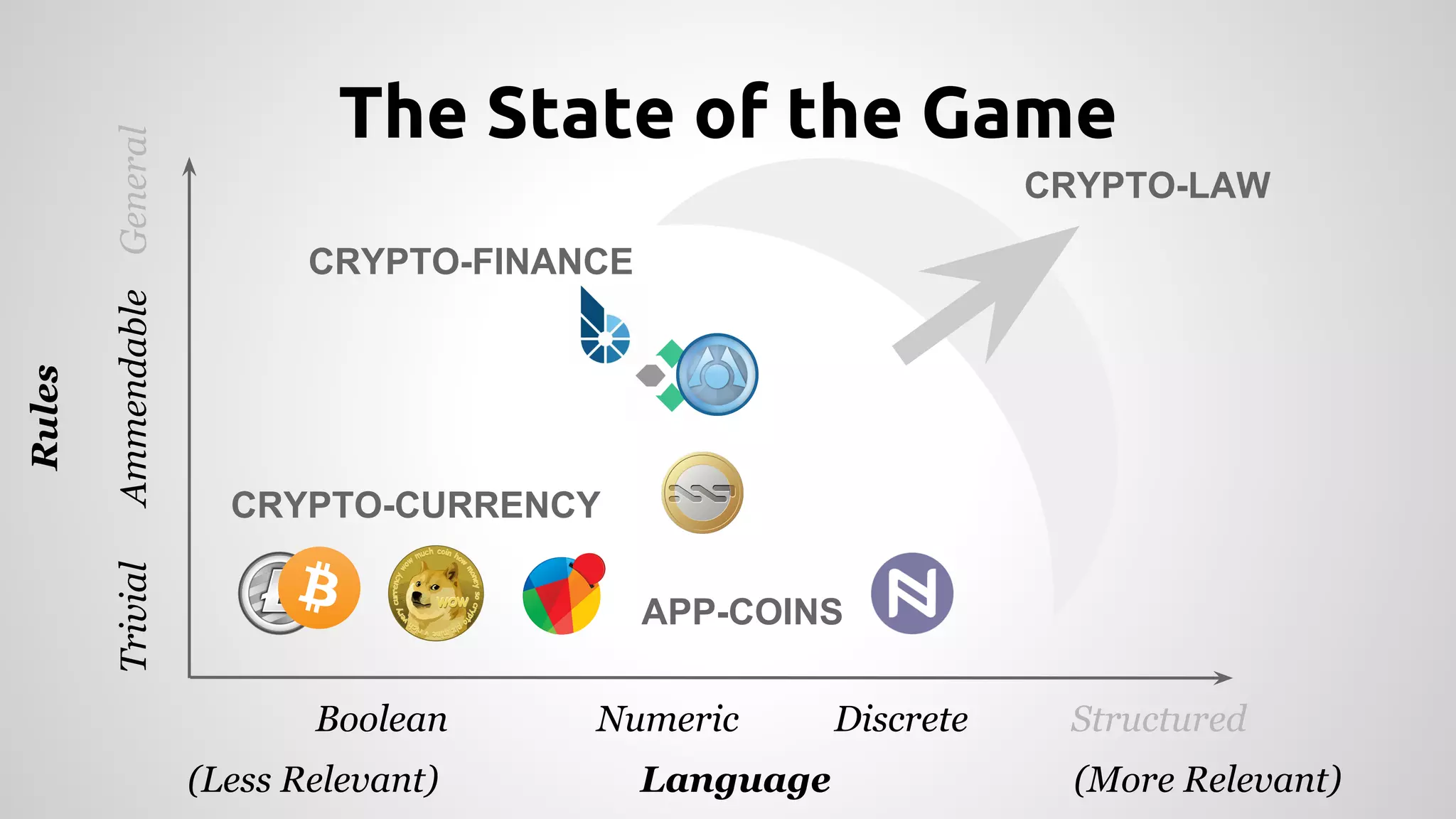
This document discusses decentralized software as a service (ÐSaaS) and its implications. ÐSaaS implements rules of interaction between parties for a service through software, without a central operator. As such services cannot be shut down en masse like traditional SaaS. This raises questions around what is considered legal as ÐSaaS cannot police users directly. There will likely be changes to social norms and laws as new technologies allow for greater transparency, individual choice and harder to police deals and information. Lawmakers will need to work with these systems to avoid disruption through education and evidence-based decisions focused on health and well-being.