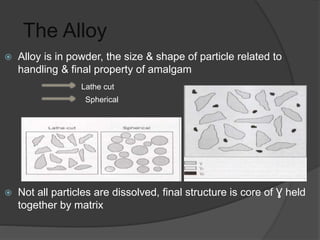
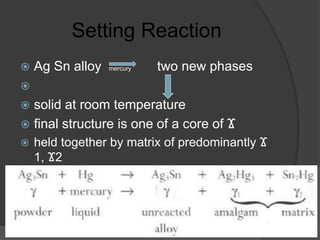
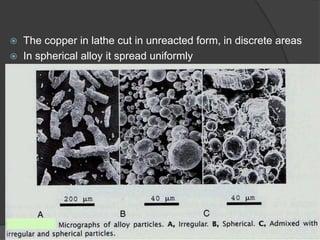
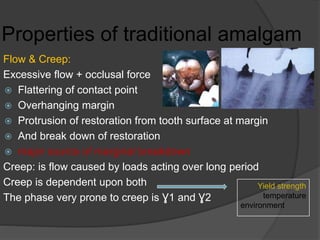
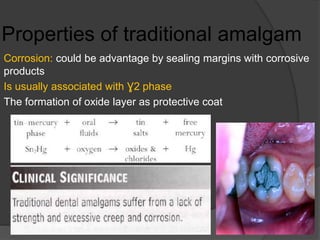
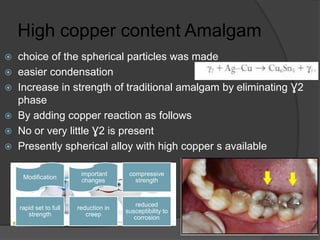
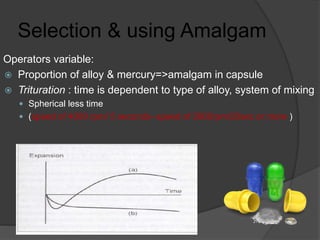
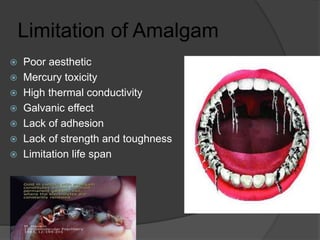
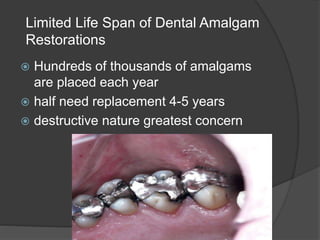
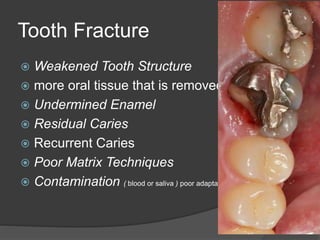
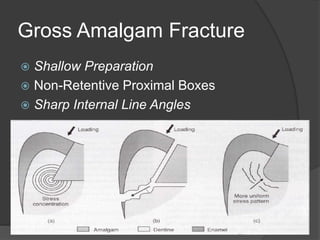
This document discusses dental amalgams, including their composition, properties, clinical use and limitations. Amalgams are composed of an alloy of silver, tin, copper and zinc mixed with liquid mercury. The setting reaction forms new phases that give amalgams their strength and other properties. High copper amalgams have increased strength and reduced creep compared to traditional amalgams. Proper selection of alloy, proportioning of alloy and mercury, condensation technique and finishing are important to ensure optimal clinical performance. While amalgams have limitations like mercury toxicity and aesthetics, with proper technique they can provide durable restorations.