerator channels) and experi- _ _
qout ¼ ðTL À TC Þ=RC , where qout is the heat rejected by the working
ences changes in temperature and pressure in the cycle. The fluid, and RC is the thermal resistance of the cold side. The energy
temperature changes of the working fluid in the four working conservation law gives
spaces in the cycle are indicated in Fig. 2.
dTL ðT À TC Þ
2.1. Expansion space mCp ¼ À L (4)
dt RC
In the expansion space, rate of heat absorbed by the working 0
Using the initial condition TL(0) ¼ TL , one has the solution for the
_
fluid from the hot side reservoir is expressed as qin ¼ ðTH À TU Þ=RH , temperature of compression space](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmodelforpredictingtheeffectofoperatingspeedonshaftpower-121028104508-phpapp02/75/Analytical-model-for-predicting-the-effect-of-operating-speed-on-shaft-power-3-2048.jpg)
![5902 C.-H. Cheng, H.-S. Yang / Energy 36 (2011) 5899e5908
À 0 Á t In practices, the times consumed by the four processes are just
TL ðtÞ ¼ TC þ TL À TC exp À (5) slightly different, and hence, the time each process needs is
mCp RC
approximated as a quarter of a cycle period. If the engine’s oper-
ating speed is u, in rad/s, the time required in each process will be
2.3. Regenerator
p/2u [¼(1/4)(2p/u)]. Let TUm and TLm be mean temperatures of the
working fluid in the expansion space and the compression space,
The effectivenesses of regenerator can be defined as
respectively, which are calculated by
0
TU À TL
eH ¼ for process 4 À 10 ; (6a) p=2u
Z
TU À TL 1
TUm ¼ TU ðtÞdt ¼ TUm ðuÞ (9a)
and p=2u
0
0
TU À TL
eC ¼ for process 2 À 30 (6b) p=2u
Z
TU À TL 1
TLm ¼ TL ðtÞdt ¼ TLm ðuÞ (9b)
Magnitudes of the regenerator effectivenesses are dependent p=2u
0
on porosity, permeability and material of porous matrix.
Temperature distribution in the regenerator can be measured by As suggested in [8,29], the operating temperature ratio is
experiments [7,24e26] to determine the regenerator effective- defined by
nesses. Furthermore, the magnitudes of the regenerator effec-
tivenesses are also dependent on the operating speed. Actually, TLm ðuÞ
they decrease with an increasing operating speed [27,28]. This is s¼ (10)
TUm ðuÞ
because the time for heat exchange between the gas and the
porous matrix of the regenerator is decreased by increasing the The mean temperature of the working fluid contained in the
operating speed. The relation between the regenerator effective- regenerator channels can be evaluated as suggested in [17,29] with
ness and the operating speed is essential and worthy of further
investigation. Note that with the imperfect regenerators, one has
TUm ðuÞ þ TLm ðuÞ
eH 1 and eC 1. Heat transfer from the regenerator to the TRm ðuÞ ¼ (11)
working fluid of mass m moving through the regenerator channels 2
in the direction from the compression space to the expansion
space (in process 4-10 ) is Qgen reject ¼ mCp(TU e TL), and the heat
0
2.5. Power output
transfer to the regenerator from the working fluid moving from
the expansion space to the compression space (in process 2-30 ) is Before calculation of the power output of the engine, one needs
0
Qgen absorb ¼ mCp(TU À TL ). to evaluate pressure difference between the expansion and the
compression spaces. In terms of gas velocity flowing through the
2.4. Mean temperatures in working spaces regenerator, diameter of the regenerative channel, and kinematic
0 0
viscosity of the working fluid at the average operating temperature,
2.4.1. From Eqs. (6a) and (6b), TU and TL can be calculated by the magnitude of Reynolds number is estimated to be 102
approximately. According to the experimental data presented by
0 Kays and London [28], at this Reynolds number the magnitude of
TU ¼ TL þ eH ðTU À TL Þ (7a)
friction factor is about 10À1 . The friction factor is defined as
and
rh Dp
0
TL ¼ TU À eC ðTU À TL Þ (7b) f ¼ (12)
Lr rU 2 =2
Substituting Eqs. (7a) and (7b) into Eqs. (3) and (5) yields two
where rh and Lr are hydraulic radius and length of the regenerative
simultaneous algebraic equations for TU(t) and TL(t). The solutions
channels, respectively, r is density of the working fluid, U is the gas
can then be carried out as
flow velocity through the regenerator, and Dp is the pressure
difference between the expansion and the compression spaces.
TU ðtÞ ¼ DU =D (8a)
Magnitude of Dp can then be evaluated as
and
Dp Lr U 2 f 10À1 Â 101 Â 10À1
TL ðtÞ ¼ DL =D (8b) ¼ w À1 w10À3 (13)
pm 2rh RTC 10 Â 101 Â 102
where
Thus, the pressure difference between the expansion and the
 À Á
D ¼ ð1 À eH Þð1 À eC Þ À exp t=nWcp RH compression spaces can be negligible. The pressure is assumed to
ÃÂ À Á Ã be uniform throughout the engine and can be calculated in terms of
À eH exp t=nWcp RC À eC ð8cÞ
the volumes and their mean temperatures of the working spaces
 À Á àÀ Á à [17,21,22,29] as
DU ¼ À exp t=nWcp RH À 1 exp t=nWcp RC À eC TH
 À Á à mR
À ð1 À eH Þ exp t=nWcp RC À 1 TC (8d) p ¼ (14)
Ve Vc Vr
þ þ
 À Á à TUm TLm TRm
DL ¼ Àð1 À eC Þ exp t=nWcp RH À 1 TH
 À Á àÀ Á à where R is gas constant; and Ve, Vc, and Vr represent instantaneous
À exp t=nWcp RH À eH exp t=nWcp RC À 1 TC ð8eÞ volumes of the expansion space, the compression space, and the](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmodelforpredictingtheeffectofoperatingspeedonshaftpower-121028104508-phpapp02/75/Analytical-model-for-predicting-the-effect-of-operating-speed-on-shaft-power-4-2048.jpg)
![C.-H. Cheng, H.-S. Yang / Energy 36 (2011) 5899e5908 5903
regenerator channels, respectively. In the derivation of the above power output can then be calculated from the obtained shaft
equation, the working fluid is assumed to be an ideal gas. Total work with
volume of the engine is V ¼ Ve þ Vc þ Vr and dead volume of the
engine is Vd ¼ Vemin þ Vcmin þ Vr, where Vemin and Vcmin are Ps ¼ Ws ðu=2pÞ; in Watt (17)
clearance volumes of the expansion and the compression spaces, In the present study, air is used as the working fluid. For air, the
respectively. molecular weight is M ¼ 2.897 Â 10À2 kg/mol and the specific heat
The function p(V) is affected by the operating speed of engine cp ¼ 1087 J/(kg$K). Meanwhile, the hot side and the cold-side
(u). Using Eq. (14), one can plot the p-V diagram at specific reservoir temperatures, TH and TC , are fixed at 1200 K and 300 K,
operating speed. Then, indicated work (W) and forced work (W_) respectively.
of a cycle can be further calculated. The definitions of the indi-
cated work and the forced work are already described in
[14,15,29], which are illustrated in Fig. 3. The indicated work is 2.6. Experimental apparatus and testing procedure
calculated by integrating the area inside the cycle in the p-V
diagram. That is, The purpose of the experiment is to measure the shaft power
Z output of engine under different operating speed for validation.
W ¼ pdV (15) Experimental apparatus is shown in Fig. 4. A non-contact infrared
heater was used for heating the engine, and surface temperatures
cycle
at the hot and the cold sides are measured by using K-type ther-
On the other hand, the forced work is represented by the shaded mocouples. In order to maintain constant heating temperature (TH),
areas shown in the plot. pb is back pressure exerted on opposite side a PID controller was used to control the temperature by adjusting
of the piston. The back pressure could usually be atmospheric the electrical voltage supplied to the infrared heater. The engine is
pressure or an elevated pressure in case a pressurized space is an aetype Stirling engine with Ross mechanism, of which the
placed on the opposite side as a buffer zone. specifications are given in Tables 1 and 2. The engine shaft was
The shaft work of engine can be determined in terms of the
indicated work and the forced work, as suggested by Senft [15,29]
as a Dynamic system
1 Hysteresis Brake
Ws ¼ EW À À E WÀ (16)
E Brake Controller
Heating system
where E is referred to as mechanism effectiveness. The mecha-
nism effectiveness is well known as a ratio measure of how well
Heater
a mechanism utilizes work if it is regarded as a work transmitter.
It is a ratio of the work it transfers out through an actuator or Torque
Controller Engine
puts into internal storage to the work it receives through Sensor
another actuator or takes from its internal source. Typical value Thermocouple
of the mechanical effectiveness is in the range of 0.7 E 0.8. In
this study, the mechanism effectiveness is assigned to be 0.7.
Note that effects of friction are included in the mechanism Speed
Monitor
effectiveness. Detailed information for the mechanism effec- Sensor
tiveness has been provided by Senft [15,29]; therefore, no
further description is provided here to save space. The shaft
Schematic of the performance test system
b
Photo of the performance test system
Fig. 3. Definitions of indicated work (W) and forced work (W_). If the area of cycle is Fig. 4. Experimental apparatus. (a) Schematic of the performance test system
reduced, W is decreased while W_ is increased. (b) Photo of the performance test system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmodelforpredictingtheeffectofoperatingspeedonshaftpower-121028104508-phpapp02/75/Analytical-model-for-predicting-the-effect-of-operating-speed-on-shaft-power-5-2048.jpg)
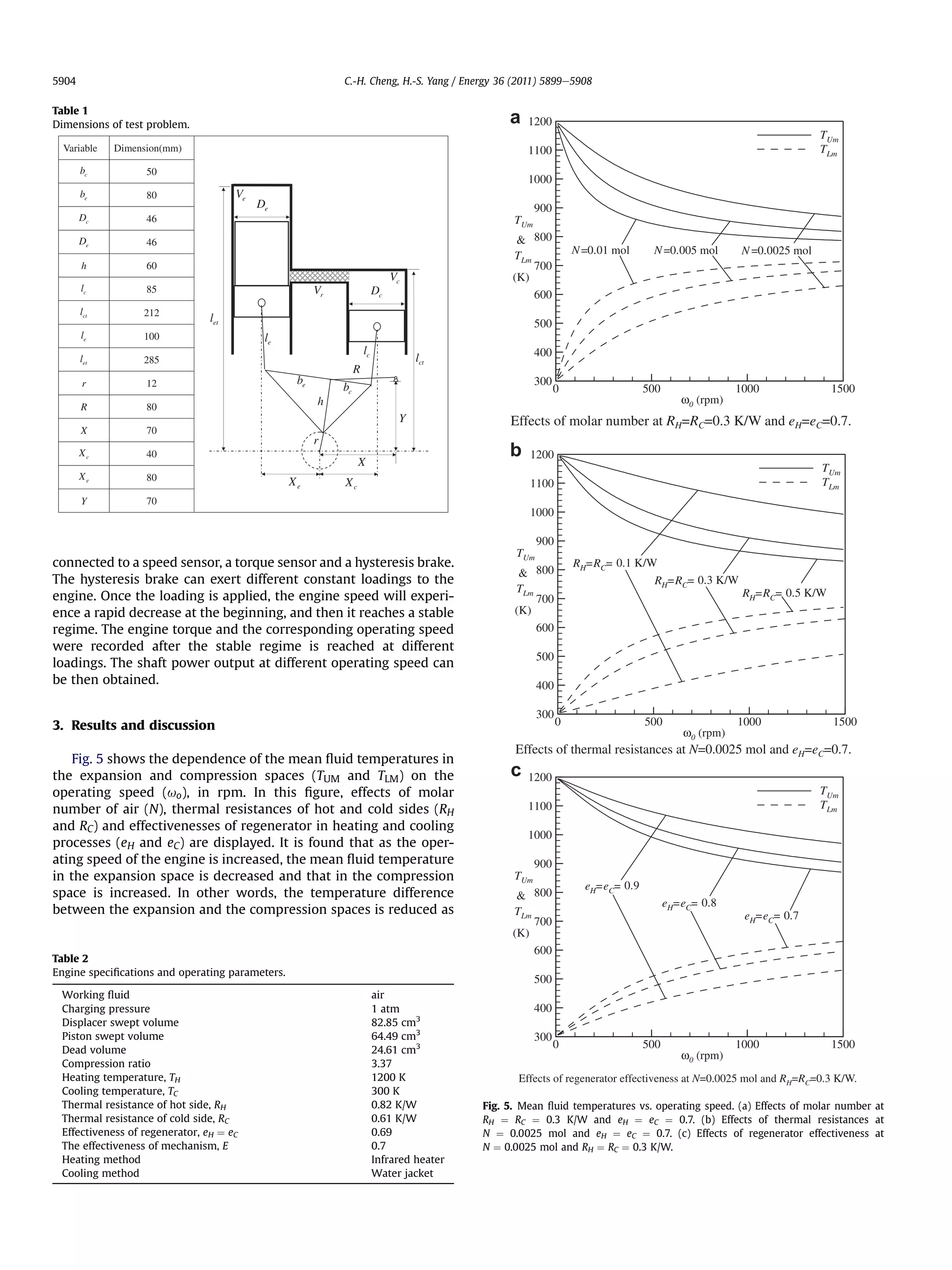
![5906 C.-H. Cheng, H.-S. Yang / Energy 36 (2011) 5899e5908
240
0
500rpm
220
1000rpm
200 1500rpm
180
p
160
(kPa)
140
120
pb =101.325 kPa
100
80
50 75 100 125 150
3
Vt (cm )
Fig. 7. Test engine.
Fig. 9. Predicted p-V diagrams at different operating speeds for the test engine.
a maximum at a critical operating speed. Over the critical operating [30,31] so that thermal resistances could be greatly reduced. As
speed, the shaft power output gradually descends in the high- long as the related information is obtained, the information can be
speed regime. In addition, the peak shaft power output and its introduced into the present model to assess the effect of mass on
accompanying critical speed are strongly dependent on the molar the performance of the engine.
number of the charged air, the thermal resistances, and the effec- A comparison between the experimental and the numerical
tivenesses of the regenerator. In the plots of this figure, it is found data for the shaft power output as a function of the operating
that as the air mass is elevated, or the thermal resistances are speed is shown in Fig. 12a, and the relative error between these
reduced, or the effectivenesses of the regenerator are increased, the two sets of data is shown in Fig. 12b as a function of the engine
shaft power output can be remarkably increased. For example, in speed. The range of the engine speed in the experiments is
Fig. 11b, at RH ¼ RC ¼ 0.5 K/W the peak shaft power is around 6 W within 130 and 400 rpm, and the maximum shaft power output
and the critical speed is 200 rpm. As the thermal resistances are is found to be 4.4 W at 200 rpm. The experimental results closely
reduced to be RH ¼ RC ¼ 0.1 K/W, the maximum shaft power is agree with the numerical predictions at high-speed regime.
increased to 29 W and the critical speed shifts to 900 rpm. Generally, the relative error is within 30%. However, in Fig. 12a,
It is important to mention that for the cases considered in the absolute error between the experimental and numerical
Fig. 11a, the effect of the charged air mass is simply evaluated at results is remarkable when the engine speed is lower than
fixed thermal resistances (0.3 K/W). As a matter of fact, the effect of 200 rpm. This may probably be attributed to the greater uncer-
the mass of charged air is rather involved. In general, when more air tainty of the measurement data at low engine speeds. For the test
is charged into the working space of the engine, the thermal engine, the engine cannot be operated at a speed lower than
conductivity of the working fluid and the heat transfer coefficient 130 rpm.
on the walls of the hot and cold sides may be significantly increased
7
200 W
Ve
W-
180 Vc 6
Ws
160 Vd
Vt 5
140 W
Ve W-
120 4
Vc Ws
Vd 100
(J) 3
Vt 80
(cm3) 2
60
40 1
20
0
0 500 1000 1500 2000
0 90 180 270 360 450 540 630 720 ω0 (rpm)
θ (deg)
Fig. 10. Predicted effects of operating speed on indicated work, forced work, and shaft
Fig. 8. Volumes’ variation for the test engine. work for the test engine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmodelforpredictingtheeffectofoperatingspeedonshaftpower-121028104508-phpapp02/75/Analytical-model-for-predicting-the-effect-of-operating-speed-on-shaft-power-8-2048.jpg)
![C.-H. Cheng, H.-S. Yang / Energy 36 (2011) 5899e5908 5907
a 10 a
6
9 Theoretical
N =0.0025 mol Experimental
8 5
7
N =0.003 mol
6 4
Ps
(W) 5 Ps
4 (W) 3
3
2
2
N =0.005 mol
1
1
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700
ω0 (rpm)
Effects of molar number at RH=RC=0.3 K/W and eH=eC=0.7. 0
0 100 200 300 400
b 30
ω0 (rpm)
RH=RC= 0.1 K/W Shaft power output vs. engine speed.
25 b
100
20 90
Relative error ⎢Ps,th-Ps,ex⎢/Ps,th (%)
Ps 80
(W) 15
70
RH=RC= 0.3 K/W
10 60
RH=RC= 0.5 K/W 50
5
40
0 30
0 500 1000 1500 2000
ω0 (rpm)
20
Effects of thermal resistances at N=0.0025 mol and eH=eC=0.7.
c 25
10
0
eH=eC= 0.9 0 100 200 300 400
ω0 (rpm)
20
Relative error vs. engine speed.
Fig. 12. Comparison between experimental and numerical data. (a) Shaft power
15 output vs. engine speed. (b) Relative error vs. engine speed.
Ps
eH=eC= 0.8
(W) 4. Conclusions
10
eH=eC= 0.7 In this study, an efficient lumped-mass model has been devel-
oped and used to predict the relationship between the operating
speed and shaft power output of the Stirling engines. Temperature
5
variations in the expansion and the compression spaces as well as
the shaft power output corresponding to different operating speeds
are of major concerns. The concept of the mechanism effectiveness
0 initiated by Senft [15,29] is introduced in this study to calculate the
0 500 1000 1500 2000
ω0 (rpm) shaft work, in terms of the indicated work, the forced work, and the
Effects of regenerator effectiveness at N=0.0025 mol and RH=RC=0.3 K/W. mechanism effectiveness. The effects of the operating parameters
on the power output of the engine are also evaluated.
Fig. 11. Predicted shaft power output vs. operating speed for the test engine. (a) Effects Results show that as the operating speed is increased, the
of molar number at RH ¼ RC ¼ 0.3 K/W and eH ¼ eC ¼ 0.7. (b) Effects of thermal
temperature difference between the expansion and the
resistances at N ¼ 0.0025 mol and eH ¼ eC ¼ 0.7. (c) Effects of regenerator effectiveness
at N ¼ 0.0025 mol and RH ¼ RC ¼ 0.3 K/W. compression spaces is reduced and as a result, the shaft work](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmodelforpredictingtheeffectofoperatingspeedonshaftpower-121028104508-phpapp02/75/Analytical-model-for-predicting-the-effect-of-operating-speed-on-shaft-power-9-2048.jpg)
![5908 C.-H. Cheng, H.-S. Yang / Energy 36 (2011) 5899e5908
output decreased. However, the shaft power output is determined [11] Wu F, Chen L, Wu C, Sun F. Optimum performance of irreversible Stirling
engine with imperfect regeneration. Energy Conversion and Management
in terms of the shaft work output and the operating speed. When
1998;39(8):727e32.
the operating speed is elevated, the shaft power output reaches its [12] Kaushik SC, Kumar S. Finite time thermodynamic analysis of endoreversible
maximum at a critical operating speed. Over the critical operating Stirling heat engine with regenerative losses. Energy 2000;25(10):
speed, the shaft power output descends in the high-speed regime. 989e1003.
[13] Kaushik SC, Kumar S. Finite time thermodynamic evaluation of irreversible
In addition, the peak shaft power output and its accompanying Ericsson and Stirling heat engines. Energy Conversion and Management 2001;
critical speed are strongly dependent on the molar number of 42(3):295e312.
charged air, the thermal resistances, and the effectivenesses of [14] Senft JR. Theoretical limits on the performance of Stirling engines. Interna-
tional Journal of Energy Research 1998;22(11):991e1000.
regenerator. As the air mass is decreased, or the thermal resis- [15] Senft JR. Extended mechanical efficiency theorems for engines and heat
tances are lowered, or the effectivenesses of the regenerator are pumps. International Journal of Energy Research 2000;24(8):679e93.
elevated, the power of the engine and the critical speed are both [16] Petrescu S, Costea M, Harman C, Florea T. Application of the direct method to
irreversible Stirling cycles with finite speed. International Journal of Energy
elevated. Research 2002;26(7):589e609.
[17] Kongtragool B, Wongwises S. Thermodynamic analysis of a Stirling engine
including dead volumes of hot space, cold space and regenerator. Renewable
Acknowledgments Energy 2006;31(3):345e59.
[18] Qin X, Chen L, Sun F, Wu C. Frequency-dependent performance of an
Financial support from the National Science Council, Taiwan, endoreversible Carnot engine with a linear phenomenological heat-transfer
law. Applied Energy 2005;81(4):365e75.
under grant NSC982C10 is greatly appreciated. [19] Karabulut H, Yucesu HS, Cinar C, Aksoy F. An experimental study on the
development of a beta-type Stirling engine for low and moderate temperature
heat sources. Applied Energy 2009;86(1):68e73.
References [20] Kongtragool B, Wongwises S. Performance of low-temperature differential
Stirling engines. Renewable Energy 2007;32(4):547e66.
[1] Tavakolpour AR, Zomorodian A, Golneshan AA. Simulation, construction [21] Cheng CH, Yu YJ. Numerical model for predicting thermodynamic cycle and
and testing of a two-cylinder solar Stirling engine powered by a flat- thermal efficiency of a beta-type Stirling engine with rhombic-drive mecha-
plate solar collector without regenerator. Renewable Energy 2008; nism. Renewable Energy 2010;35(11):2590e601.
33(1):77e87. [22] Cheng CH, Yu YJ. Dynamic simulation of a beta-type Stirling engine with cam-
[2] Mancini T, Heller P, Butler B, Osborn B, Schiel W, Goldberg V, et al. Dish- drive mechanism via the combination of the thermodynamic and dynamic
Stirling systems: an overview of development and status. Journal of solar models. Renewable Energy 2011;36(2):714e25.
energy Engineering, Transactions of the ASME 2003;125(2):135e51. [23] Sripakagorn A, Srikam C. Design and performance of a moderate temperature
[3] Petrescu S, Petre C, Costea M, Malancioiu O, Boriaru N, Dobrovicescu A, difference Stirling engine. Renewable Energy 2011;36(6):1728e33.
et al. A methodology of computation, design and optimization of solar [24] Andersen SK, Carlsen H, Thomsen PG. Preliminary results from simulations of
Stirling power plant using hydrogen/oxygen fuel cells. Energy 2010;35(2): temperature oscillations in Stirling engine regenerator matrices. Energy 2006;
729e39. 31(10e11):1371e83.
[4] Cullen B, McGovern J. Energy system feasibility study of an Otto cycle/Stirling [25] Timoumi Y, Tlili I, Nasrallah SB. Design and performance optimization of GPU-
cycle hybrid automotive engine. Energy 2010;35(2):1017e23. 3 Stirling engines. Energy 2008;33(7):1100e14.
[5] Ross B. Status of the emerging technology of Stirling machines. IEEE Aerospace [26] Tlili I, Timoumi Y, Nasrallah SB. Analysis and design consideration of mean
and Electronic Systems Magazine 1995;10(6):34e9. temperature differential Stirling engine for solar application. Renewable
[6] Timoumi Y, Tlili I, Nasrallah SB. Performance optimization of Stirling engines. Energy 2008;33(8):1911e21.
Renewable Energy 2008;33(9):2134e44. [27] Lee GT, Kang BH, Lee JH. Effectiveness enhancement of a thermal regenerator
[7] Thombare DG, Verma SK. Technological development in the Stirling cycle in an oscillating flow. Applied Thermal Engineering 1998;18(8):653e60.
engines. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2008;12(1):1e38. [28] Kays WM, London AL. Compact heat exchangers. New York: McGraw-Hill;
[8] Schmidt G. Theorie der Lehmannschen calorischen maschine. Zeit Des Ver- 1964.
eines Ddeutsch Ing 1871;15(1e12):97e112. [29] Senft JR. Mechanical efficiency of heat engines. Cambridge Univ Pr; 2007.
[9] Blank DA, Wu C. Power optimization of an extra-terrestrial, solar-radiant [30] Lee JF, Sears FW, Turcotte DL. Statistical thermodynamics. Addison-Wesley
Stirling heat engine. Energy 1995;20(6):523e30. Pub. Co.; 1973.
[10] Erbay LB, Yavuz H. Analysis of the Stirling heat engine at maximum power [31] Stiel LI, Thodos G. The thermal conductivity of nonpolar substances in the
conditions. Energy 1997;22(7):645e50. dense gaseous and liquid regions. AIChE Journal 1964;10(1):26e30.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmodelforpredictingtheeffectofoperatingspeedonshaftpower-121028104508-phpapp02/75/Analytical-model-for-predicting-the-effect-of-operating-speed-on-shaft-power-10-2048.jpg)