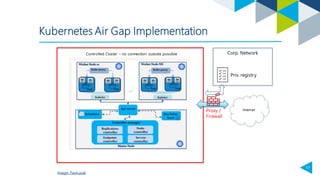
1. An air-gapped Kubernetes environment restricts internet access to increase security by preventing downloads of malicious data and attacks from outside entities.
2. Implementing an air-gapped Kubernetes cluster is more difficult than a standard one and requires additional effort for maintenance, but provides protections such as preventing data exfiltration by third parties.
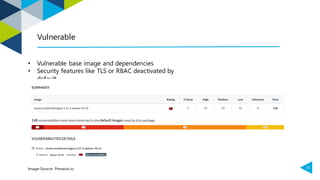
3. Deploying components like the ELK stack in an air-gapped environment requires manually downloading, transferring, and installing charts and images due to the lack of access to external registries and repositories. Processes and permissions must be tightly controlled to maintain security.