Embed presentation
Download to read offline

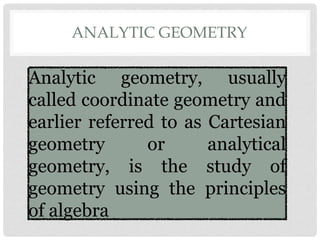
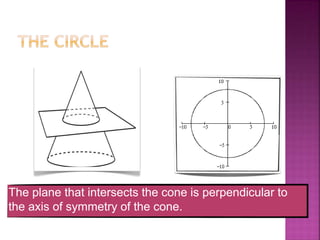
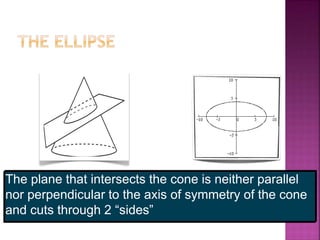
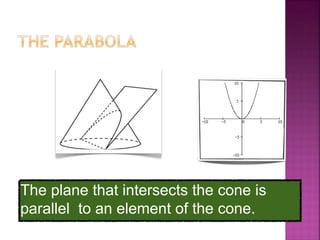
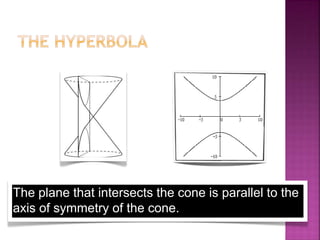
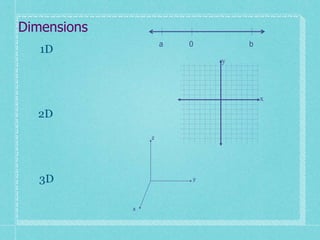
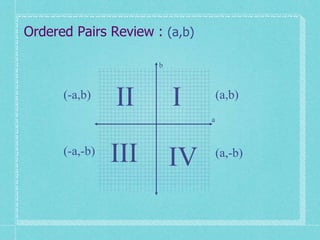
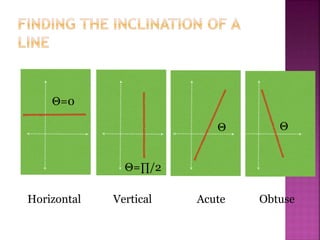

The document discusses analytic geometry, which is the study of geometry using algebraic principles. It examines different types of plane intersections with cones, such as planes that are parallel, perpendicular, or neither parallel nor perpendicular to the cone's axis of symmetry. It also covers one, two, and three dimensional spaces, ordered pairs, angles including horizontal, vertical, acute and obtuse, and finding the inclination of a line using its slope-intercept form equation.