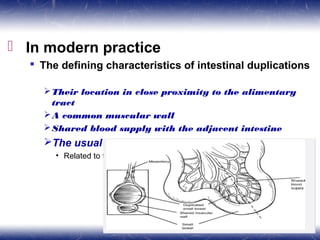
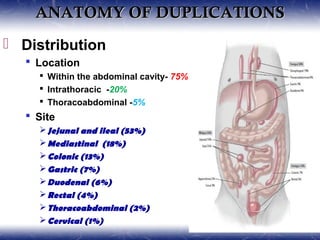
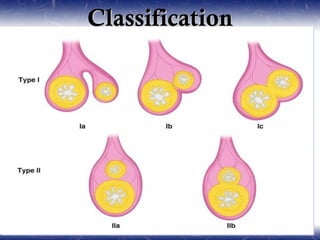
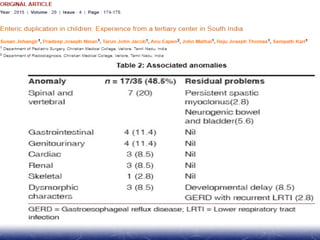
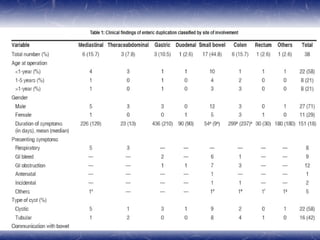
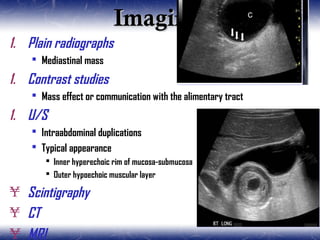
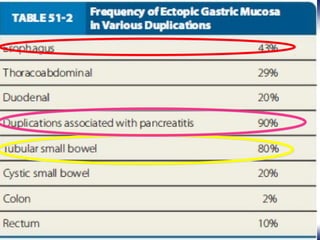
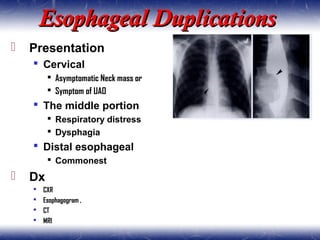
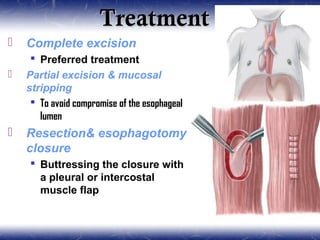
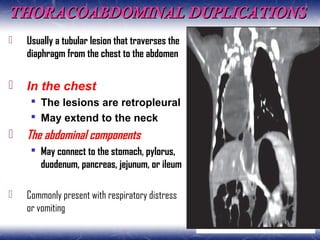
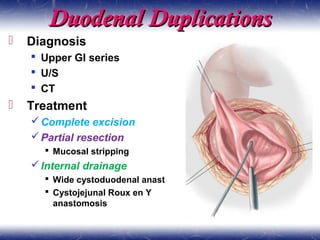
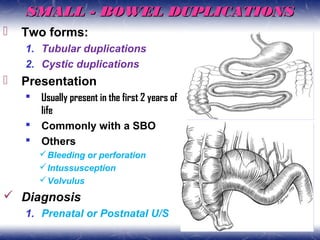
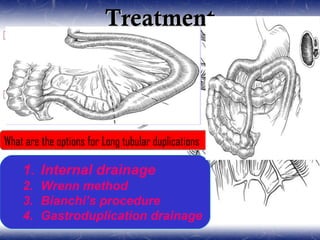
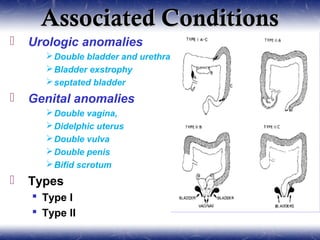
This document outlines the key points about gastrointestinal duplications. It discusses the epidemiology, embryology, anatomy, classification, clinical presentation, diagnosis, management and outcomes of gastrointestinal duplications. Gastrointestinal duplications are rare congenital abnormalities that can occur anywhere along the alimentary tract. They are defined by their proximity to the gastrointestinal tract, shared muscular wall and blood supply with the adjacent intestine. Complete surgical excision is typically the ideal treatment, with the goal of eliminating symptoms while preserving function and preventing future complications. Prognosis after surgical treatment is generally good, though outcomes can be poorer if associated with severe malformations.