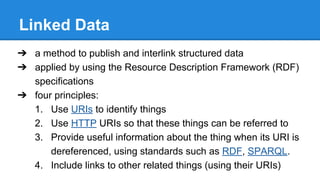
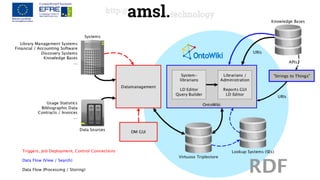
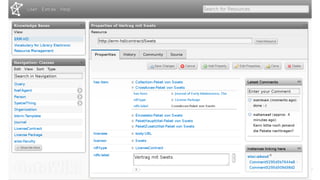
The document outlines the development of an Electronic Resource Management (ERM) system using linked data principles, highlighting challenges such as managing diverse information formats and changing business models. Key features include workflow and license management, as well as the integration of heterogeneous data into a flexible model for improved interoperability. The OntoWiki tool is introduced for RDF content management, emphasizing its open-source nature and collaborative development effort by various institutions.