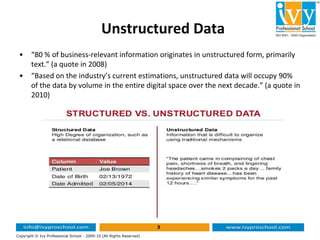
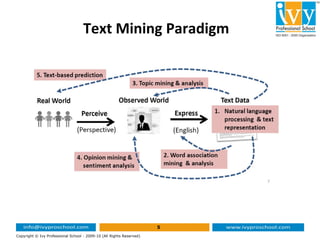
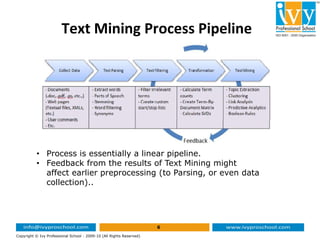
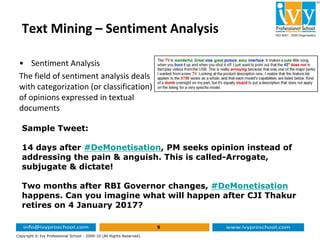
This document provides an introduction to text mining and analytics. It discusses how organizations encounter large amounts of textual data from various sources daily. It states that 80% of business information originates in unstructured text form. Text analytics uses algorithms to convert unstructured text into structured data that can be analyzed using statistical techniques. The key part of text mining is preprocessing the text to extract meaningful structured data through techniques like tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, part-of-speech tagging and named entity recognition. This structured data can then be analyzed through applications such as text clustering, trend analysis and sentiment analysis.