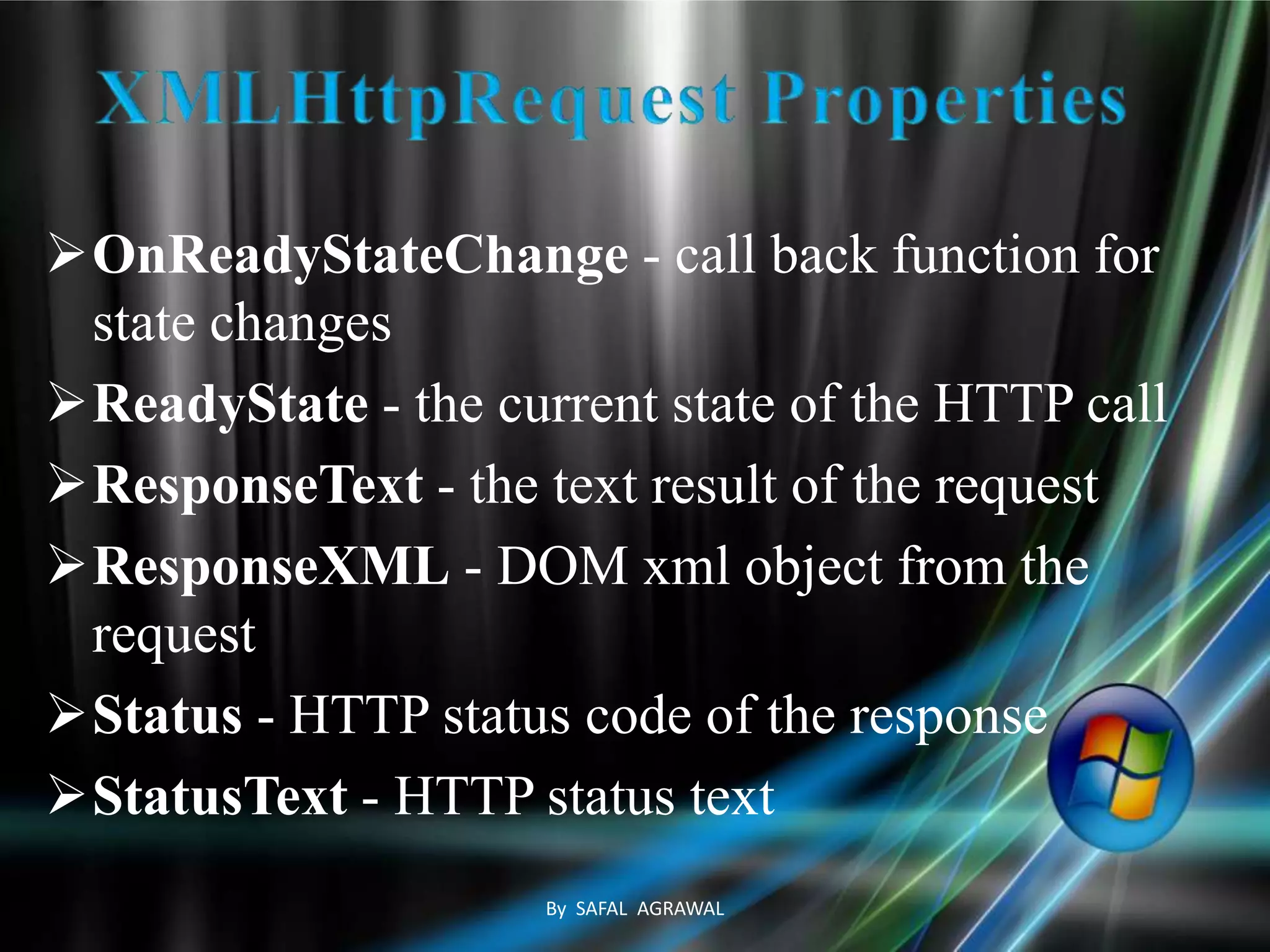
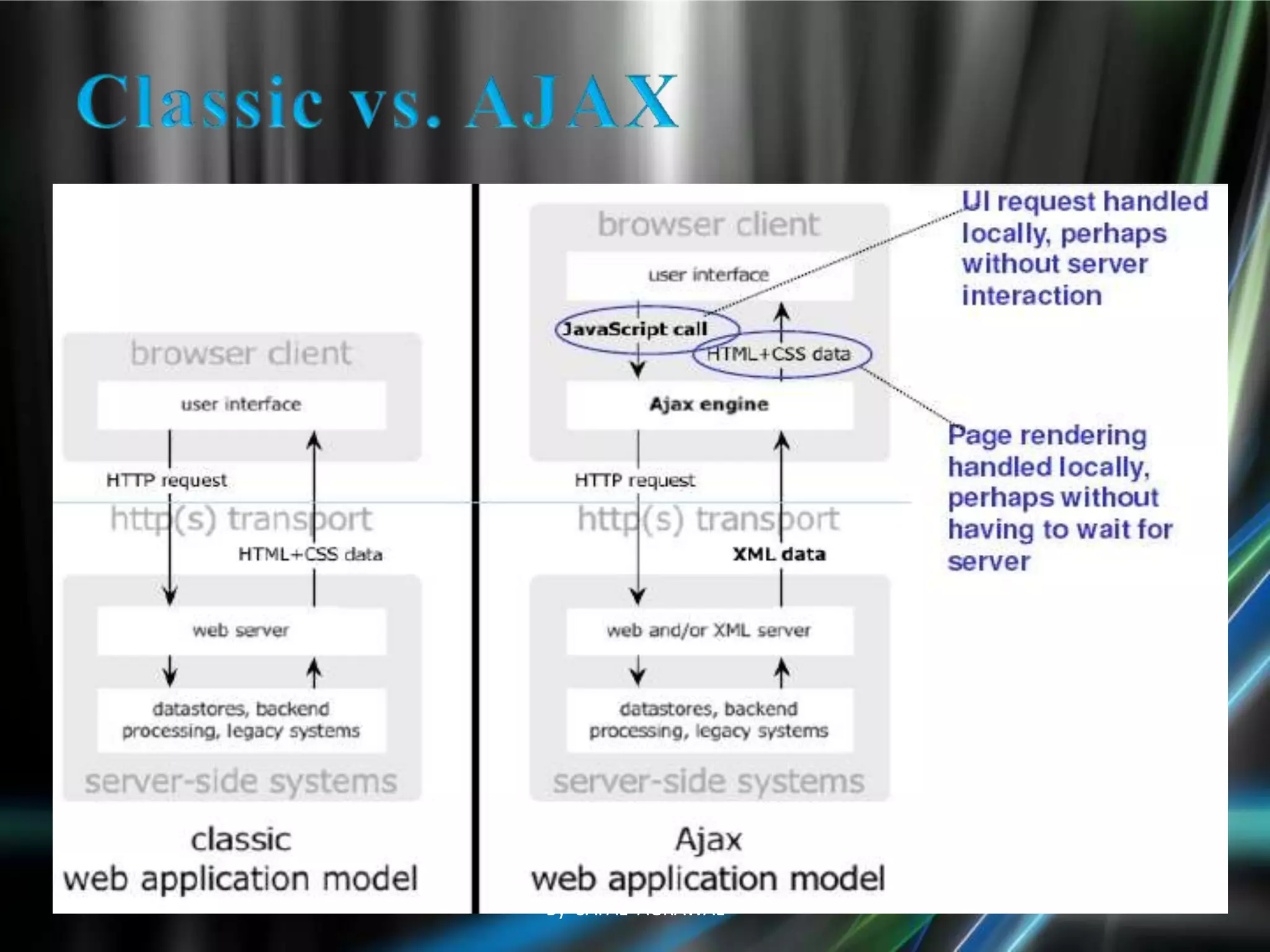
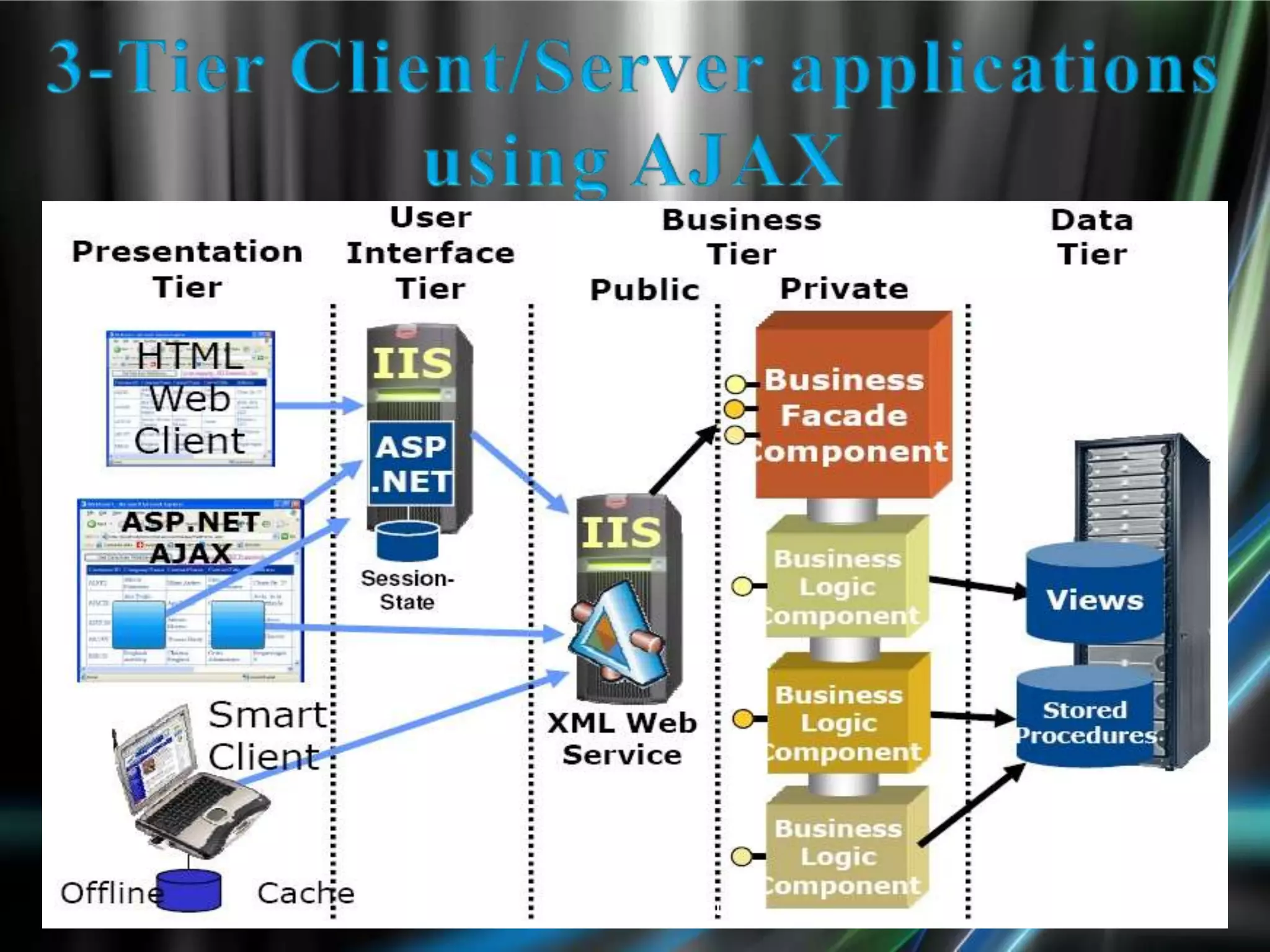
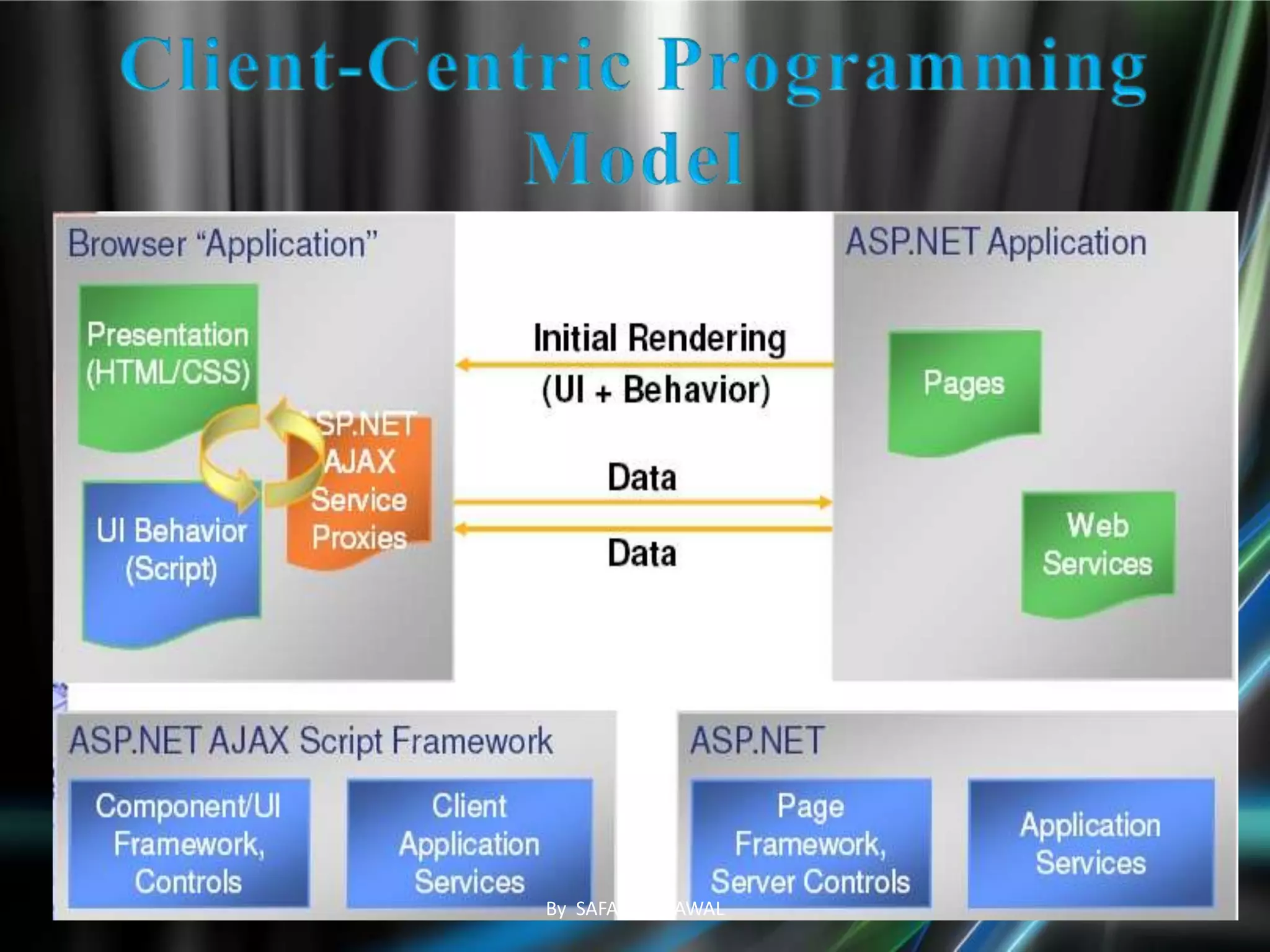
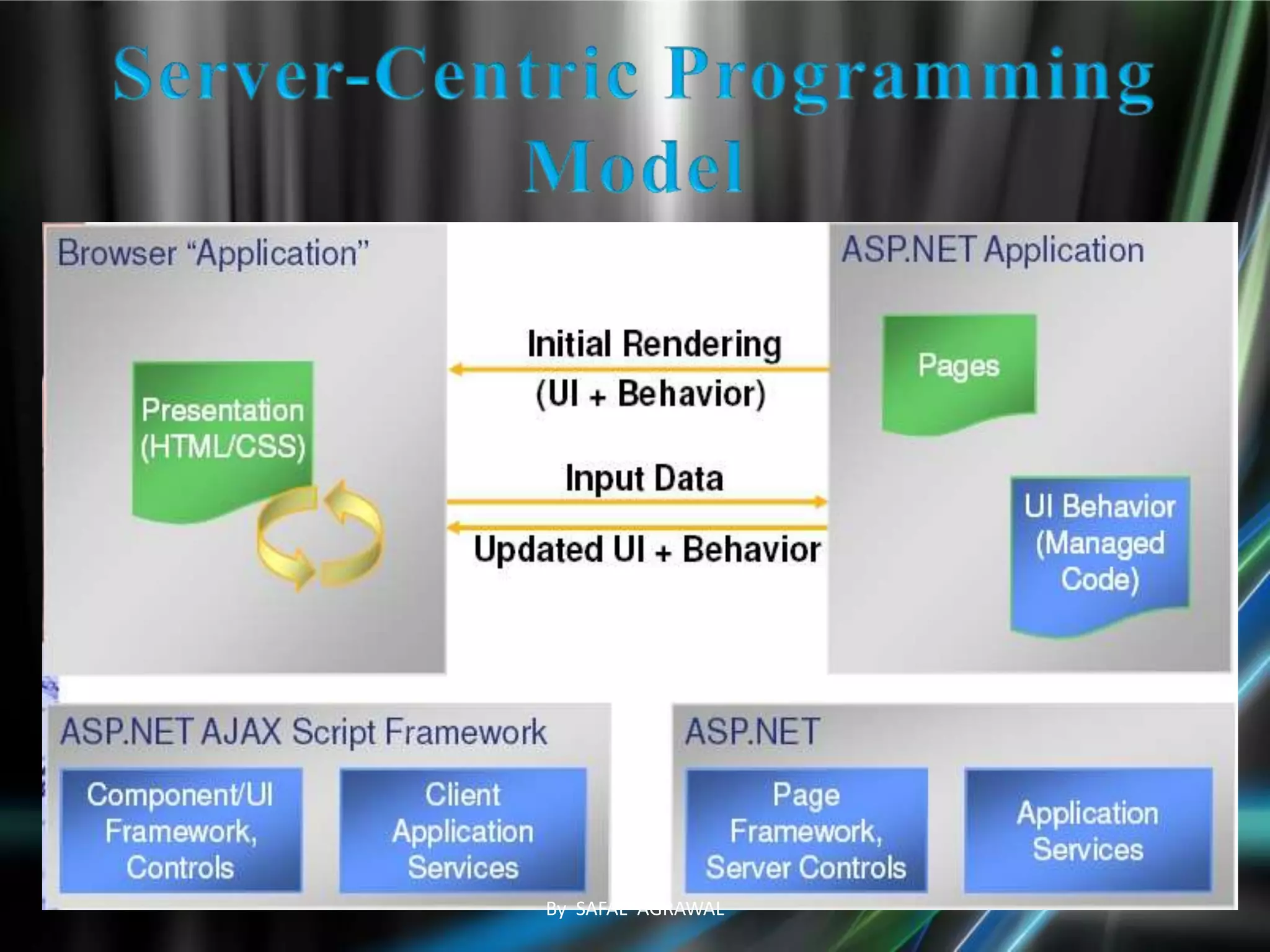
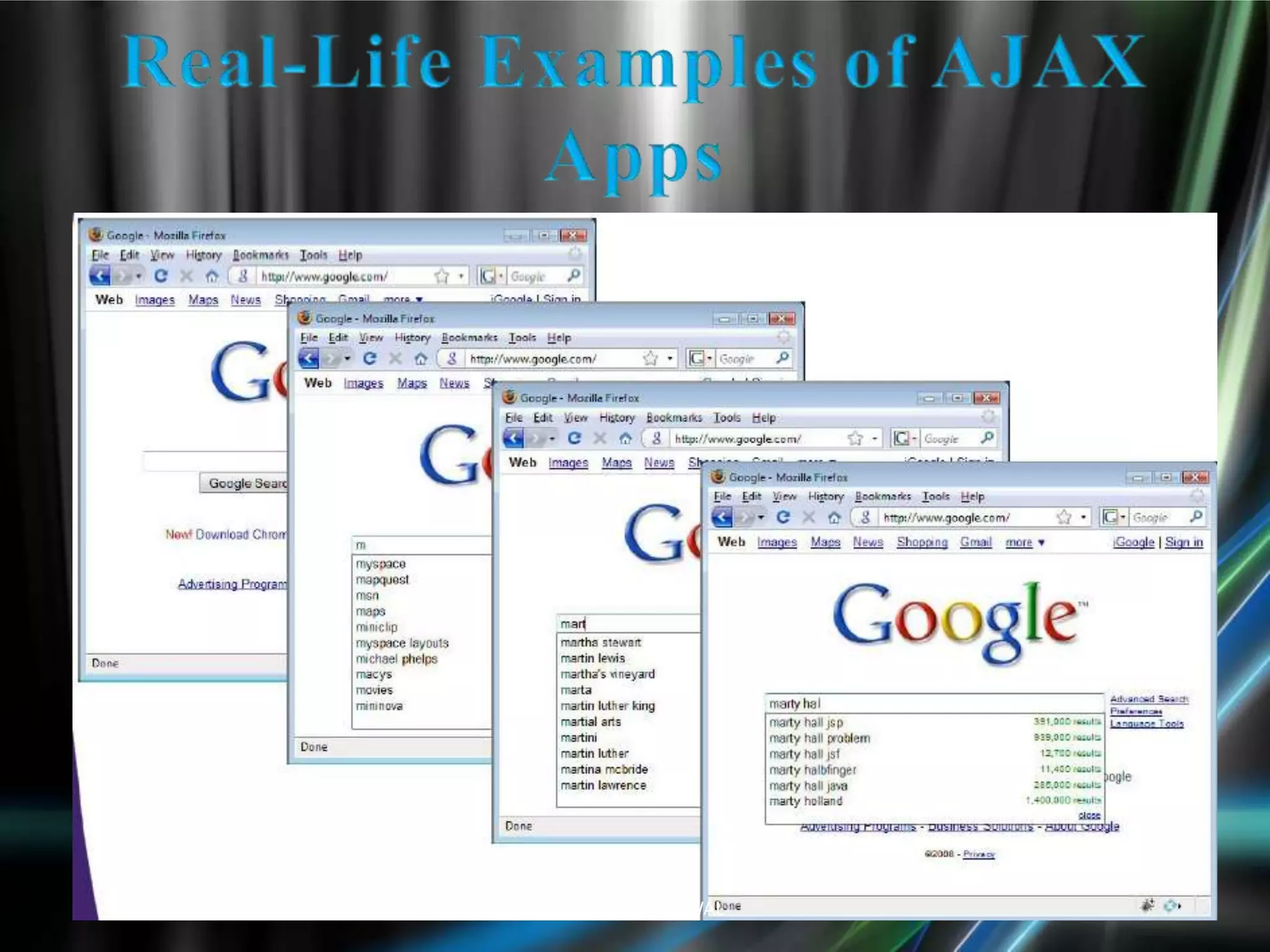
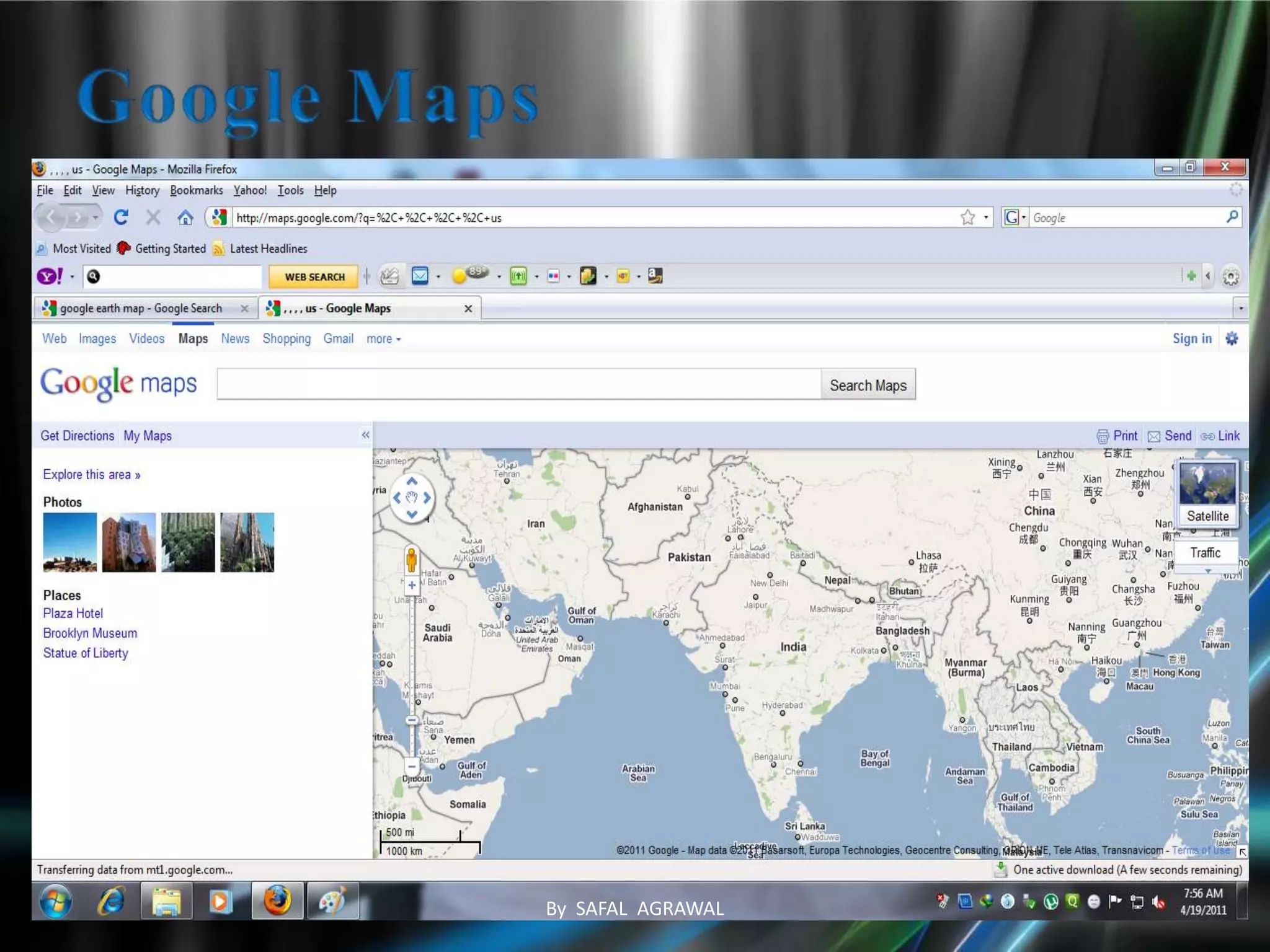
The document discusses AJAX, its technologies, and its advantages over traditional web applications. It highlights how AJAX allows for asynchronous data retrieval and partial screen updates, improving user experience by eliminating the need for page reloads. Additionally, it covers the integration of AJAX with ASP.NET and its impact on creating more interactive web applications.