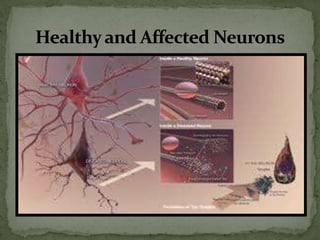
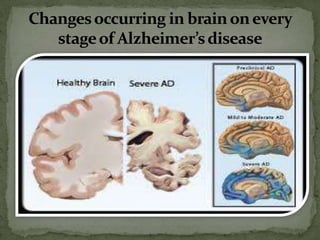
Alzheimer's disease is a neurological disorder that causes memory loss and cognitive decline. It was first described by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1901 when examining patient Auguste D. The causes are not fully understood but involve genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Early signs include memory problems and other cognitive declines. As it progresses, damage occurs in areas controlling language, reasoning, and thought, and patients have trouble recognizing family and friends. By the final stage, plaques and tangles have spread throughout the brain, causing severe impairment and dependence on others for care. While some drugs can temporarily stabilize symptoms, there is no cure for Alzheimer's disease.