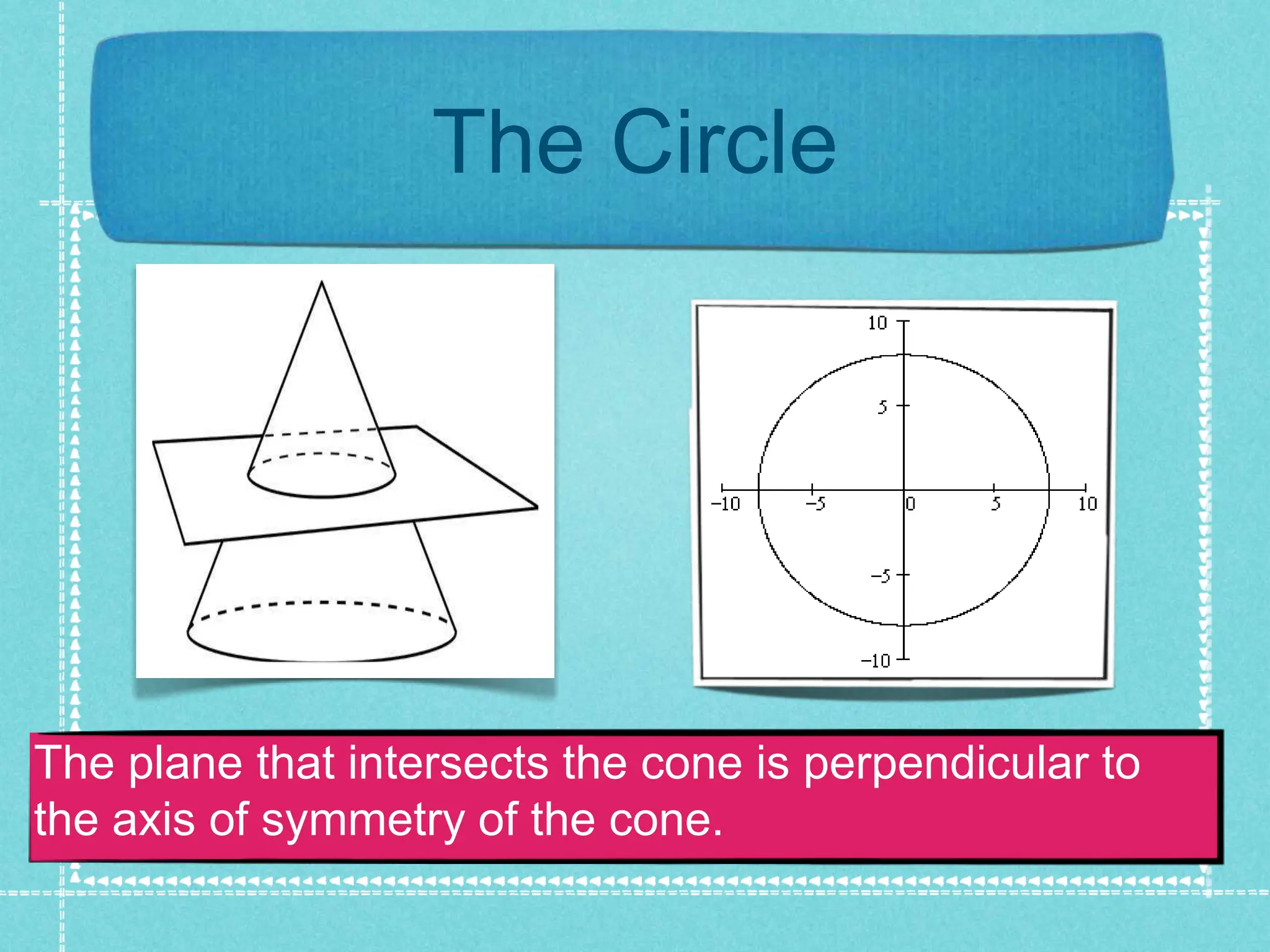
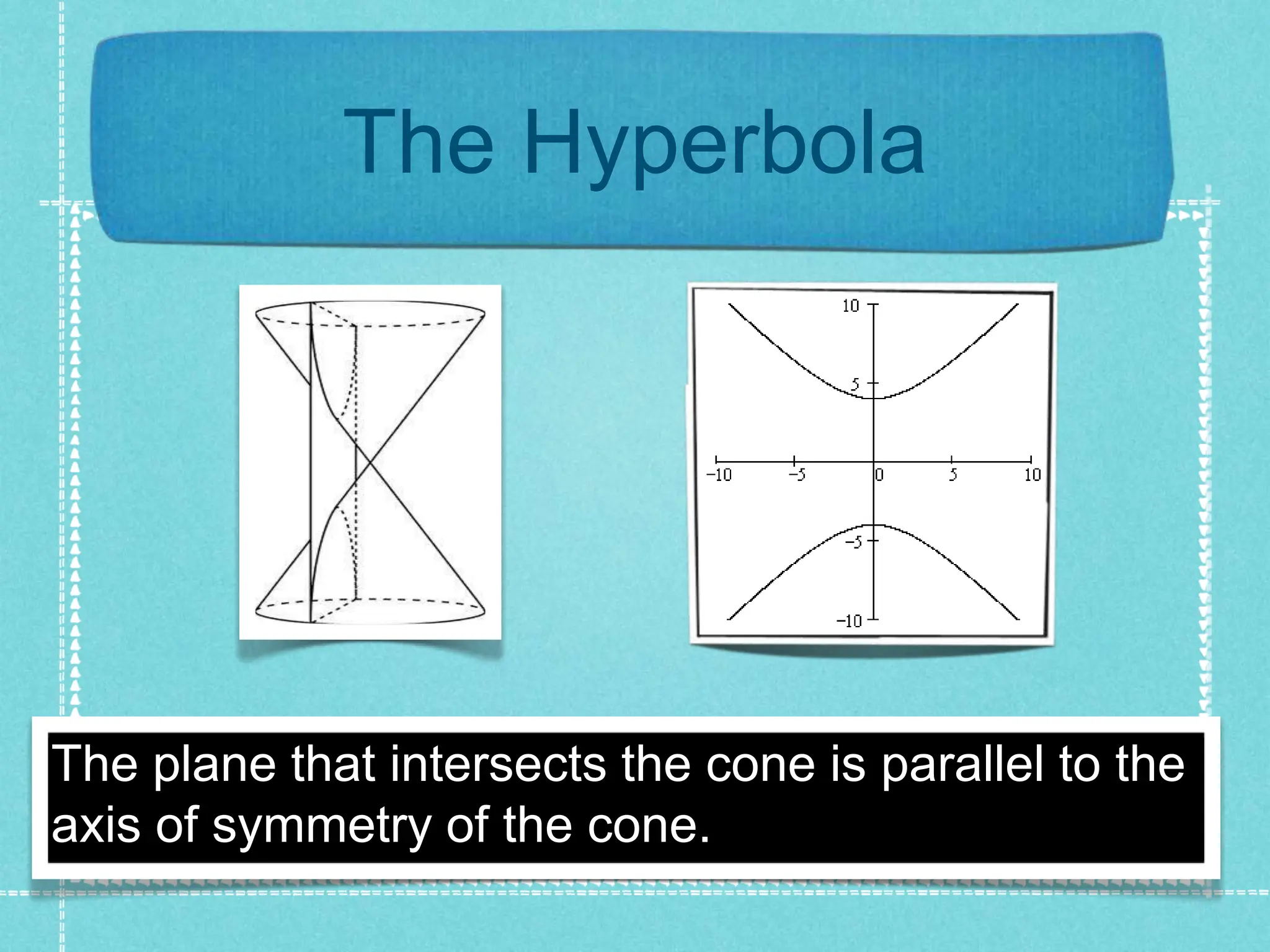
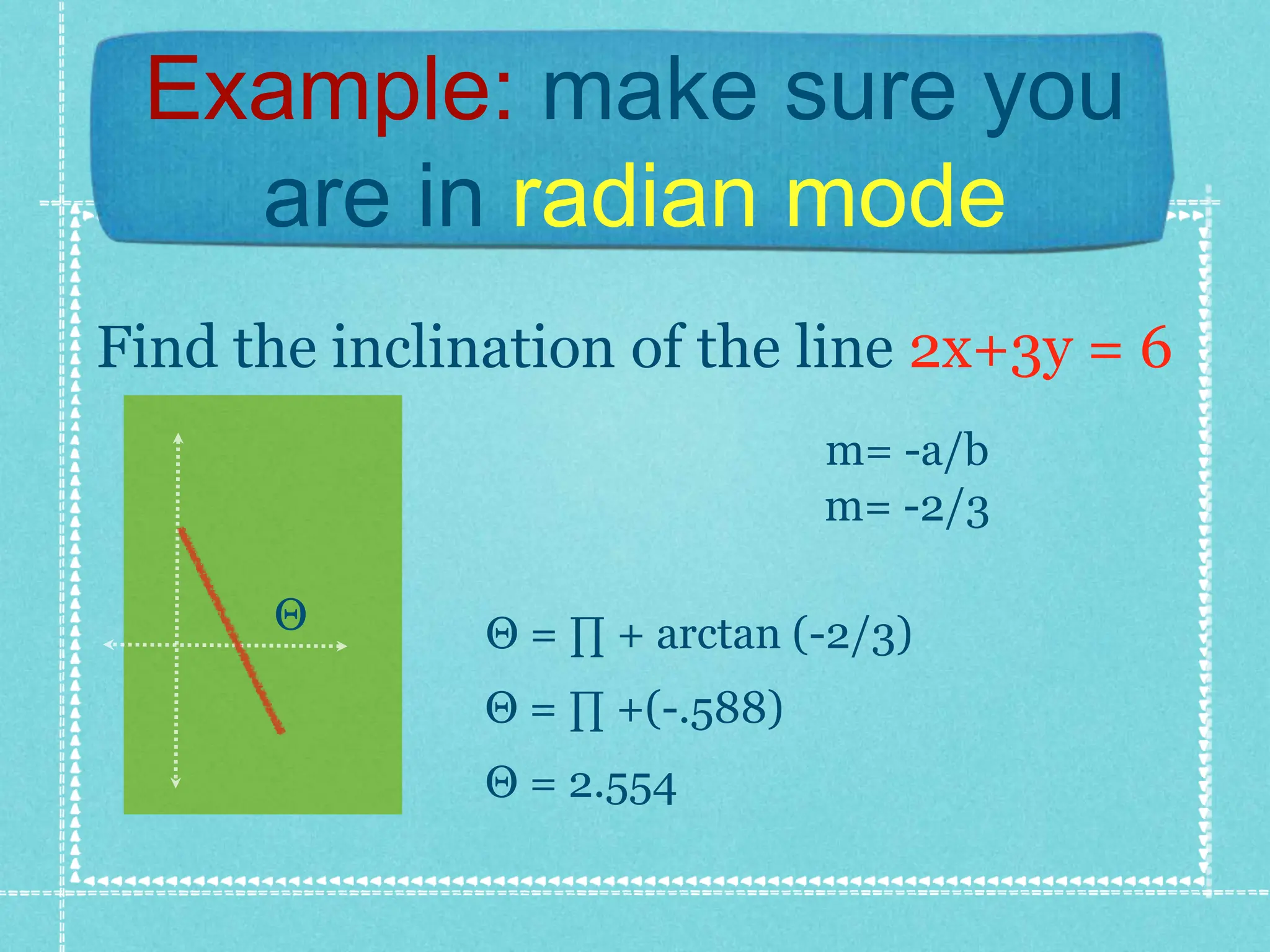
The document discusses conic sections and analytic geometry. It defines conic sections as shapes formed by the intersection of a plane and a cone. Specifically, it states that a circle is formed when the plane is perpendicular to the cone's axis of symmetry, an ellipse is formed when the plane is neither parallel nor perpendicular, a parabola is formed when the plane is parallel to an element of the cone, and a hyperbola is formed when the plane is parallel to the cone's axis of symmetry. It also briefly discusses dimensions, ordered pairs, finding the inclination of lines, and provides an example of finding the inclination of a line using arctan.