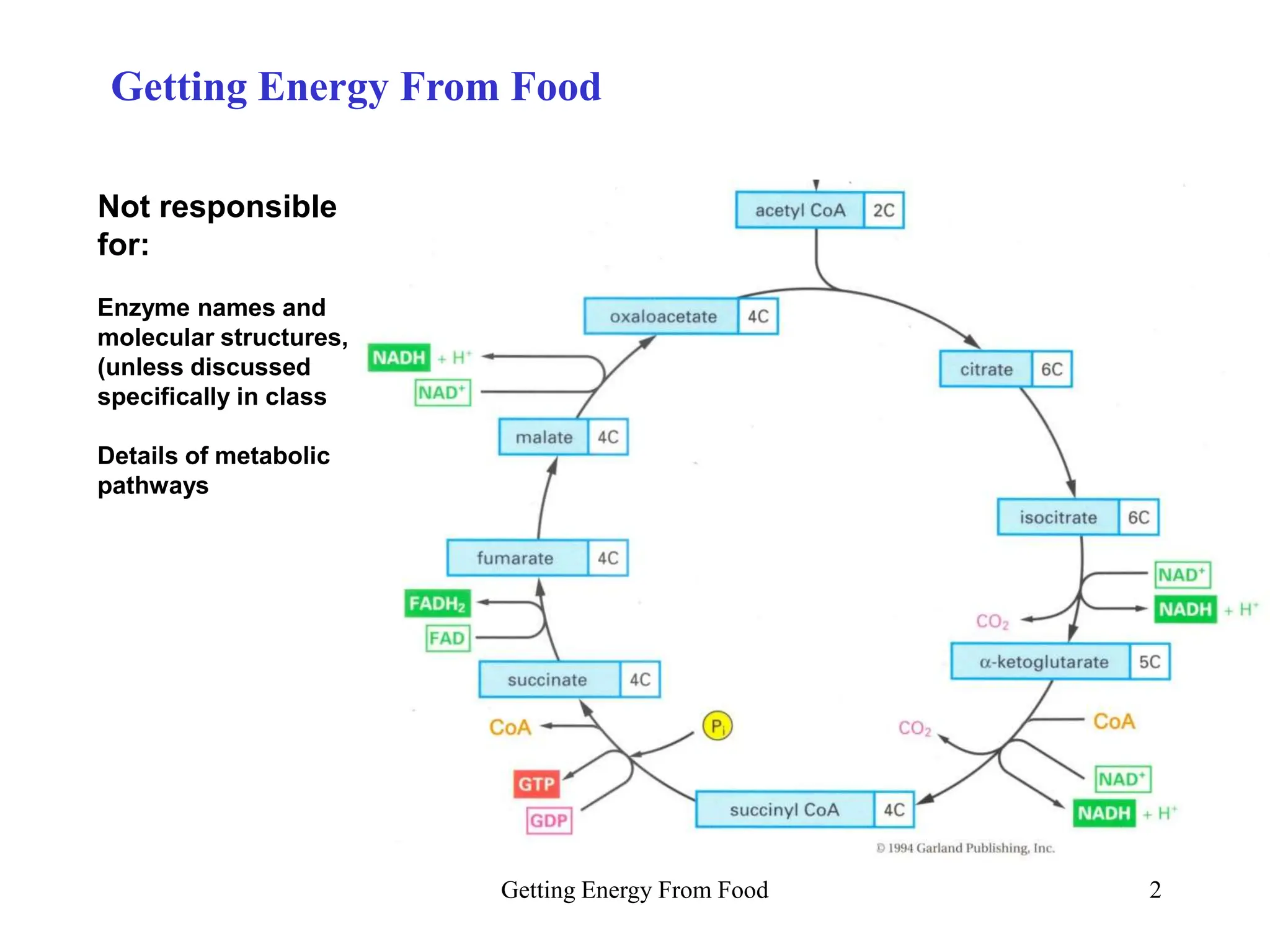
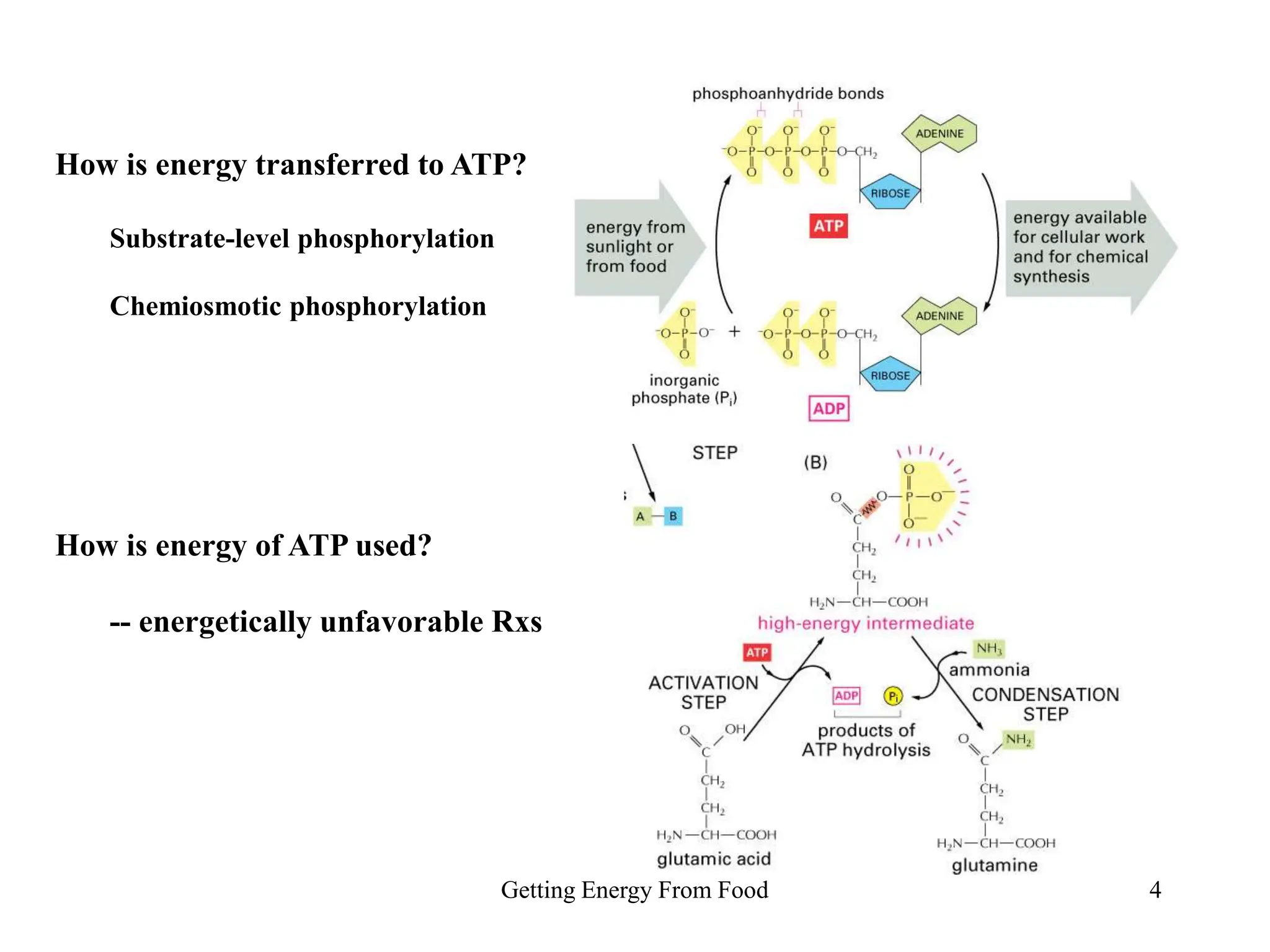
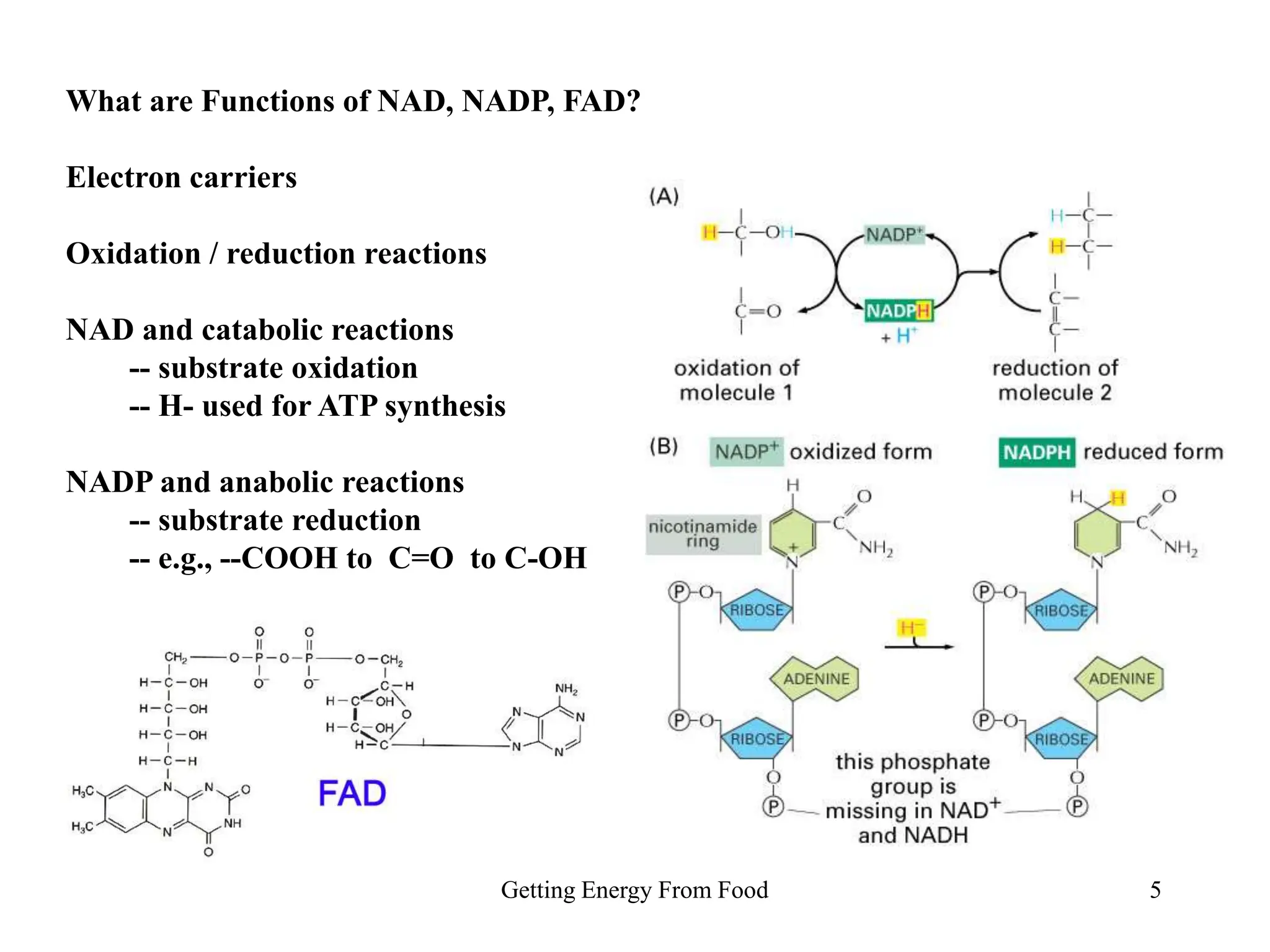
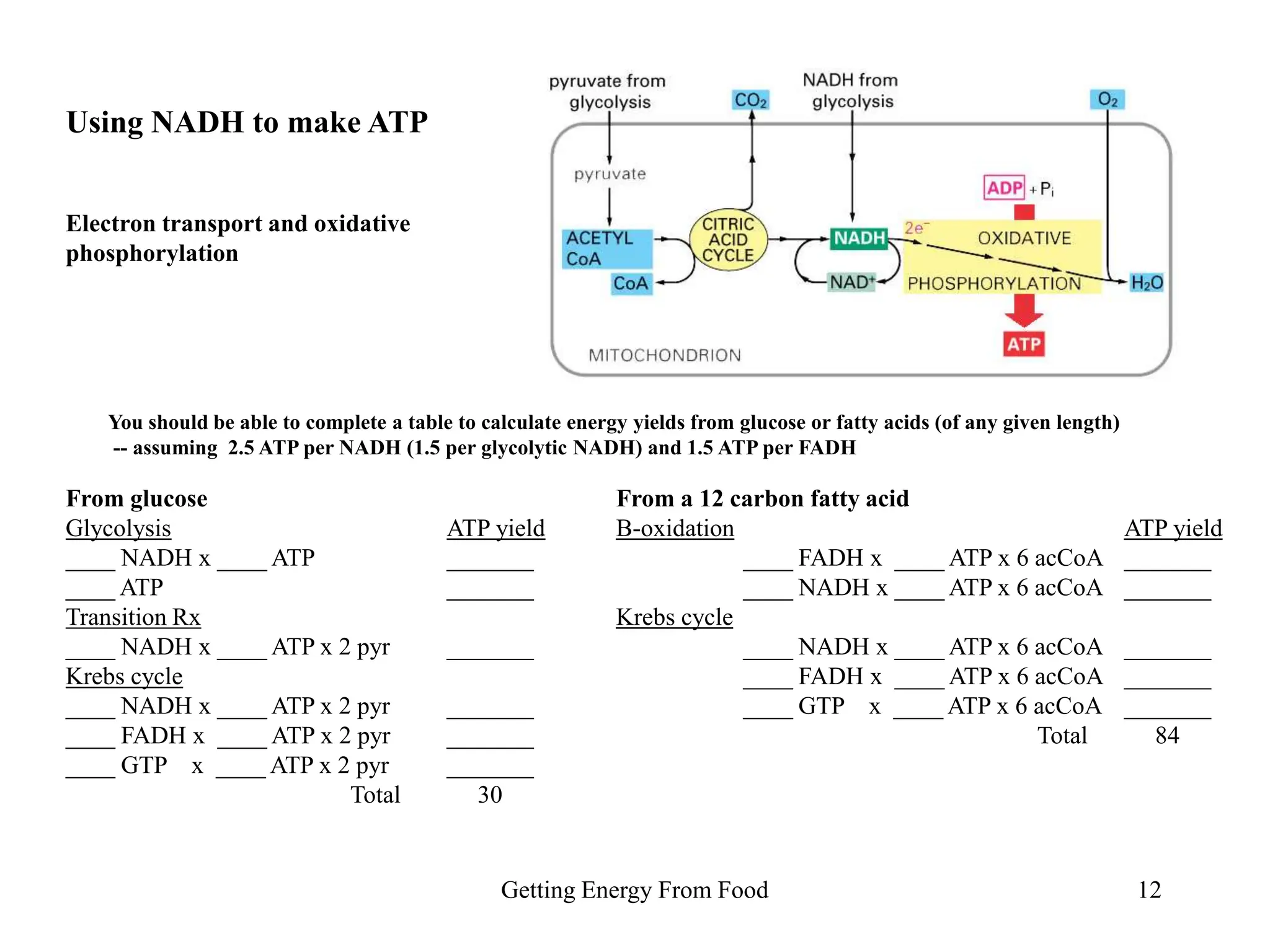
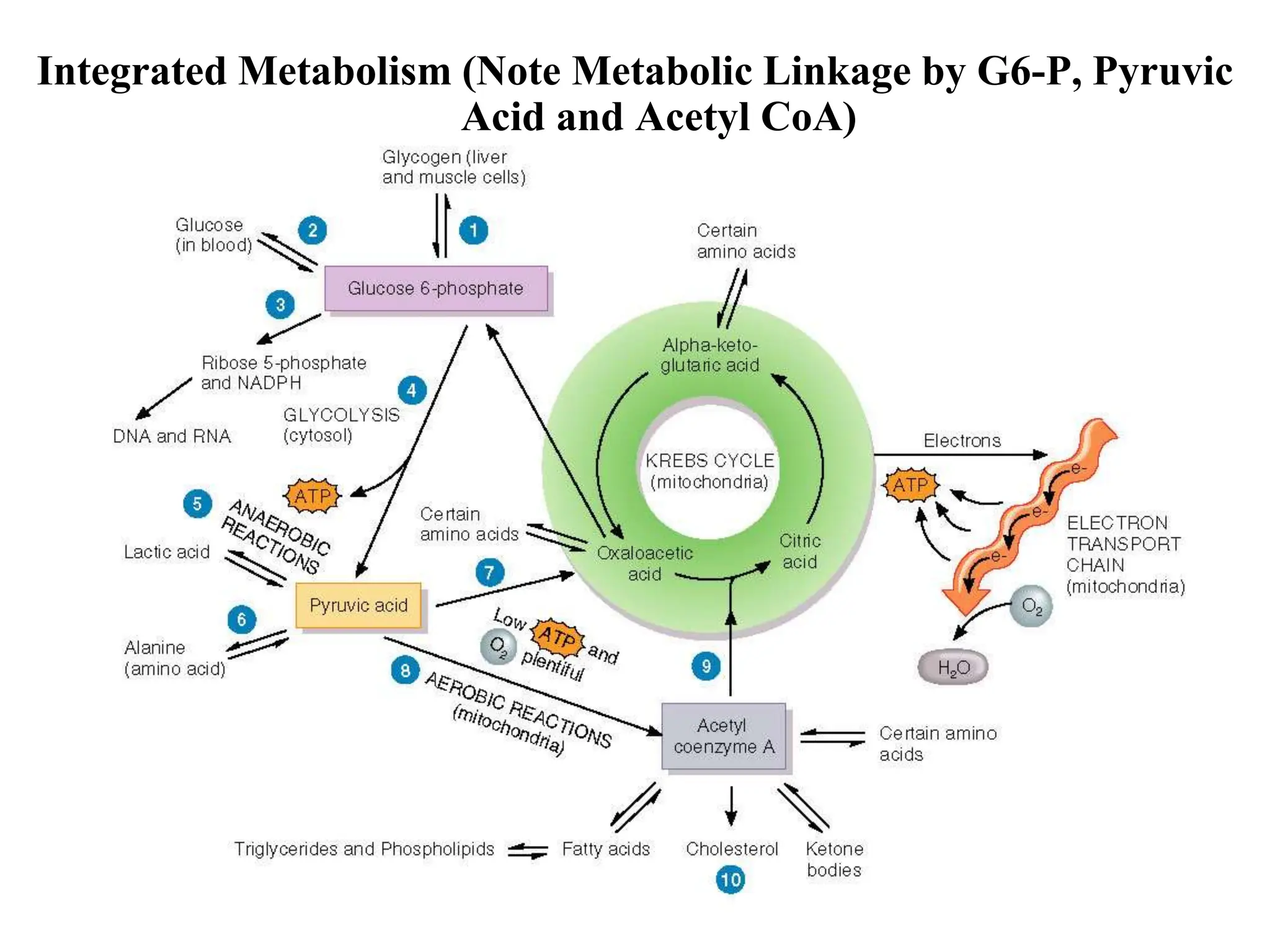
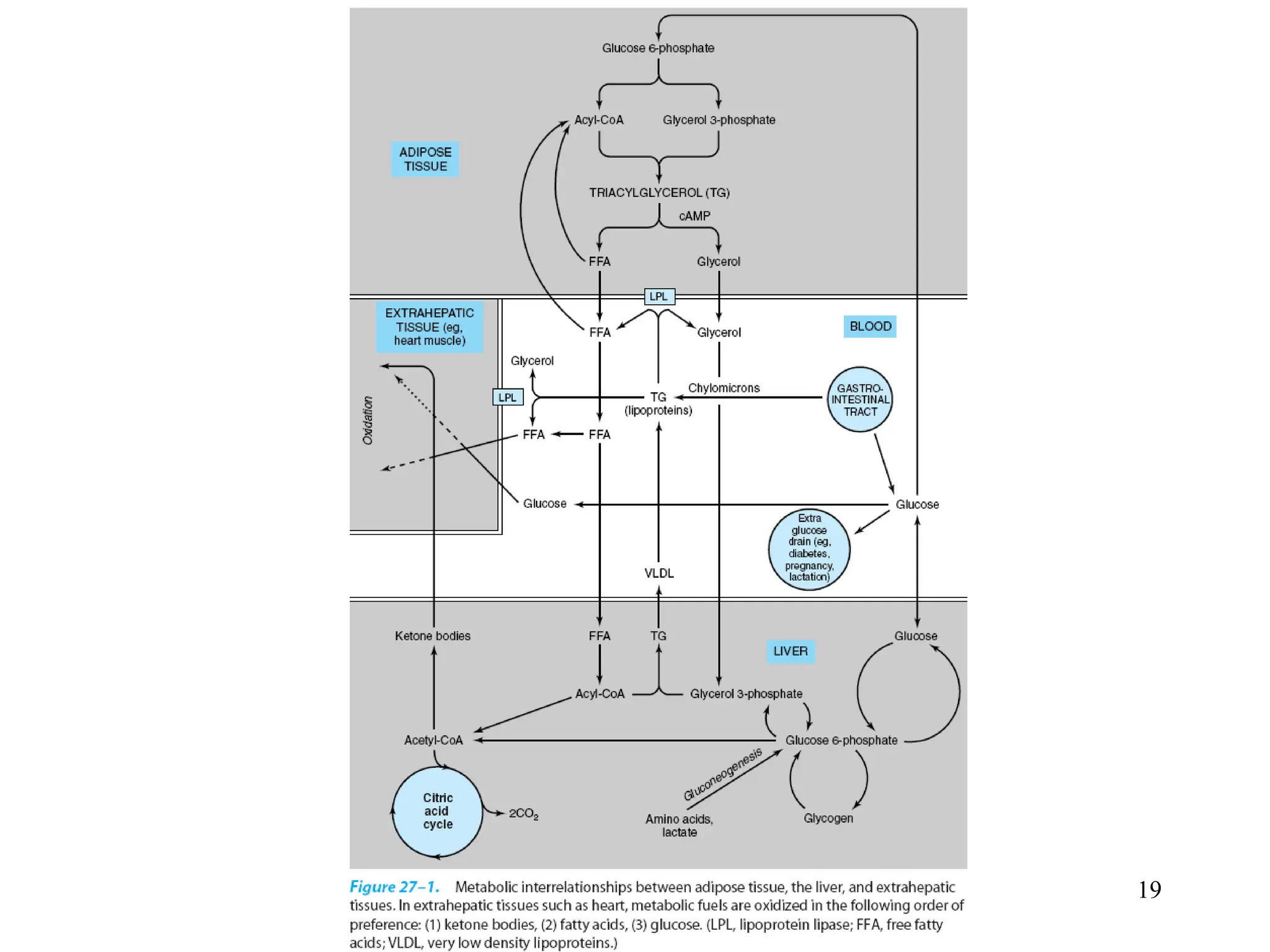
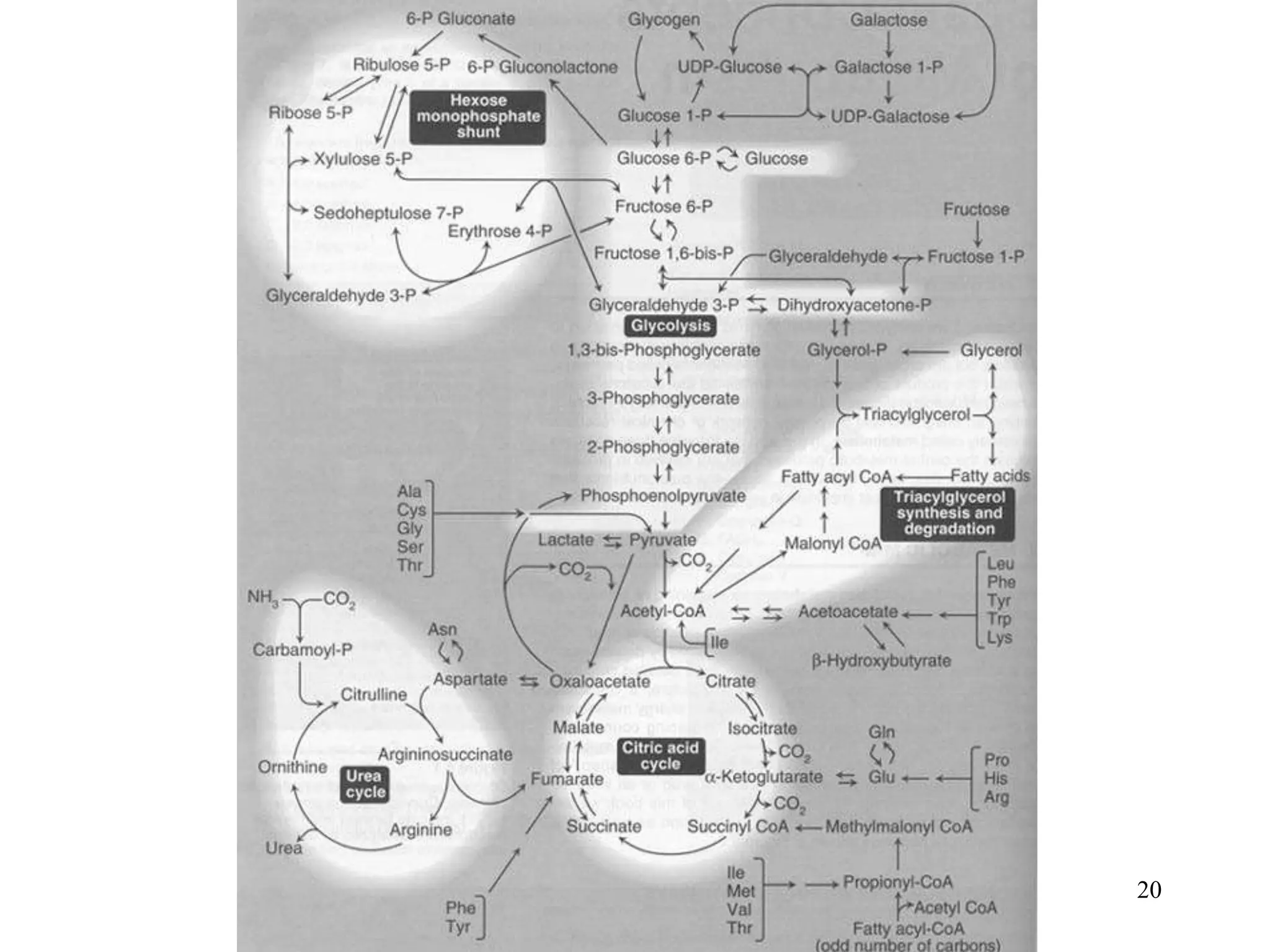
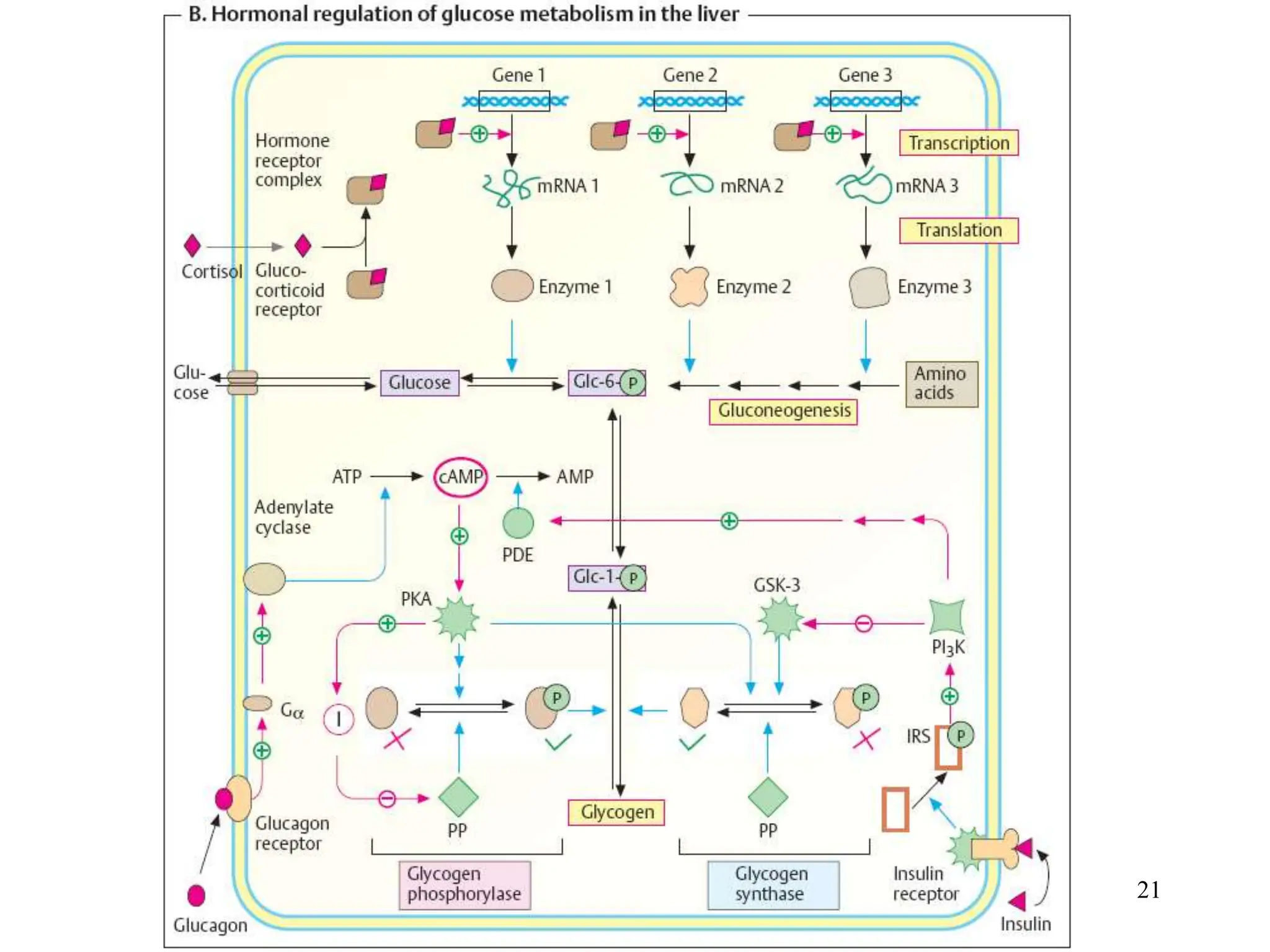
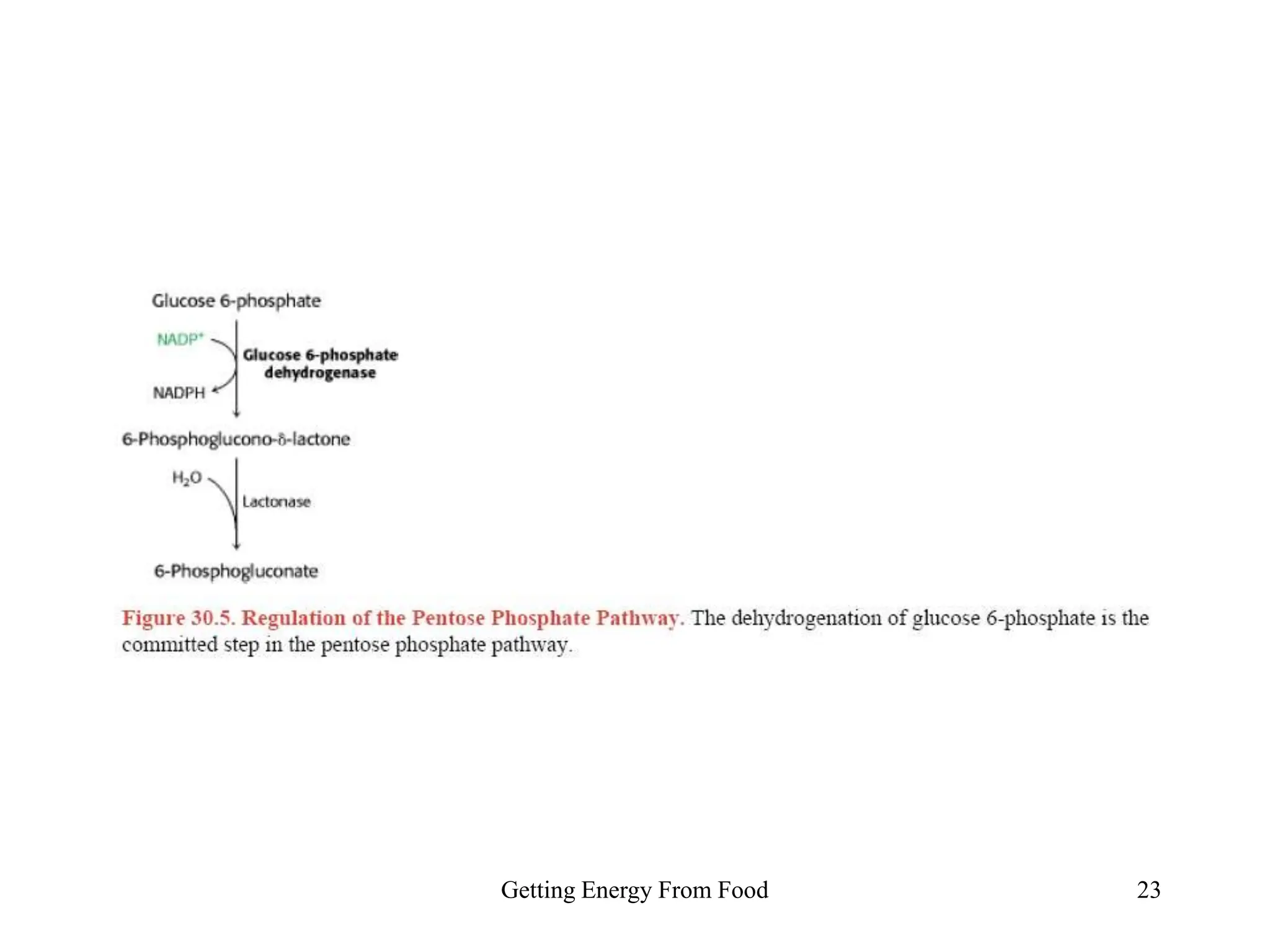
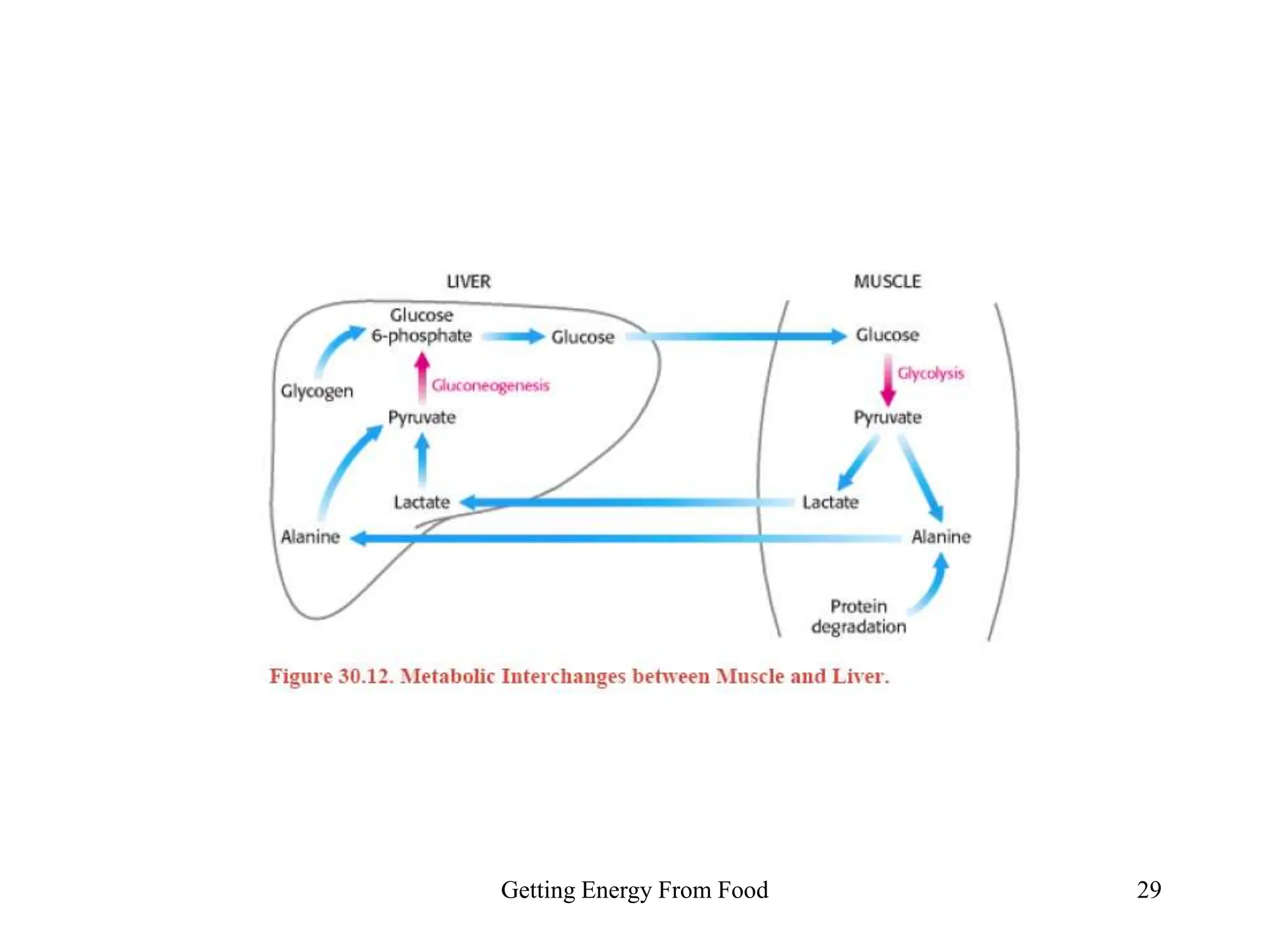
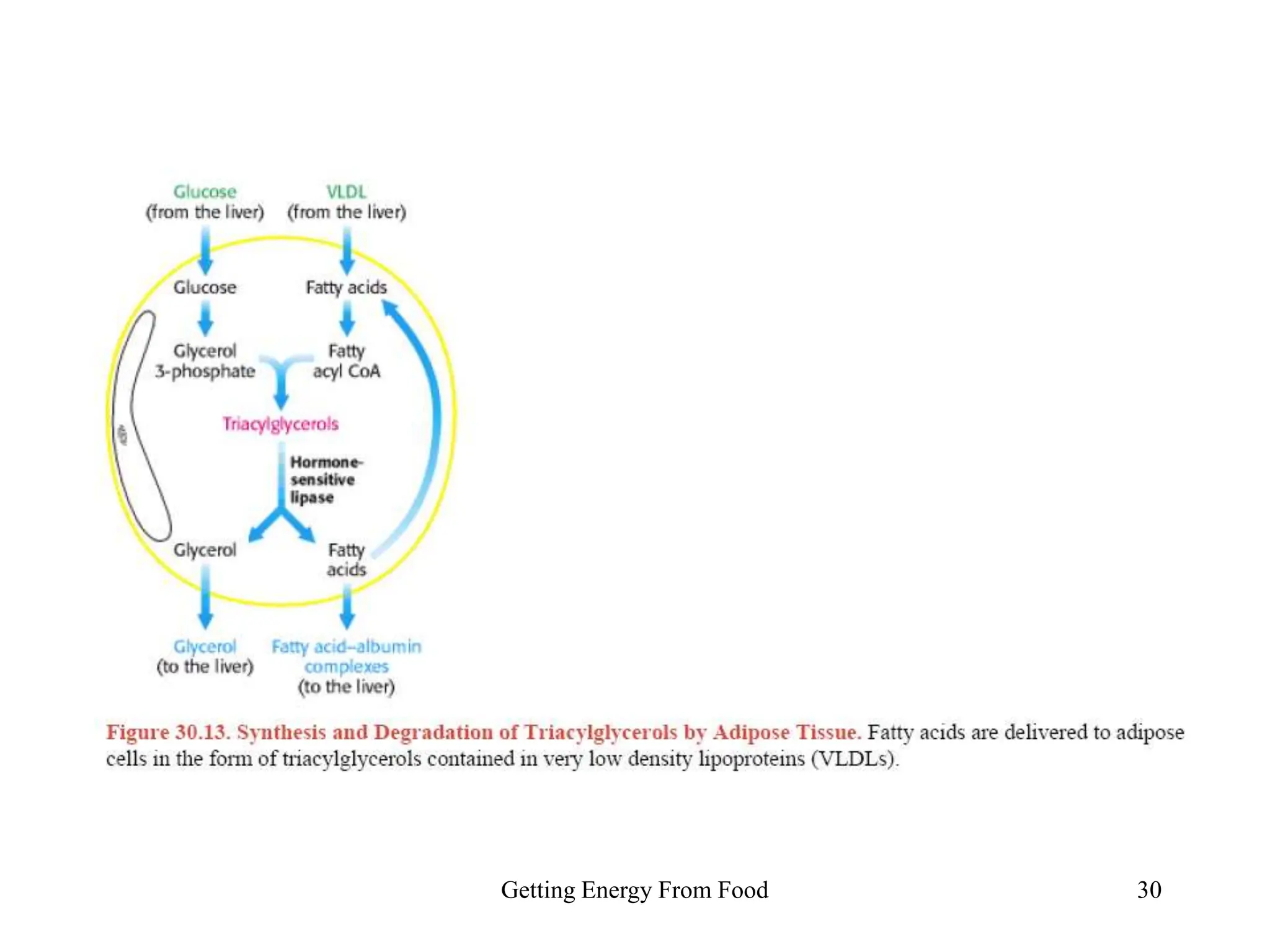
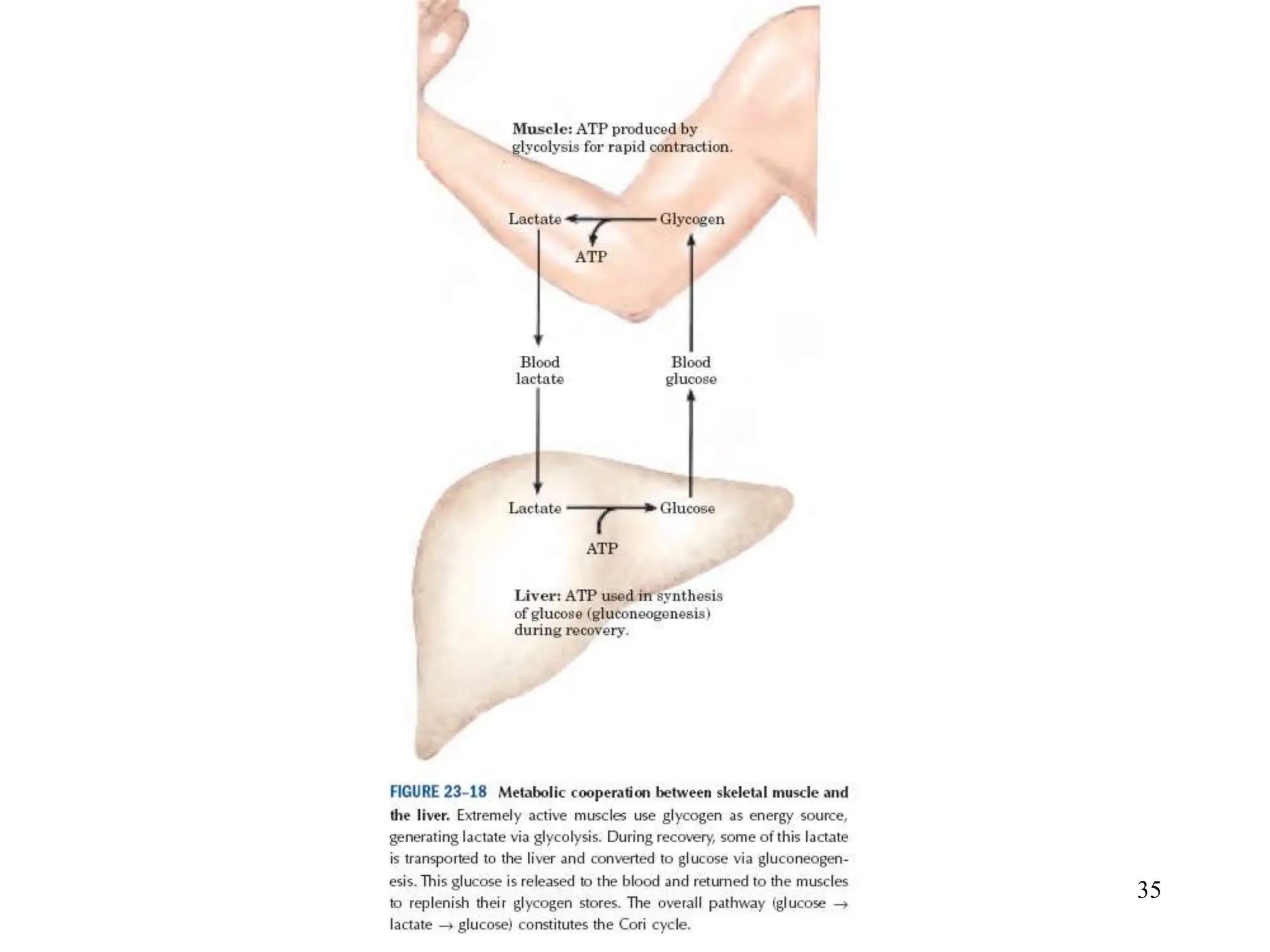
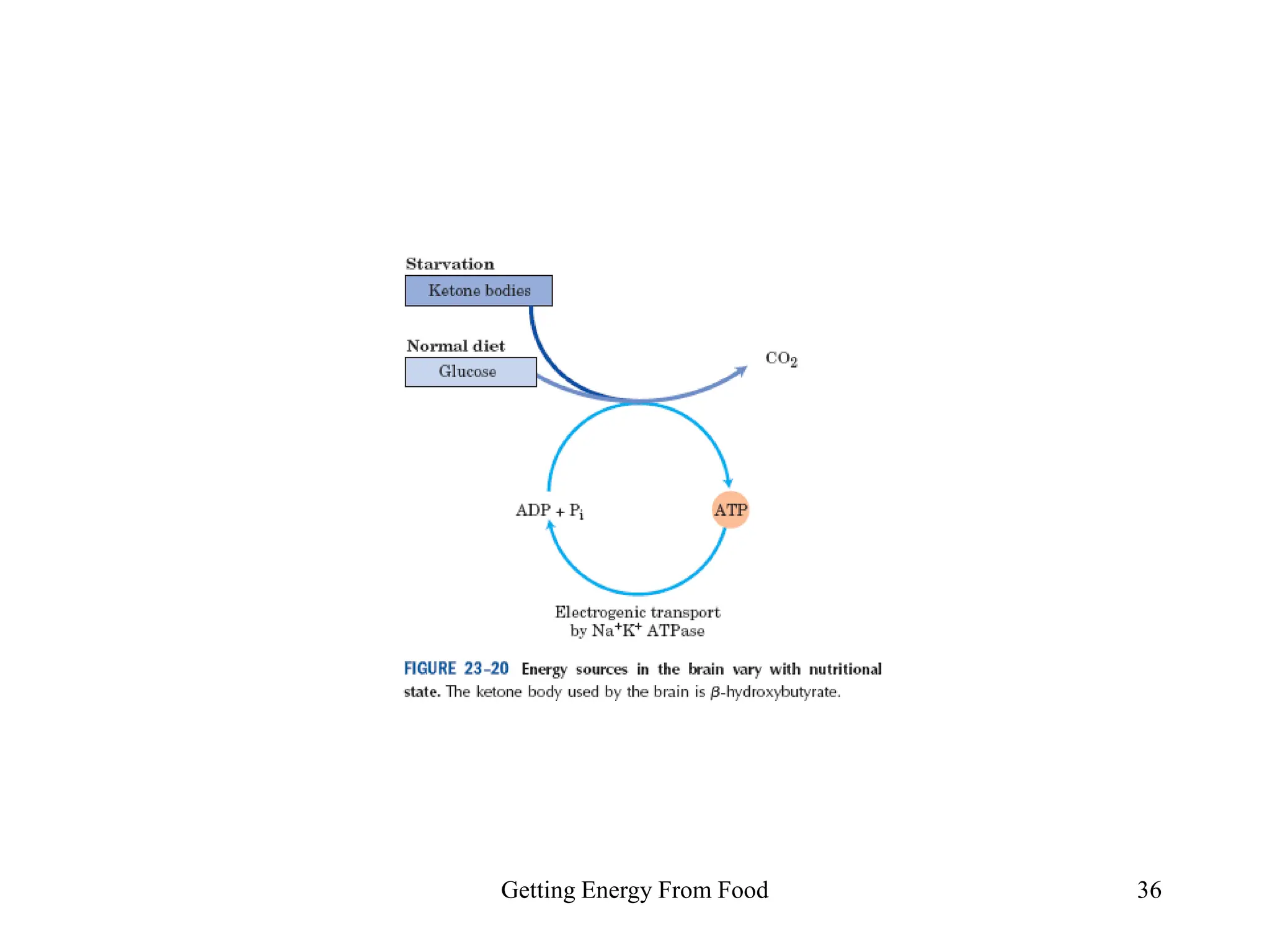
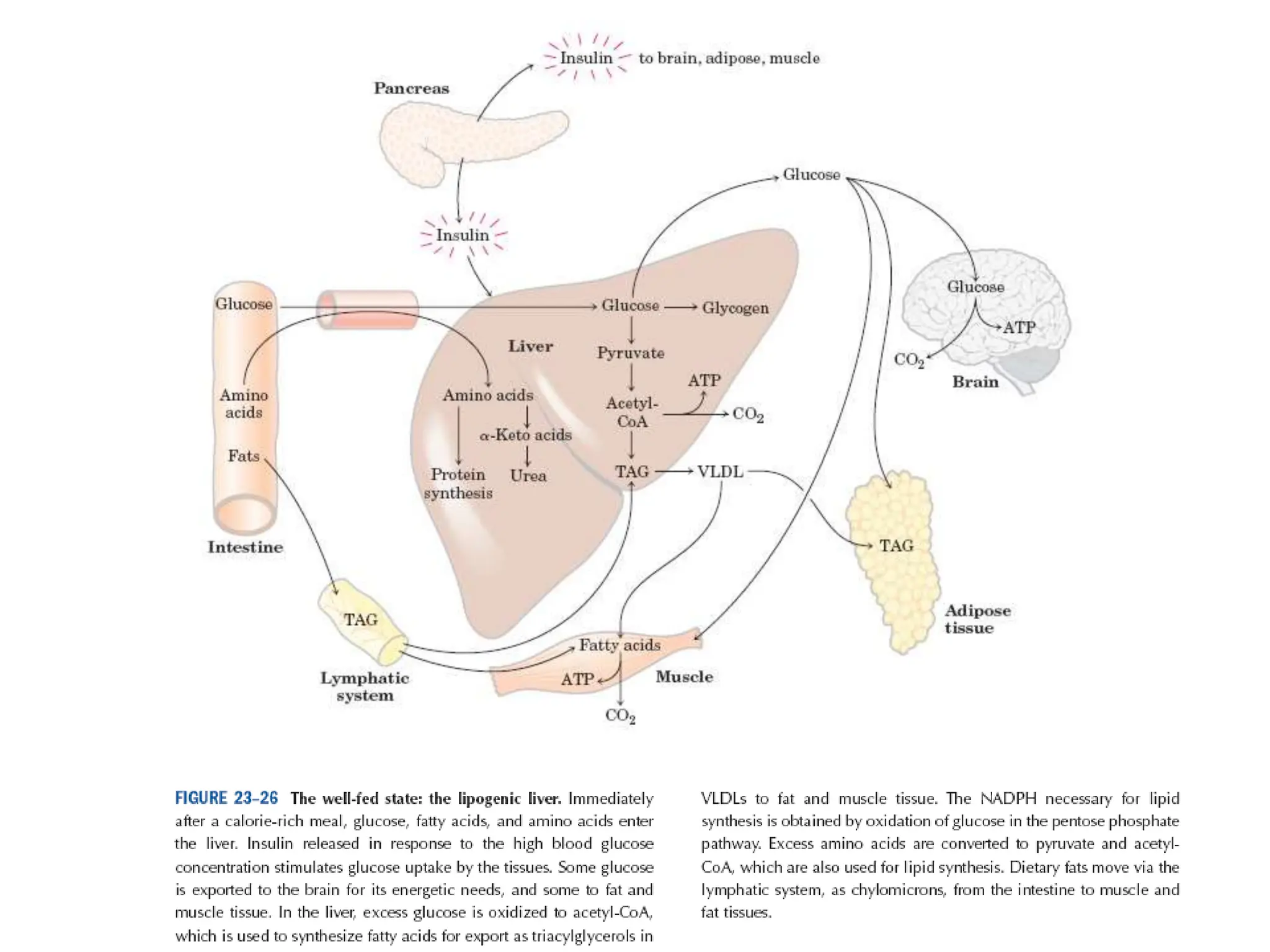
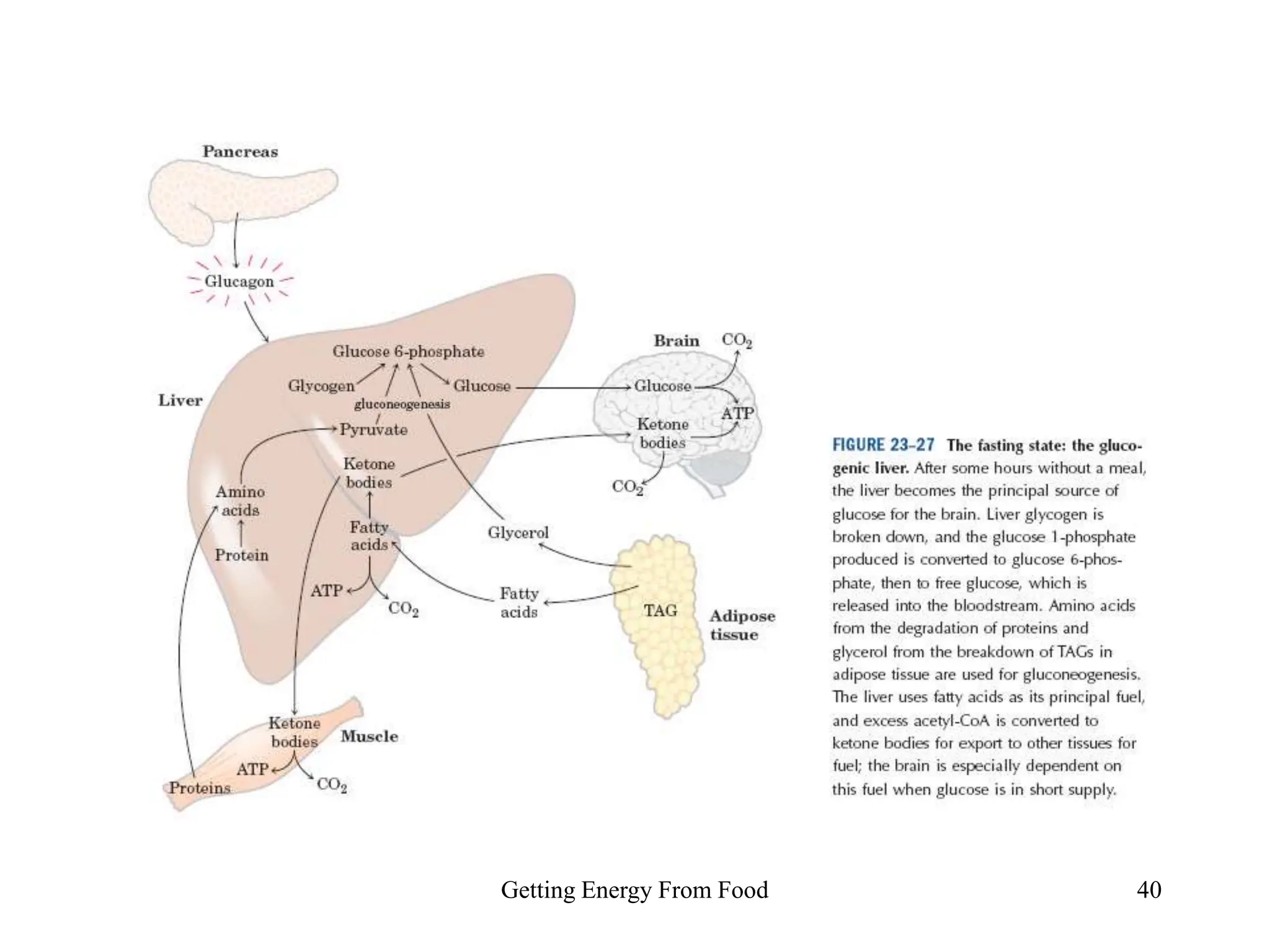
The document discusses how cells derive energy from the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins through metabolic pathways. The major pathways discussed are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These pathways break down nutrients into smaller units, produce ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation, and generate electron carriers like NADH and FADH2. The pathways are integrated through shared intermediates like pyruvate and acetyl-CoA to allow the cell to efficiently derive energy from different nutrient sources.