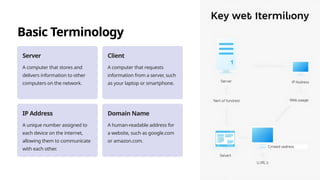
The document provides an overview of the internet, detailing its evolution from early networks like ARPANET to the modern-day applications including communication, entertainment, and commerce. It explains basic terminology such as servers, clients, IP addresses, and domain names, as well as how users can connect to the internet through various means like wireless and wired connections. The document also introduces essential internet protocols, programming languages, and tools for navigation and communication.