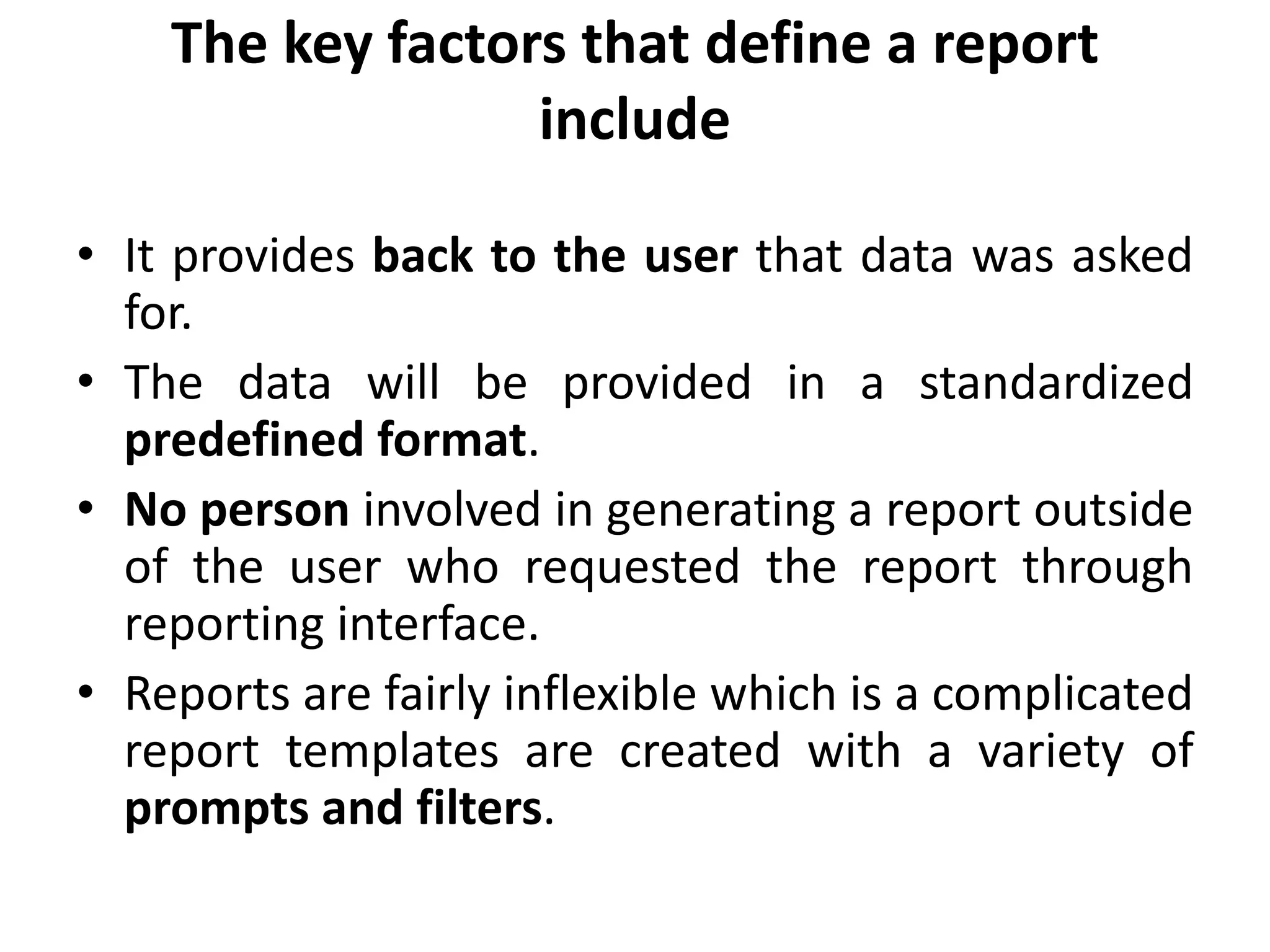
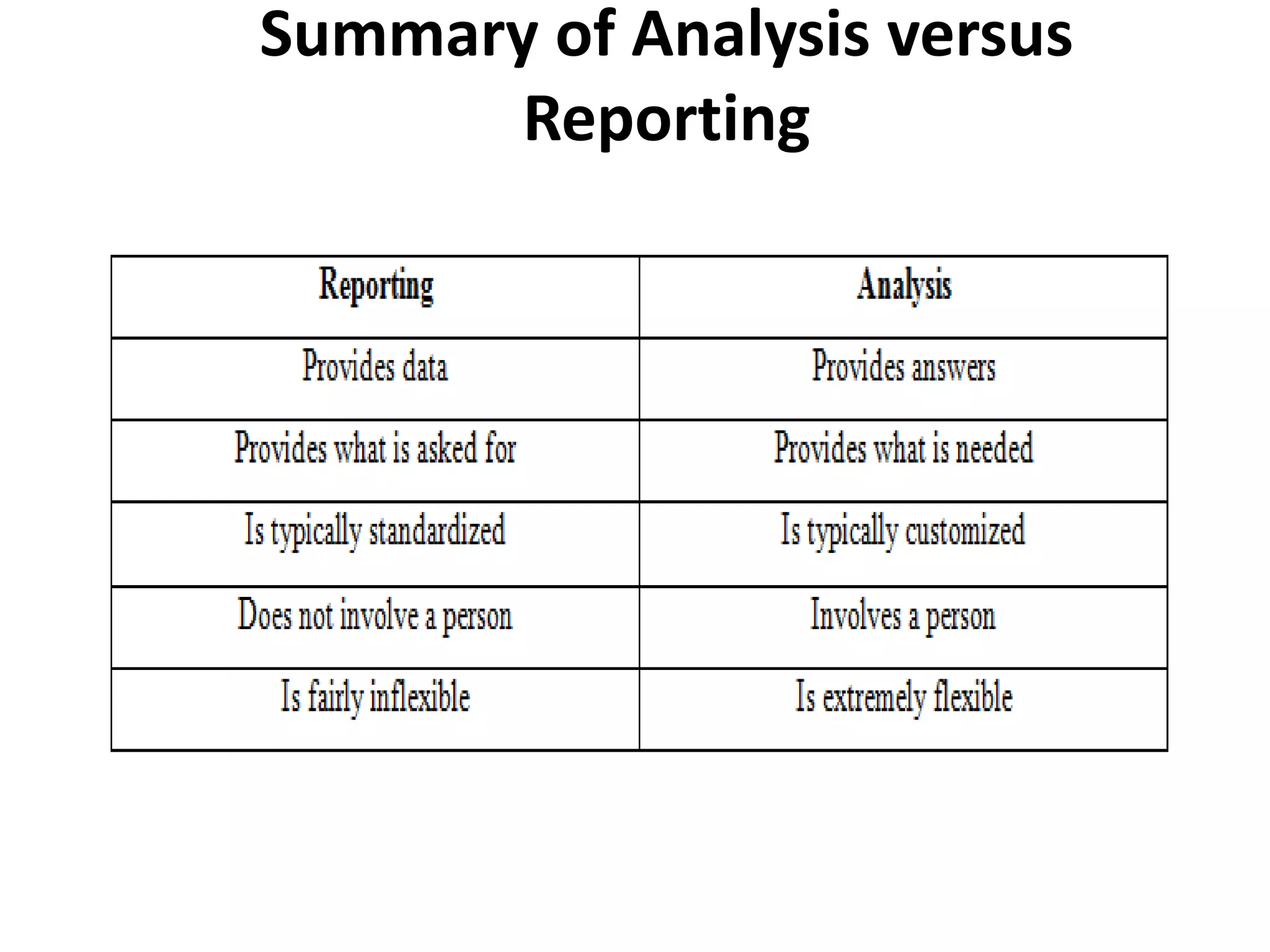
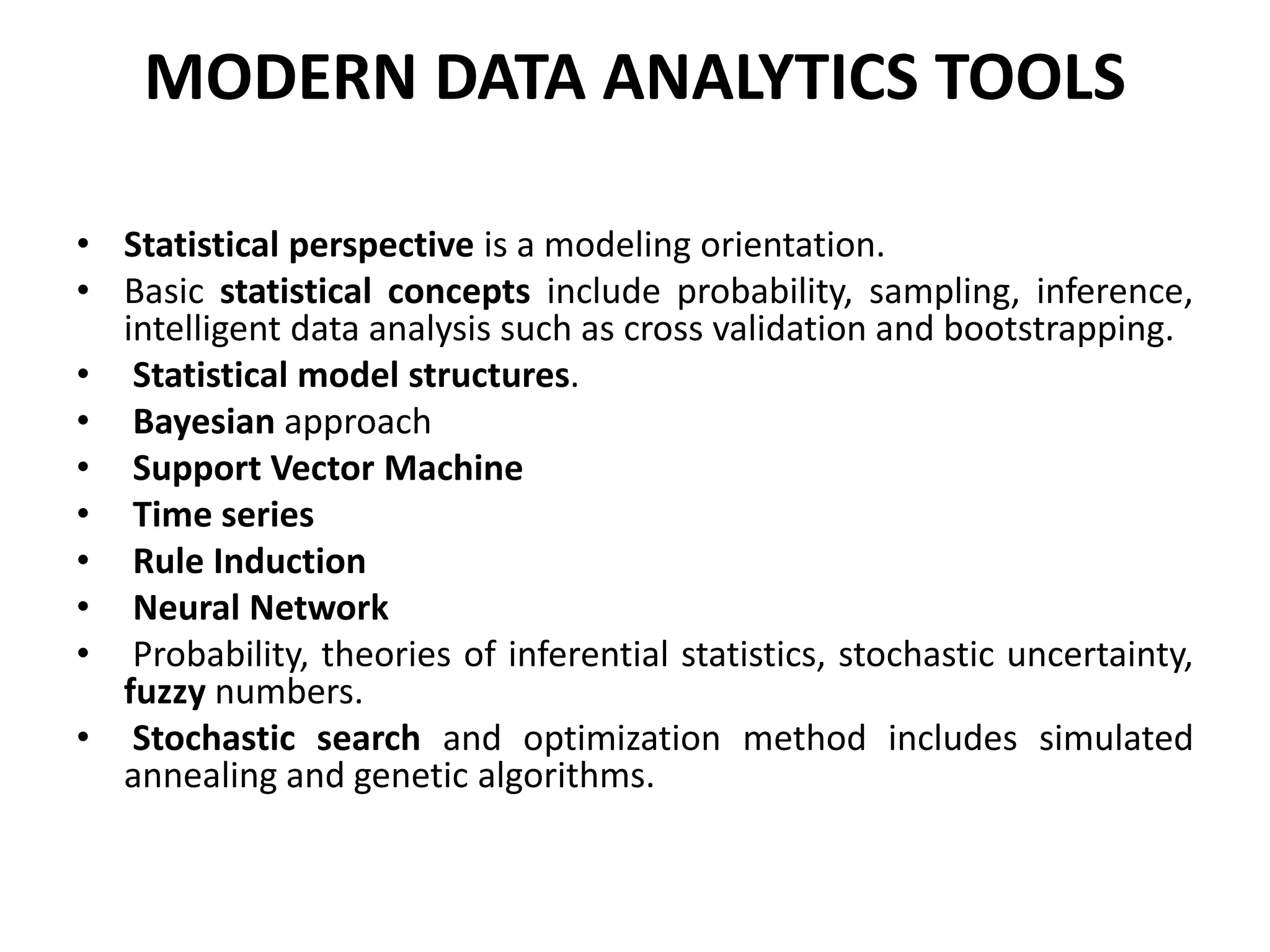
Reporting involves users selecting predefined reports to view results in standardized formats like tables and graphs. Reports are inflexible and generated without human involvement beyond the initial request. Analysis provides answers to specific questions through a customized and flexible process that involves a person guiding the analysis. Both reporting and analysis are needed to succeed with big data.