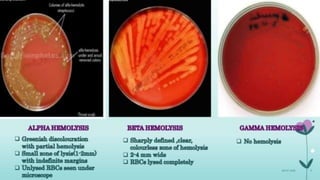
Here are some commonly used media for isolating the microorganisms:
Pseudomonas - King's B medium
Azospirillum - Ashby's mannitol agar
Azatobacter - Jensen's nitrogen-free medium
Rhizobium - Yeast extract mannitol agar
Escherichia coli - Eosin methylene blue agar, MacConkey agar
Fungi - Potato dextrose agar, Sabouraud dextrose agar
Yeast - Potato dextrose agar
Actinomycetes - Starch casein agar