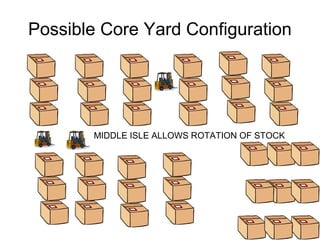
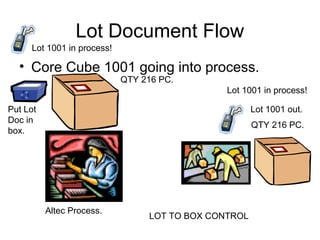
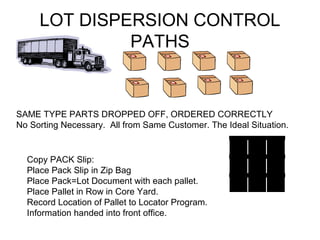
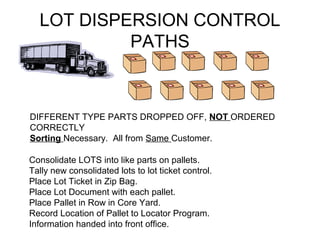
The document outlines plans to reorganize a core yard to improve efficiency. It proposes creating a middle access aisle to allow picking from both sides, rotating stock to prevent shrink wrap degradation, and arranging all items in labeled rows from left to right. A locator program would track inventory and pick the oldest stock first to fulfill orders. Lot control procedures are also described to track customer cores through the receiving, storage, and production processes. Tally counters or flip cards would help workers count cores as they are sorted onto pallets to consolidate lots while maintaining visibility of quantities from each customer.