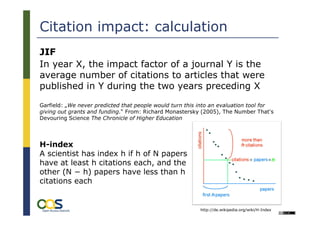
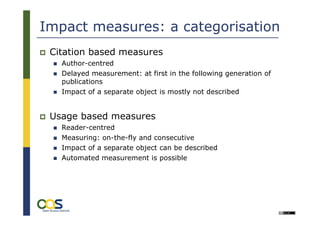
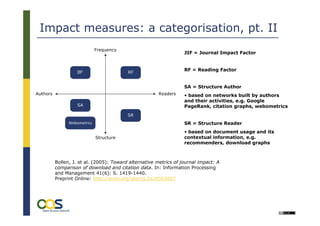
The document discusses alternative impact measures for open access publications, emphasizing the need for usage-based metrics to complement traditional citation-based measures due to their shortcomings. It highlights the challenges of generating and standardizing interoperable usage information from distributed services, along with the importance of creating a technical infrastructure for open access statistics. The project aims to establish common standards for exchanging usage data and improving the evaluation process for open access materials.