Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




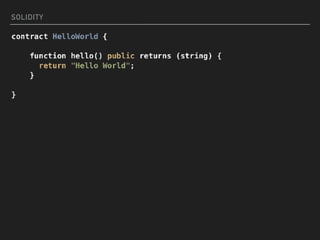
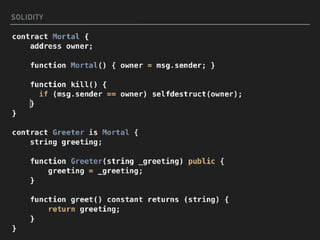
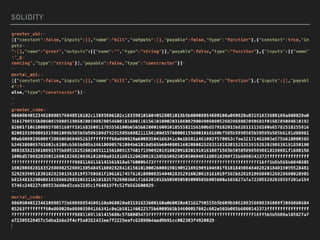

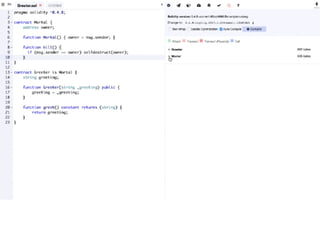

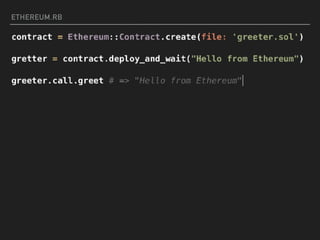
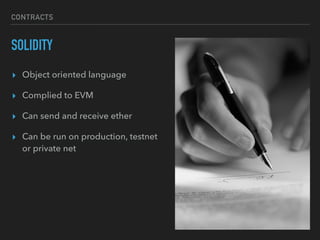

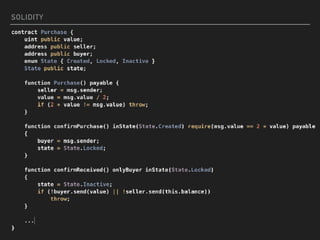
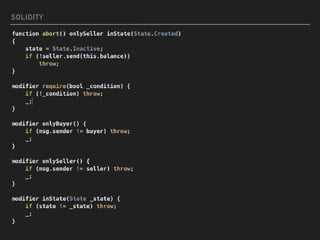






This document introduces smart contracts on Ethereum using the Solidity programming language. It explains that Ethereum builds upon Bitcoin by introducing a Turing-complete virtual machine that allows for more complex smart contracts. Solidity is an object-oriented language that compiles to bytecode run on the Ethereum Virtual Machine. Smart contracts can send and receive cryptocurrency and be deployed on the Ethereum mainnet or testnets. The document outlines some current limitations of Ethereum and provides useful links for developing with Solidity.























