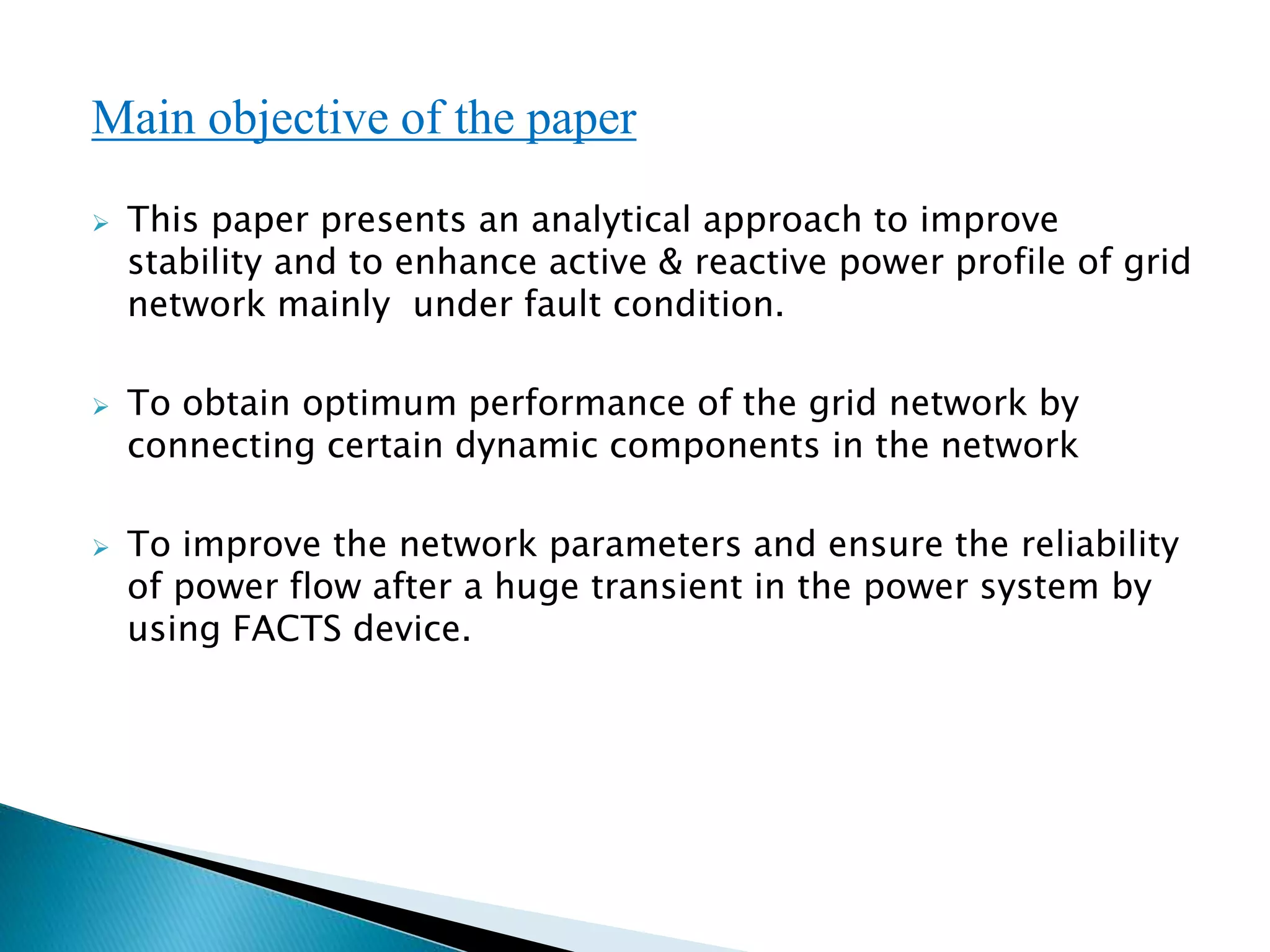
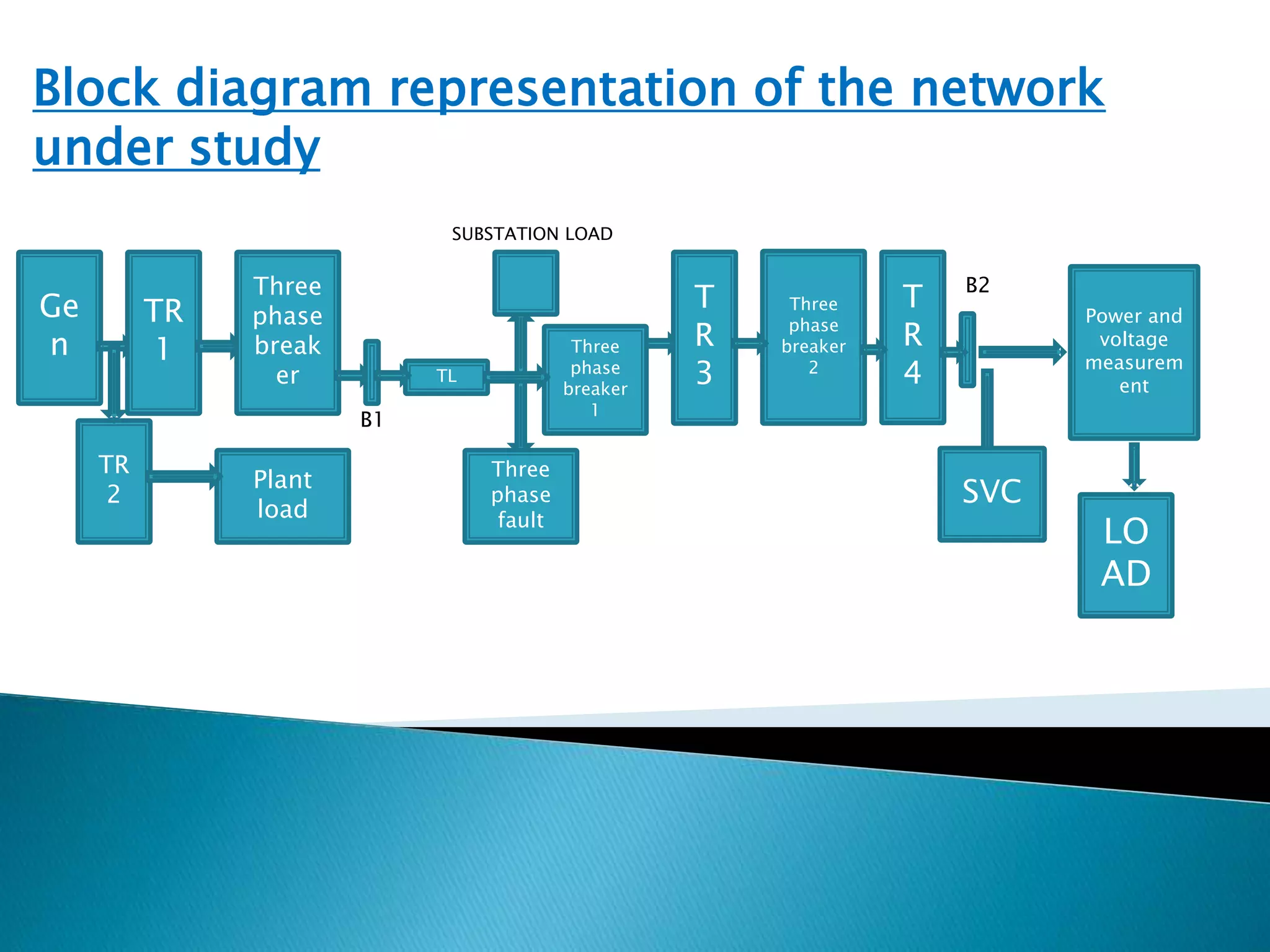
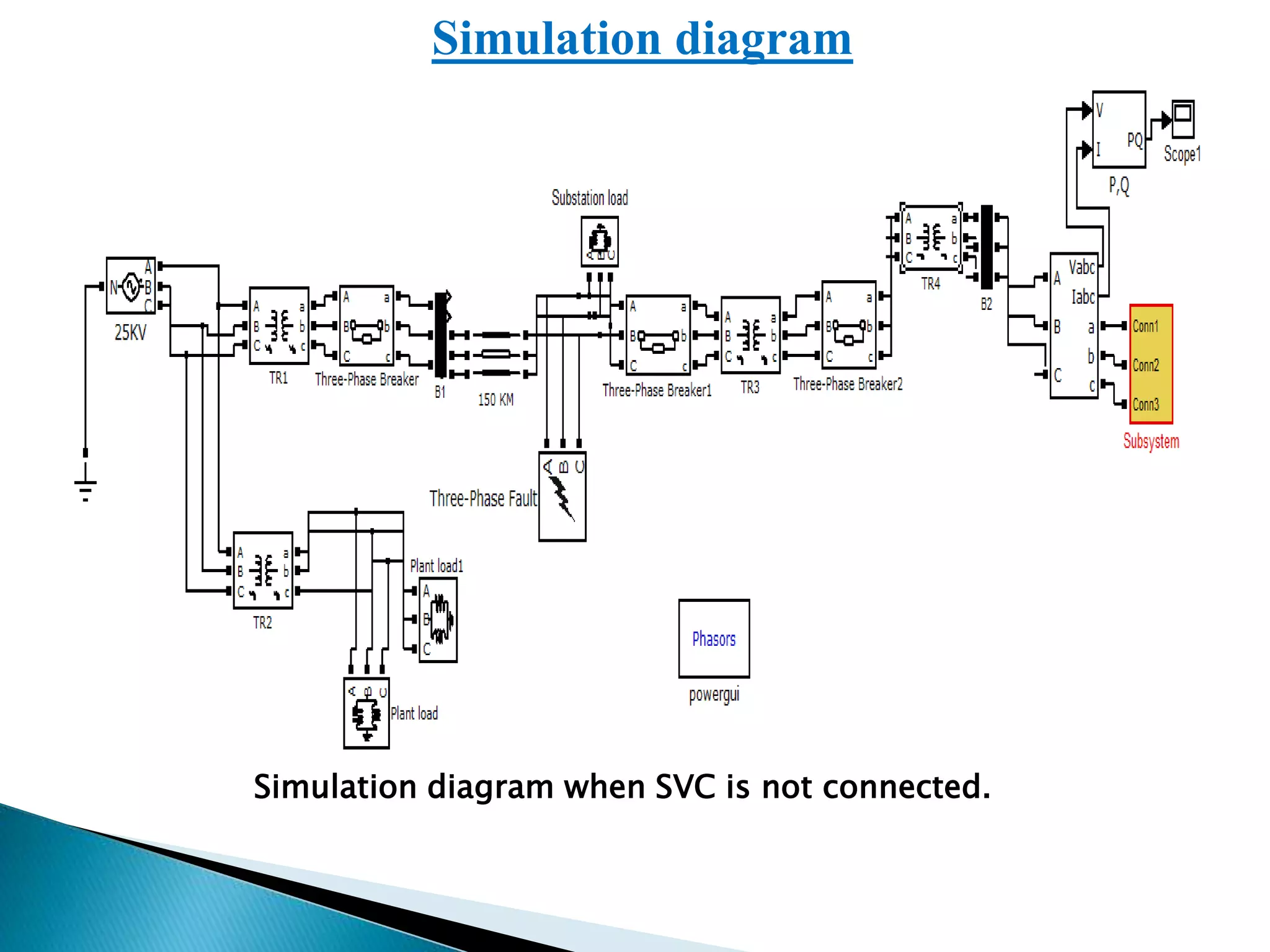
This paper presents an analytical approach to enhance the stability and power profile of a power system grid, particularly under fault conditions. It discusses the performance improvement achieved by connecting dynamic components like Static Var Compensators (SVC) to ensure reliability after transient events. The results indicate enhanced voltage and reactive power profiles, outlining future steps for further improvements in the power network.




![[1] Power system performance improvement by using an SVC device ,Ali Abdulwahhab
Abdulrazzaq; Mircea Eremia; Lucian Toma ,2014 International Symposium on
Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering (ISFEE),Year: 2014 ,Pages: 1 - 6 ,IEEE Conference
Publications.
[2] Fishow, A.G, “Transient ans Steady State Stability margin to state a power system
stability standardization”, published in UPS of Russia.
[3] Canizarea.C. A, Bhattacharrya. K ,Haghighat. H,Pan. J,Tang. C and Samahy. E. I,
“Reactive Power Despatch Problem in the context of Captive Electricity Market Generation,
Transmission and Distribution”, Vol.4, IET issue, February 2010.
[4] Application of static VAr compensators to increase power system damping,E. -Z. Zhou
,IEEE Transactions on Power Systems ,Year: 1993, Volume: 8, Issue: 2 ,Pages: 655 - 661
,Cited by: Papers (95) ,IEEE Journals & Magazines.
[5] Optimal placement and sizing of SVC for loss minimization and voltage security
improvement using differential evolution algorithm ,Shraddha Udgir; Laxmi Srivastava;
Manjaree Pandit,International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in
Engineering (ICRAIE-2014) Year: 2014, Pages: 1 - 6 Cited by: Papers (3) IEEE Conference
Publications.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optronix201754-180713113852/75/An-Analytical-Approach-to-Improve-Stability-and-to-Enhance-Active-Reactive-Power-Profile-of-a-Grid-Network-mainly-under-Fault-Condition-16-2048.jpg)
![[6] Improve power oscillation stability in a grid connected wind power system by
using a Static Var Compensator ,Van-Tri Bui; Dinh-Nhon Truong; Dac-Loc Ho,
2017 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE),Year:
2017,Pages: 200 – 203,IEEE Conference Publications.
[7] Best locations of shunt SVCs for steady state voltage stability enhancement
Ibrahim B. M. Taha ,2015 IEEE Conference on Energy Conversion
(CENCON),Year:2015,Pages:430-435,IEEE Conference Publications.
[8] Rajamani.K,Hambarde. U.K “ Islanding and Loadshedding Scheme for Captive
Power Plant Power Delivery”, IEEE Transactions, Vol. 14, Jul 1999.
[9] NEMA Standards Publication ICs 1-1988, General Standards for Industrial
Control and Systems; ICs 2-1988, Industrial Control Devices, Controllers and
Assemblies; ICs 3-1988.
[10] Bindon. R.E, “Emergency operation of large steam turbine generator”,
presented at South Eastern Electric Exchange, Atlanta, Georgia, October 13-14,
1966.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optronix201754-180713113852/75/An-Analytical-Approach-to-Improve-Stability-and-to-Enhance-Active-Reactive-Power-Profile-of-a-Grid-Network-mainly-under-Fault-Condition-17-2048.jpg)
![[11] IEEE Std 141-1986, IEEE Recommended Practice for Electric Power
Distribution for Industrial Plants (ANSI).
[12] IEEE Std 242-1986, IEEE Recommended Practice for Protection
and Coordination of Industrial and Commercial Power Systems (ANSI).
19458.
[13] SenguptaT.K.,”Studies on Assessment of Power Frequency in
Interconnected Grid – Its Computer based Control and Protection”,
Research Paper, The Faculty of Engineering and
Technology,Department of Electrical Engineering,Jadavpur University,
2008.
[14] Krishnamurti.P,“Captive Power Plant Quality Journal” of TCE
Limited, Vol.4-I-pp.10,April 2006.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optronix201754-180713113852/75/An-Analytical-Approach-to-Improve-Stability-and-to-Enhance-Active-Reactive-Power-Profile-of-a-Grid-Network-mainly-under-Fault-Condition-18-2048.jpg)
