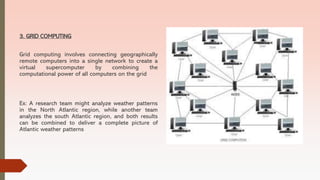
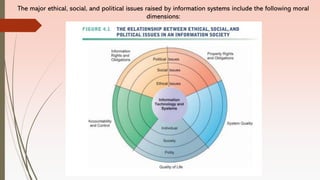
This document discusses trends in computer hardware and software platforms as well as ethical, social, and political issues related to information systems. It covers emerging mobile digital platforms, consumerization of IT, grid computing, virtualization, and cloud computing as trends in hardware. For software trends, it discusses open-source software, software outsourcing, and cloud-based services. Finally, it examines five moral dimensions of the information age and how technological advances can threaten privacy, property rights, accountability, system quality, and quality of life.